J Bacteriol Virol.
2014 Mar;44(1):84-94. 10.4167/jbv.2014.44.1.84.
Regulation of microRNA-7-5p and LRP6 by Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded RNAs in Burkitt's Lymphoma Cell Line Akata
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Lifescience, College of Medicine, The Catholic University Seoul, Korea. sukklee@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2135361
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2014.44.1.84
Abstract
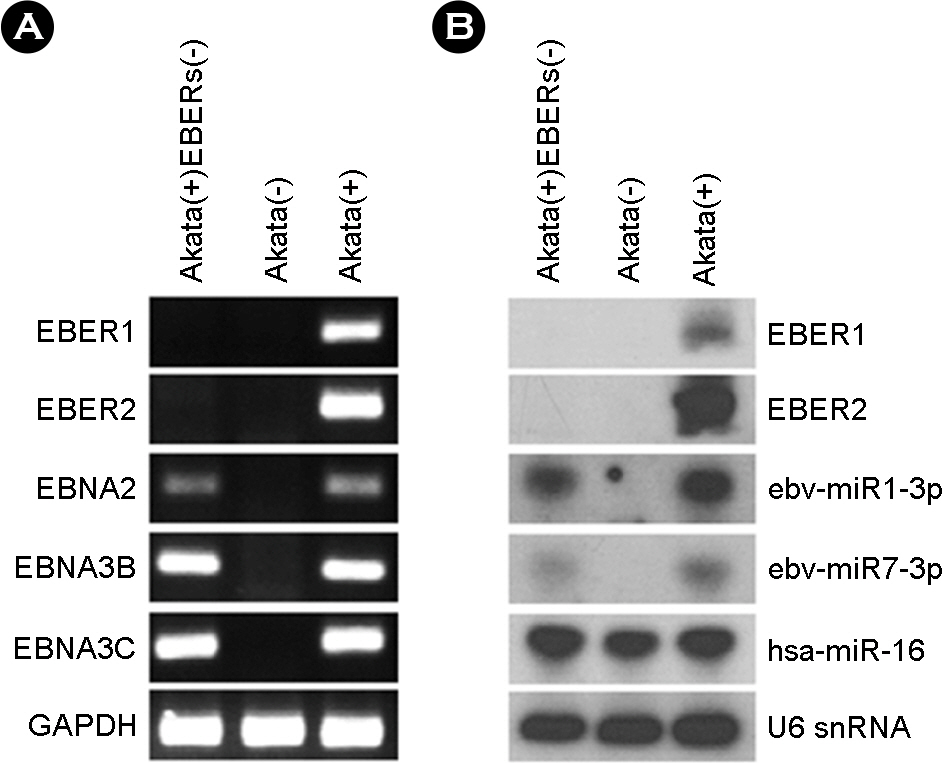
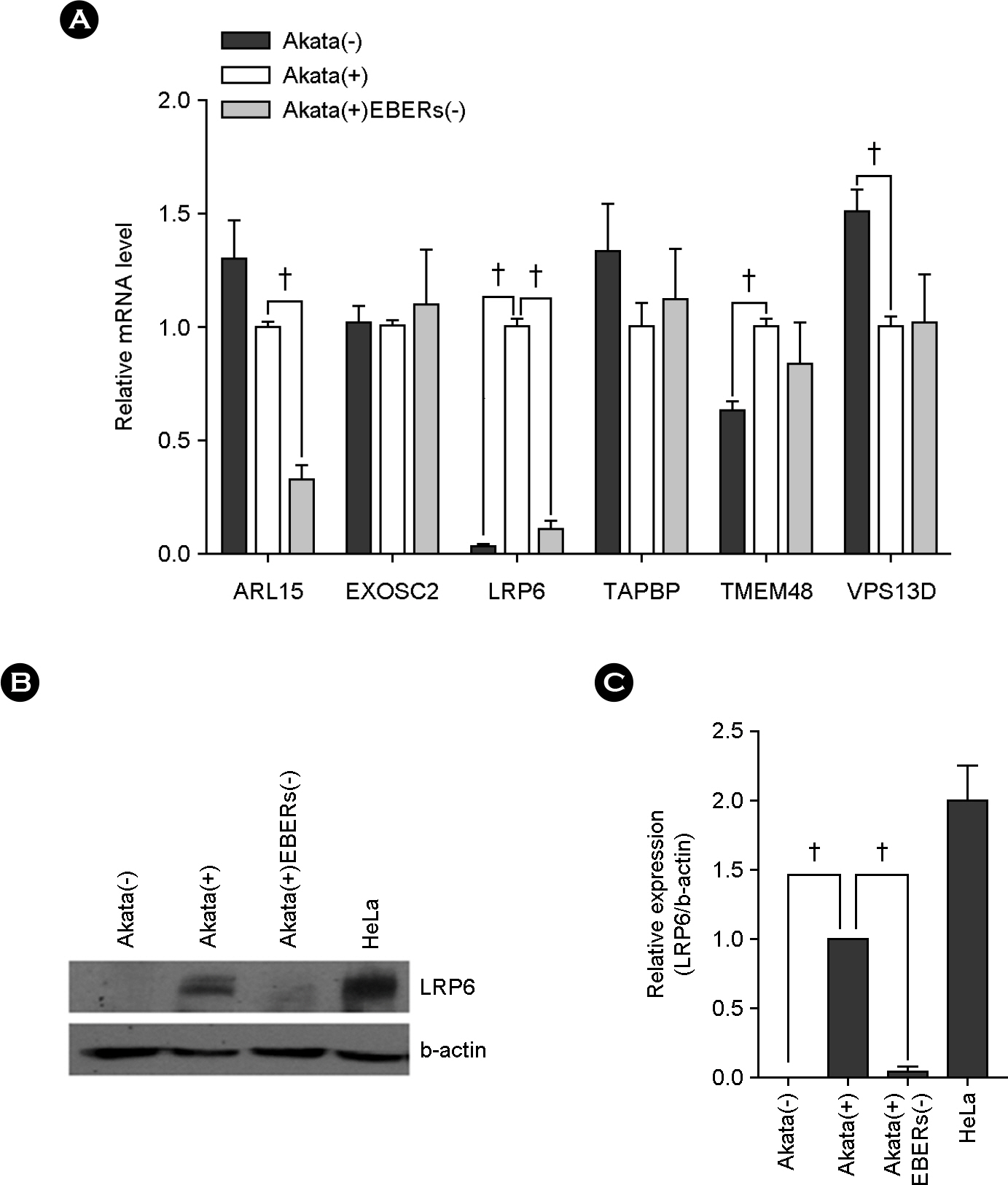
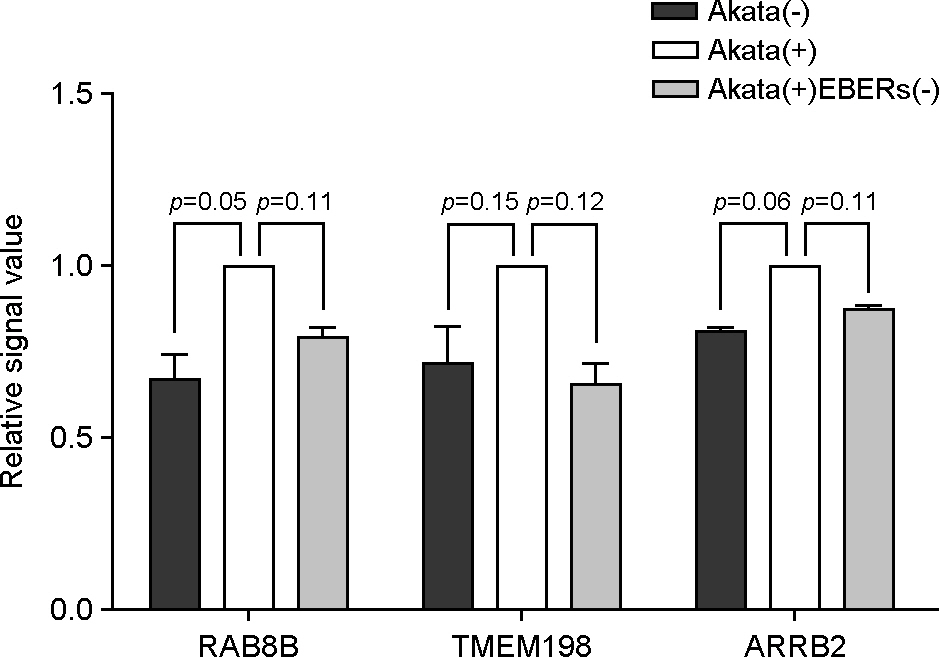
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded small non-coding RNAs (EBERs) are abundantly expressed in various EBV-associated malignancies, and play critical roles in cell proliferation, tumorigenesis, and apoptosis resistance. However, the mechanism how EBERs regulate cell function awaits further clarification. In this study, we investigated the effect of EBERs on the expression of cellular microRNA (miRNA) and mRNA expression. To test the effect of EBERs while unaffected by other EBV genes, we used EBERs-deleted recombinant EBV infected Burkitt's lymphoma cell line (Akata(+)EBERs(-)) as well as EBV-infected (Akata(+)) and EBV uninfected (Akata(-)) cell lines. They all have the same genetic backgrounds. First, 15 different cellular miRNAs which have reverse complementary sequences to EBERs and have reported targets were selected by bioinformatics analysis. When RT-PCR was carried out for the 16 miRNAs using RNAs from Akata(+), Akata(-), and Akata(+)EBERs(-) cells, hsa-miR-7-5p was the only one showing down-regulated expression in Akata(+) than in Akata(-) and Akata(+)EBERs(-) cells. Bioinformatics and mRNA microarray analyses for Akata(+), Akata(-), and Akata(+)EBERs(-) cell lines were then carried