Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Dec;8(4):345-353. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.4.345.
Microarray Analysis of Gene Expression Alteration in Human Middle Ear Epithelial Cells Induced by Asian Sand Dust
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jjsong23@gmail.com
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Life Science, Institute of Environmental Medicine for Green Chemistry, Dongguk University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2128908
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.4.345
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
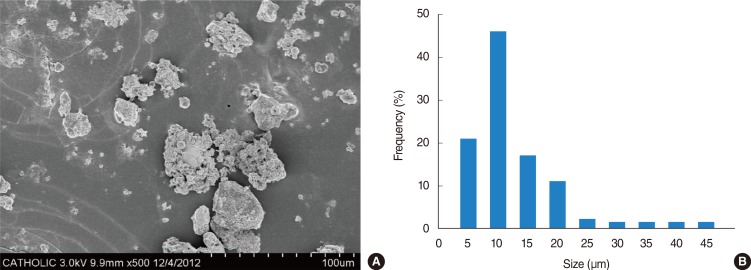
The primary aim of this study is to evaluate the gene expression profile of Asian sand dust (ASD)-treated human middle ear epithelial cell (HMEEC) using microarray analysis.
METHODS
The HMEEC was treated with ASD (400 microg/mL) and total RNA was extracted for microarray analysis. Molecular pathways among differentially expressed genes were further analyzed. For selected genes, the changes in gene expression were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
RESULTS
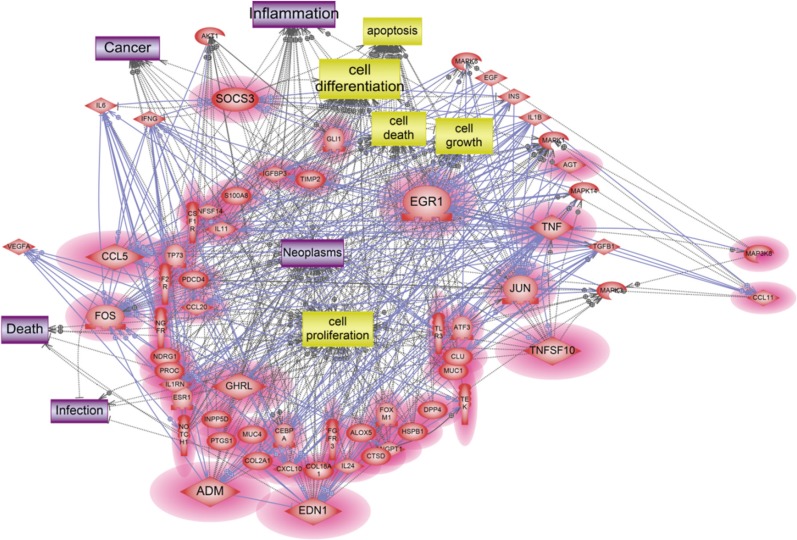
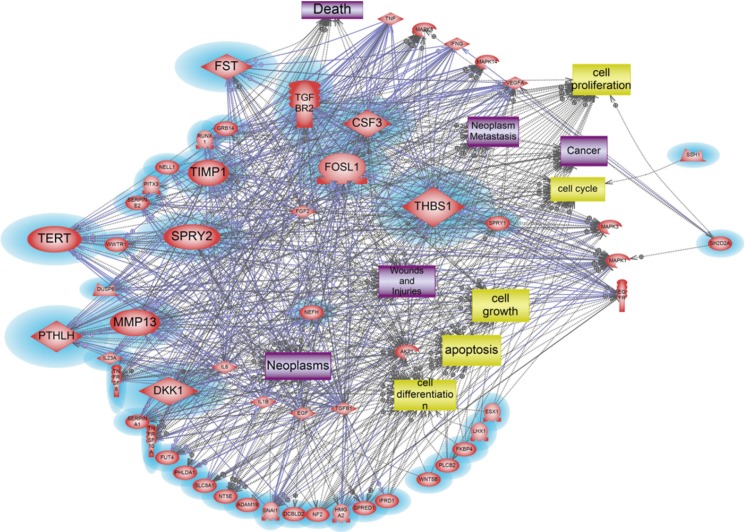
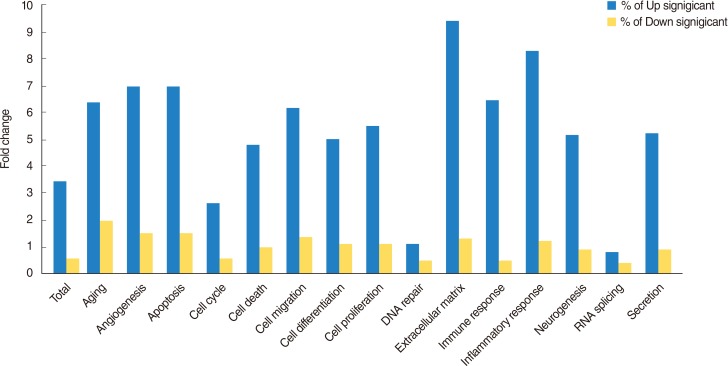
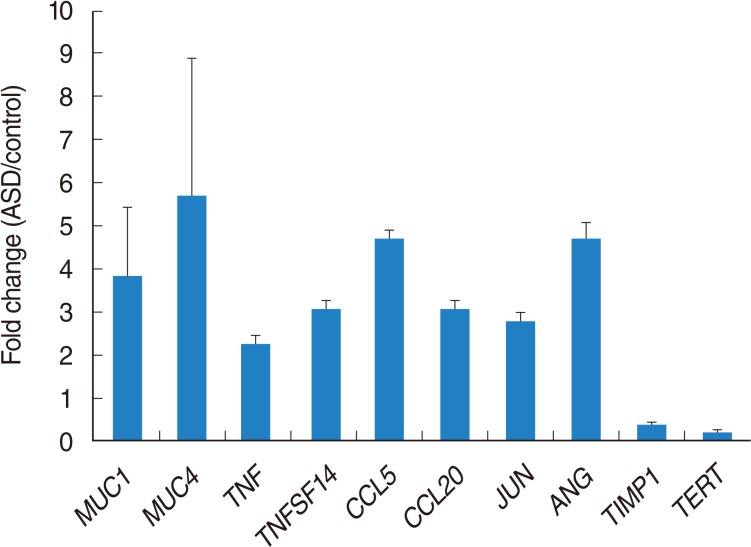
A total of 1,274 genes were differentially expressed by ASD. Among them, 1,138 genes were 2 folds up-regulated, whereas 136 genes were 2 folds down-regulated. Up-regulated genes were mainly involved in cellular processes, including apoptosis, cell differentiation, and cell proliferation. Down-regulated genes affected cellular processes, including