Therapeutic Effects of Fermented Red Ginseng in Allergic Rhinitis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. helenmed@snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Food and Nutrition, and Research Institute of Human Ecology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Research Center, Bifido Inc., Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Hotel Culinary Arts, Anyang Science University, Anyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2130361
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2011.3.2.103
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Allergic rhinitis is clinically defined as a disorder of the nose induced by IgE mediated inflammation after allergen exposure of the nasal mucosa. Many reports have stated that Panax ginseng and fermented red ginseng have anti-inflammatory effects, especially against Th2-type inflammation. This study was conducted to evaluate the therapeutic effects of fermented red ginseng in allergic rhinitis.
METHODS
In this 4-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 59 patients with persistent perennial allergic rhinitis were randomly divided into two groups: those receiving fermented red ginseng tablets (experimental group) and those receiving placebo (control group). The primary efficacy variable was the total nasal symptom score (TNSS; rhinorrhea, sneezing, itchy nose, and nasal congestion). Secondary efficacy variables were the Rhinitis Quality of Life (RQoL) score and skin reactivity to inhalant allergens, as determined by the skin prick test.
RESULTS
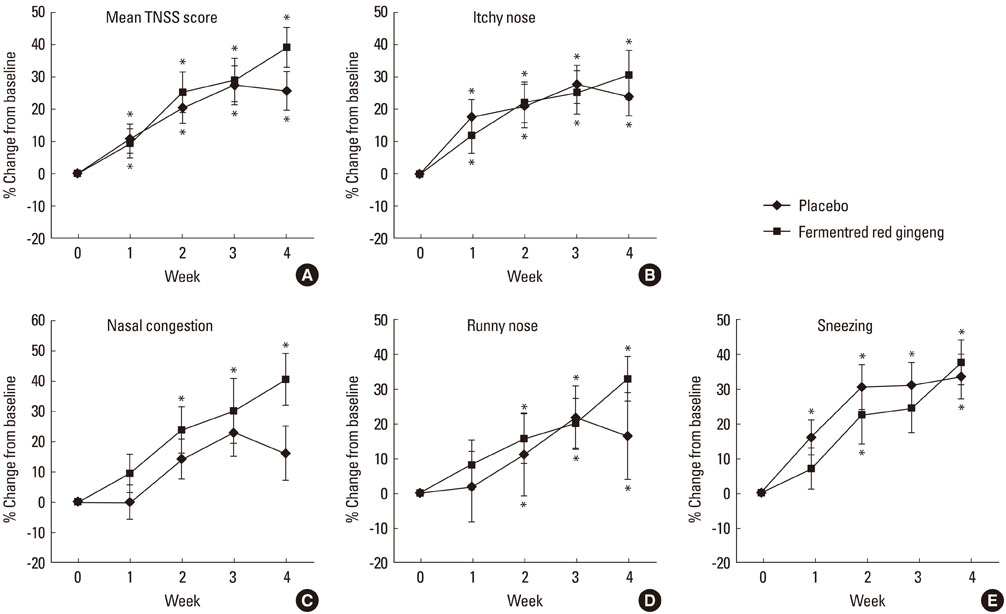
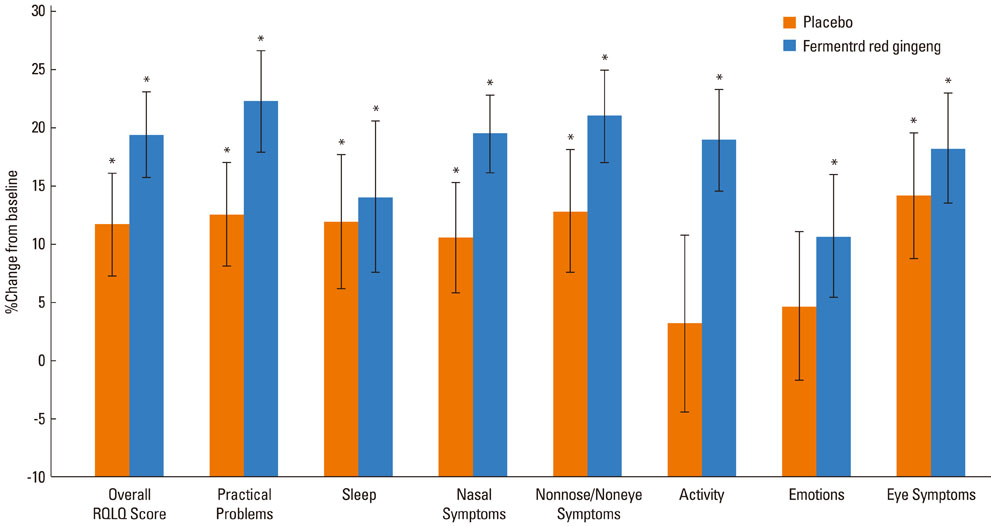
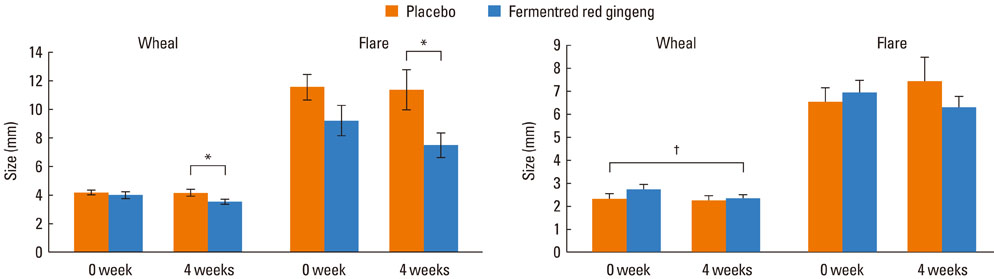
There was no significant difference in the TNSS score and TNSS duration score between the experimental and placebo groups in weeks 1, 2, 3, or 4. For nasal congestion, fermented red ginseng was significantly effective (P<0.005), while placebo caused no change. The activity and emotion of RQoL improved markedly secondary to treatment with fermented red ginseng (P<0.05), while placebo caused no change. Additionally, fermented red ginseng reduced skin reactivity to sensitized perennial allergens (P<0.05). Fermented red ginseng was well tolerated.