out to predict putative targets of hsa-miR-7-5p. Among the 6 predicted targets of hsa-miR-7-5p, only low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) was up-regulated in EBERs-expressing cells when tested by RT-PCR and Western blot. However, luciferase reporter assay showed that the 3'-UTR of LRP6 was not directly targeted by hsa-miR-7-5p. Our data suggest that both hsa-miR-7-5p and LRP6 are regulated by EBERs in Akata cells, and these genes may partly mediate the tumorigenic function of EBERs in Burkitt's lymphoma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis
Blotting, Western
Burkitt Lymphoma*
Carcinogenesis
Cell Line*
Cell Proliferation
Computational Biology
Herpesvirus 4, Human
Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein-6
Luciferases
MicroRNAs
RNA*
RNA, Messenger
RNA, Small Untranslated
Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein-6
Luciferases
MicroRNAs
RNA
RNA, Messenger
RNA, Small Untranslated
Figure
Reference
-
1). Thompson MP, Kurzrock R. Epstein-Barr virus and cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004; 10:803–21.
Article2). Kieff E, Rickinson A. Epstein-Barr virus. Knipe D, Howley P, editors. Fields virology. Philadelphia: Raven Press;2007. p. 2603–54.3). Rosa MD, Gottlieb E, Lerner MR, Steitz JA. Striking similarities are exhibited by two small Epstein-Barr virus-encoded ribonucleic acids and the adenovirus-associated ribonucleic acids VAI and VAII. Mol Cell Biol. 1981; 1:785–96.
Article4). Rymo L. Identification of transcribed regions of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in Burkitt lymphoma-derived cells. J Virol. 1979; 32:8–18.
Article5). Arrand JR, Young LS, Tugwood JD. Two families of sequences in the small RNA-encoding region of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) correlate with EBV types A and B. J Virol. 1989; 63:983–6.