apoptosis, cell cycle, cell differentiation, and cell proliferation. The 10 genes including ADM, CCL5, EDN1, EGR1, FOS, GHRL, JUN, SOCS3, TNF, and TNFSF10 were identified as main modulators in up-regulated genes. A total of 11 genes including CSF3, DKK1, FOSL1, FST, TERT, MMP13, PTHLH, SPRY2, TGFBR2, THBS1, and TIMP1 acted as main components of pathway associated with 2-fold down regulated genes.
CONCLUSION
We identified the differentially expressed genes in ASD-treated HMEEC. Our work indicates that air pollutant like ASD, may play an important role in the pathogenesis of otitis media.
MeSH Terms
-
Air Pollution
Apoptosis
Asian Continental Ancestry Group*
Cell Cycle
Cell Differentiation
Cell Proliferation
Dust*
Ear, Middle*
Epithelial Cells*
Gene Expression*
Humans*
Microarray Analysis*
Otitis Media
Particulate Matter
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA
Silicon Dioxide*
Transcriptome
Dust
Particulate Matter
RNA
Silicon Dioxide
Figure
Reference
-
1. He M, Ichinose T, Yoshida S, Yamamoto S, Inoue K, Takano H, et al. Asian sand dust enhances murine lung inflammation caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012; 1. 258(2):237–247. PMID: 22118940.
Article2. Chen PS, Tsai FT, Lin CK, Yang CY, Chan CC, Young CY, et al. Ambient influenza and avian influenza virus during dust storm days and background days. Environ Health Perspect. 2010; 9. 118(9):1211–1216. PMID: 20435545.
Article3. Naota M, Shiotsu S, Shimada A, Kohara Y, Morita T, Inoue K, et al. Pathological study of chronic pulmonary toxicity induced by intratracheally instilled Asian sand dust (kosa). Toxicol Pathol. 2013; 1. 41(1):48–62. PMID: 22744225.