CONCLUSIONS
Fermented red ginseng improved nasal congestion symptoms and RQoL in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Chinese Herbal Medicine to Treat Allergic Rhinitis: Evidence From a Meta-Analysis
Xu Zhang, Feng Lan, Yuan Zhang, Luo Zhang
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(1):34-42. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.1.34.Chinese Society of Allergy Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis
Lei Cheng, Jianjun Chen, Qingling Fu, Shaoheng He, Huabin Li, Zheng Liu, Guolin Tan, Zezhang Tao, Dehui Wang, Weiping Wen, Rui Xu, Yu Xu, Qintai Yang, Chonghua Zhang, Gehua Zhang, Ruxin Zhang, Yuan Zhang, Bing Zhou, Dongdong Zhu, Luquan Chen, Xinyan Cui, Yuqin Deng, Zhiqiang Guo, Zhenxiao Huang, Zizhen Huang, Houyong Li, Jingyun Li, Wenting Li, Yanqing Li, Lin Xi, Hongfei Lou, Meiping Lu, Yuhui Ouyang, Wendan Shi, Xiaoyao Tao, Huiqin Tian, Chengshuo Wang, Min Wang, Nan Wang, Xiangdong Wang, Hui Xie, Shaoqing Yu, Renwu Zhao, Ming Zheng, Han Zhou, Luping Zhu, Luo Zhang
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(4):300-353. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.4.300.Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of fermented red ginseng against high fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia in rats
Myeong-Hwan Kim, Eun-Jin Lee, Jeong-Mu Cheon, Ki-Jun Nam, Tae-Ho Oh, Kil-Soo Kim
Lab Anim Res. 2016;32(4):217-223. doi: 10.5625/lar.2016.32.4.217.Ginsenoside Rb1 Attenuates TGF-β1-Induced MUC4/5AC Expression and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
Tae Yeong Choi, Joon-Hee Kim, Sooyeon Jo, Sangjae Lee, Hyung-Gyun Na, Yoon Seok Choi, Si-Youn Song, Yong-Dae Kim, Chang Hoon Bae
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2021;64(4):232-239. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2020.00150.