Article6). Ambros V. MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 2003; 113:673–6.7). Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004; 116:281–97.8). Meister G, Tuschl T. Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature. 2004; 431:343–9.
Article9). Mack GS. MicroRNA gets down to business. Nat Biotechnol. 2007; 25:631–8.
Article10). Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, Wu Q, Callis TE, Hammond SM, et al. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. Nat Genet. 2006; 38:228–33.
Article11). Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J, Ford LP. Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005; 33:1290–7.
Article12). Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, et al. Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:3753–6.
Article13). Eis PS, Tam W, Sun L, Chadburn A, Li Z, Gomez MF, et al. Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:3627–32.
Article14). He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature. 2005; 435:828–33.
Article15). Donnell CA, Pollock WJ, Sybers WA. Thyroid carcinosarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987; 111:1169–72.16). Ebert MS, Sharp PA. Emerging roles for natural microRNA sponges. Curr Biol. 2010; 20:R858–61.
Article17). Cazalla D, Yario T, Steitz JA. Down-regulation of a host microRNA by a Herpesvirus saimiri noncoding RNA. Science. 2010; 328:1563–6.18). Cook HL, Lytle JR, Mischo HE, Li MJ, Rossi JJ, Silva DP, et al. Small nuclear RNAs encoded by Herpesvirus saimiri upregulate the expression of genes linked to T cell activation in virally transformed T cells. Curr Biol. 2005; 15:974–9.
Article19). Murthy S, Kamine J, Desrosiers RC. Viral-encoded small RNAs in herpes virus saimiri induced tumors. EMBO J. 1986; 5:1625–32.