Article4. Yeo NK, Hwang YJ, Kim ST, Kwon HJ, Jang YJ. Asian sand dust enhances rhinovirus-induced cytokine secretion and viral replication in human nasal epithelial cells. Inhal Toxicol. 2010; 10. 22(12):1038–1045. PMID: 20879958.
Article5. Yadav MK, Chae SW, Song JJ. In vitro Streptococcus pneumoniae biofilm formation and in vivo middle ear mucosal biofilm in a rat model of acute otitis induced by S. pneumoniae. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 9. 5(3):139–144. PMID: 22977710.6. Dostal M, Hertz-Picciotto I, James R, Keller J, Dejmek J, Selevan S, et al. Childhood morbidity and air pollution in the Teplice program. Cas Lek Cesk. 2001; 10. 140(21):658–661. PMID: 11766454.7. Rovers MM, de Kok IM, Schilder AG. Risk factors for otitis media: an international perspective. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; 7. 70(7):1251–1256. PMID: 16481051.
Article8. Heinrich J, Frye C, Holscher B, Meyer I, Pitz M, Cyrys J, et al. Environmental surveys in the areas of Bitterfeld, Hettstedt and a comparative area in 1992-2000. Gesundheitswesen. 2002; 12. 64(12):675–682. PMID: 12516020.9. Song JJ, Lee JD, Lee BD, Chae SW, Park MK. Effect of acrolein, a hazardous air pollutant in smoke, on human middle ear epithelial cells. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; 10. 77(10):1659–1664. PMID: 23953484.
Article10. Song JJ, Kwon JY, Park MK, Seo YR. Microarray analysis of gene expression alteration in human middle ear epithelial cells induced by micro particle. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; 10. 77(10):1760–1764. PMID: 24012219.
Article11. Ichinose T, Nishikawa M, Takano H, Sera N, Sadakane K, Mori I, et al. Pulmonary toxicity induced by intratracheal instillation of Asian yellow dust (Kosa) in mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005; 7. 20(1):48–56. PMID: 21783567.
Article12. Kang IG, Jung JH, Kim ST. Asian sand dust enhances allergen-induced th2 allergic inflammatory changes and mucin production in BALB/c mouse lungs. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 7. 4(4):206–213. PMID: 22754714.
Article13. Nikitin A, Egorov S, Daraselia N, Mazo I. Pathway studio: the analysis and navigation of molecular networks. Bioinformatics. 2003; 11. 19(16):2155–2157. PMID: 14594725.14. Yamada P, Hatta T, Du M, Wakimizu K, Han J, Maki T, et al. Inflammatory and degranulation effect of yellow sand on RBL-2H3 cells in relation to chemical and biological constituents. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2012; 10. 84:9–17. PMID: 22835726.
Article15. Song Y, Ichinose T, Morita K, Nakanishi T, Kanazawa T, Yoshida Y. Asian sand dust causes subacute peripheral immune modification with NF-κB activation. Environ Toxicol. 2015; 5. 30(5):549–558. PMID: 24376072.
Article16. Yanagisawa R, Takano H, Ichinose T, Mizushima K, Nishikawa M, Mori I, et al. Gene expression analysis of murine lungs following pulmonary exposure to Asian sand dust particles. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2007; 9. 232(8):1109–1118. PMID: 17720957.
Article17. Wisdom R, Johnson RS, Moore C. c-Jun regulates cell cycle progression and apoptosis by distinct mechanisms. EMBO J. 1999; 1. 18(1):188–197. PMID: 9878062.
Article18. Wei X, Xu H, Kufe D. Human MUC1 oncoprotein regulates p53-responsive gene transcription in the genotoxic stress response. Cancer Cell. 2005; 2. 7(2):167–178. PMID: 15710329.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Asian Sand Dust Enhances the Inflammatory Response and Mucin Gene Expression in the Middle Ear
- Asian Sand Dust Up-Regulates MUC4 Expression in Human Upper Airway Epithelial Cells
- From Historical Dust ail to Early Warning of Asian Dust Events in Korea
- Asian Dust Particles Induce TGF-beta1 via Reactive Oxygen Species in Bronchial Epithelial Cells
- The Health Effects of Asian Dust Event