Reference
-
1. Howarth PH, Salagean M, Dokic D. Allergic rhinitis: not purely a histamine-related disease. Allergy. 2000. 55:Suppl 64. 7–16.2. Cruz AA, Popov T, Pawankar R, Annesi-Maesano I, Fokkens W, Kemp J, Ohta K, Price D, Bousquet J. Common characteristics of upper and lower airways in rhinitis and asthma: ARIA update, in collaboration with GA(2)LEN. Allergy. 2007. 62:Suppl 84. 1–41.3. Yun TK. Brief introduction of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J Korean Med Sci. 2001. 16:Suppl. S3–S5.4. Nocerino E, Amato M, Izzo AA. The aphrodisiac and adaptogenic properties of ginseng. Fitoterapia. 2000. 71:Suppl 1. S1–S5.5. Kim ST, Jang JH, Kwon JH, Moon KD. Change in the chemical components of red and white ginseng after puffing. Korean J Food Preserv. 2009. 16:355–361.6. Bae EA, Trinh HT, Yoon HK, Kim DH. Compound K, a metabolite of ginsenoside Rb1, inhibits passive cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction in mice. J Ginseng Res. 2009. 33:93–98.7. Babayigit A, Olmez D, Karaman O, Bagriyanik HA, Yilmaz O, Kivcak B, Erbil G, Uzuner N. Ginseng ameliorates chronic histopathologic changes in a murine model of asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008. 29:493–498.8. Hyun MS, Hur JM, Shin YS, Song BJ, Mun YJ, Woo WH. Comparison study of white ginseng, red ginseng, and fermented red ginseng on the protective effect of LPS-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 cells. J Appl Biol Chem. 2009. 52:21–27.9. Dahl R, Kapp A, Colombo G, de Monchy JG, Rak S, Emminger W, Riis B, Grønager PM, Durham SR. Sublingual grass allergen tablet immunotherapy provides sustained clinical benefit with progressive immunologic changes over 2 years. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. 121:512–518.e2.10. Fokkens WJ, Jogi R, Reinartz S, Sidorenko I, Sitkauskiene B, van Oene C, Faris MA, Ellsworth A, Caldwell MF. Once daily fluticasone furoate nasal spray is effective in seasonal allergic rhinitis caused by grass pollen. Allergy. 2007. 62:1078–1084.11. Park KH, Cho JS, Lee KH, Shin SY, Moon JH, Cha CI. Rhinoconjunctivitis quality of life questionnaire (RQLQ) as an evaluator of perennial allergic rhinitis patients-the first report. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2002. 45:254–262.12. Ciebiada M, Gorska-Ciebiada M, DuBuske LM, Gorski P. Montelukast with desloratadine or levocetirizine for the treatment of persistent allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006. 97:664–671.13. MacLennan AH, Wilson DH, Taylor AW. The escalating cost and prevalence of alternative medicine. Prev Med. 2002. 35:166–173.14. Schafer T. Epidemiology of complementary alternative medicine for asthma and allergy in Europe and Germany. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004. 93:S5–S10.15. Vliagoftis H, Kouranos VD, Betsi GI, Falagas ME. Probiotics for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and asthma: systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008. 101:570–579.16. Cingi C, Conk-Dalay M, Cakli H, Bal C. The effects of spirulina on allergic rhinitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2008. 265:1219–1223.17. Kim SY, Kang HR, Kim JH, Son KM, Jeong JM, Park SH, Hwang YI, Jang SH, Kim DG, Jung KS. The effects of extracts from green tea, guajava leaves and rose petals on allergic rhinitis: a randomized double blind control study. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. 29:89–95.18. Lee HB. Alternative and complement therapies for asthma. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2002. 12:247–252.19. Kiefer D, Pantuso T. Panax ginseng. Am Fam Physician. 2003. 68:1539–1542.20. Fulder SJ. Ginseng and the hypothalamic-pituitary control of stress. Am J Chin Med. 1981. 9:112–118.21. Hiai S, Yokoyama H, Oura H, Kawashima Y. Evaluation of corticosterone secretion-inducing activities of ginsenosides and their prosapogenins and sapogenins. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1983. 31:168–174.22. Lee YJ, Chung E, Lee KY, Lee YH, Huh B, Lee SK. Ginsenoside-Rg1, one of the major active molecules from Panax ginseng, is a functional ligand of glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997. 133:135–140.23. Ligor T, Ludwiczuk A, Wolski T, Buszewski B. Isolation and determination of ginsenosides in American ginseng leaves and root extracts by LC-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2005. 383:1098–1105.24. Liou CJ, Huang WC, Tseng J. Short-term oral administration of ginseng extract induces type-1 cytokine production. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2006. 28:227–240.25. Jeong YJ, Paeng JW, Choi DC, Lee BJ. Effects of Korean red ginseng extracts on airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a murine asthma model. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 30:43–49.26. van Oene CM, van Reij EJ, Sprangers MA, Fokkens WJ. Quality-assessment of disease-specific quality of life questionnaires for rhinitis and rhinosinusitis: a systematic review. Allergy. 2007. 62:1359–1371.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on Stress Responses and beta-Adrenergic Receptor Function in a Normal Population
- Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy Against Allergic Respiratory Diseases
- Effects of cetirizine in dogs with chronic atopic dermatitis: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial
- Study on Chemoprevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Ginseng: An Introduction to the Protocol
- Effects of Korean Red Ginseng on Cardiovascular Risks in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome: a Double-blind Randomized Controlled Study