Article20). Takada K. Cross-linking of cell surface immunoglobulins induces Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt lymphoma lines. Int J Cancer. 1984; 33:27–32.
Article21). Yajima M, Kanda T, Takada K. Critical role of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-encoded RNA in efficient EBV-induced B-lymphocyte growth transformation. J Virol. 2005; 79:4298–307.
Article22). Kim SY, Lee SK. Inhibition of transfer infection of Epstein-Barr virus to epithelial cells by integrin beta6 siRNA. J Bacteriol Virol. 2012; 42:346–52.23). Kriz V, Pospíchalová V, Masek J, Kilander MB, Slavík J, Tanneberger K, et al. beta-arrestin promotes Wnt-induced Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein 6 (Lrp6) phosphorylation via increased membrane recruitment of Amer1 Protein. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289:1128–41.24). Demir K, Kirsch N, Beretta CA, Erdmann G, Ingelfinger D, Moro E, et al. RAB8B is required for activity and caveolar endocytosis of LRP6. Cell Rep. 2013; 4:1224–34.
Article25). Liang J, Fu Y, Cruciat CM, Jia S, Wang Y, Tong Z, et al. Transmembrane protein 198 promotes LRP6 phosphorylation and Wnt signaling activation. Mol Cell Biol. 2011; 31:2577–90.
Article26). Shimizu N, Tanabe Tochikura A, Kuroiwa Y, Takada K. Isolation of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-negative cell clones from the EBV-positive Burkitt's lymphoma (BL) line Akata: malignant phenotypes of BL cells are dependent on EBV. J Virol. 1994; 68:6069–73.
Article27). Samanta M, Iwakiri D, Kanda T, Imaizumi T, Takada K. EB virus-encoded RNAs are recognized by RIG-I and activate signaling to induce type I IFN. EMBO J. 2006; 25:4207–14.
Article28). Samanta M, Iwakiri D, Takada K. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA induces IL-10 through RIG-I-mediated IRF-3 signaling. Oncogene. 2008; 27:4150–60.
Article29). Komano J, Maruo S, Kurozumi K, Oda T, Takada K. Oncogenic role of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNAs in Burkitt's lymphoma cell line Akata. J Virol. 1999; 73:9827–31.
Article30). Gregorovic G, Bosshard R, Karstegl CE, White RE, Pattle S, Chiang AK, et al. Cellular gene expression that correlates with EBER expression in Epstein-Barr Virus-infected lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Virol. 2011; 85:3535–45.
Article31). Houmani JL, Davis CI, Ruf IK. Growth-promoting properties of Epstein-Barr virus EBER-1 RNA correlate with ribosomal protein L22 binding. J Virol. 2009; 83:9844–53.
Article32). Eilebrecht S, Pellay FX, Odenwälder P, Brysbaert G, Benecke BJ, Benecke A. EBER2 RNA-induced transcriptome changes identify cellular processes likely targeted during Epstein Barr Virus infection. BMC Res Notes. 2008; 1:100.
Article33). Kefas B, Godlewski J, Comeau L, Li Y, Abounader R, Hawkinson M, et al. microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor and the Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2008; 68:3566–72.
Article34). Fang Y, Xue JL, Shen Q, Chen J, Tian L. MicroRNA-7 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2012; 55:1852–62.
Article35). Zhang N, Li X, Wu CW, Dong Y, Cai M, Mok MT, et al. microRNA-7 is a novel inhibitor of YY1 contributing to colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2013; 32:5078–88.
Article36). Saydam O, Senol O, Würdinger T, Mizrak A, Ozdener GB, Stemmer Rachamimov AO, et al. miRNA-7 attenuation in Schwannoma tumors stimulates growth by upregulating three oncogenic signaling pathways. Cancer Res. 2011; 71:852–61.
Article37). Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004; 20:781–810.
Article38). Tung EK, Wong BY, Yau TO, Ng IO. Upregulation of the Wnt co-receptor LRP6 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis and enhances cell invasion. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e36565.
Article39). Li Y, Lu W, He X, Schwartz AL, Bu G. LRP6 expression promotes cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by altering beta-catenin subcellular distribution. Oncogene. 2004; 23:9129–35.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Occurring in Thyroid Gland
- Application of Epstein-Barr Virus Cell Lines (CCL85 EB-3) in Performing the EBER mRNA In Situ Hybridization as a Positive Control
- A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus-positive Diffuse, Large B-cell Lymphoma after Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma
- Epstein-Barr Virus Positive Follicular Lymphoma of Lymph Node
- Epstein-Barr virus latent genes