J Korean Med Assoc.
2004 May;47(5):465-470. 10.5124/jkma.2004.47.5.465.
The Health Effects of Asian Dust Event
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Korea. hojang@dku.edu
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Korea. chosuh@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2137882
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2004.47.5.465
Abstract
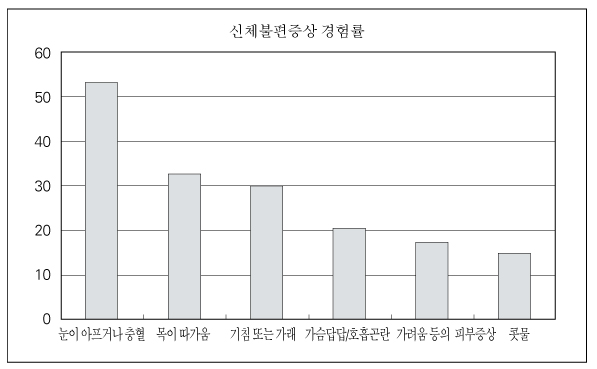
- The Korean peninsula has a long history of spring time dust clouds blown by winds from the arid deserts of Mongolia and China, these are called Yellow sand or Asian dust event. Public concern about the possible adverse effects of these dust events has increased, because the dust arrives in Korea after having passed over heavily industrialized eastern China. Most studies on the Asian dust have been focused on the physiochemical properties of the dust. Just several studies have been published on the matter of the health effects of the Asian dust both domestically and internationally. Even though the dust of crustal origin like the Asian dust is not considered as harmful as the dust from the exhaust gas, many people have experienced the eye symptoms and the respiratory symptoms such as cough, sputum, and chest tightness during the yellow sand period. However it is not clear that the increased risk of experiencing respiratory symptoms during the dust period leads to increased risk of hospitalization or mortality. Limited epidemiologic studies suggest that the aged people and the patients with cardiopulmonary disease are more susceptible to possible harmful effects of the Asian dust.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Toxicity and health effects of Asian dust: a literature review
Ho-Jang Kwon
J Korean Med Assoc. 2012;55(3):234-242. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2012.55.3.234.Toxicity and health effects of Asian dust: a literature review
Ho-Jang Kwon
J Korean Med Assoc. 2012;55(3):234-242. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2012.55.3.234.Guideline for the prevention and management of particulate matter/Asian dust particle-induced adverse health effect on the patients with pulmonary diseases
Sun Young Kyung, Young Sam Kim, Woo Jin Kim, Moo Suk Park, Jin Woo Song, Hokee Yum, Hyoung Kyu Yoon, Chin Kook Rhee, Sung Hwan Jeong
J Korean Med Assoc. 2015;58(11):1060-1069. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2015.58.11.1060.
Reference
-
2. Taylor DA. Dust in the wind. Environ Health Perspect. 2002. 110(2):A80–A87.
Article6. Kwon HJ, Cho SH, Chun Y, Lagarde F, Pershagen G. Effects of the Asian dust events on daily mortality in Seoul, Korea. Environ Res. 2002. 90:1–5.
Article7. Chen YS, Sheen PC, Chen ER, Liu YK, Wu TN, et al. Effects of Asian dust storm events on daily mortality in Taipei, Taiwan. Environ Res. in press.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Toxicity and health effects of Asian dust: a literature review
- Perceptions of the Asian Dust: Analysis of the Newspaper Articles about the Asian Dust
- Public Perceptions of the Risk of Asian Dust Storms in Seoul and its Metropolitan Area
- Effects of the Severe Asian Dust Events on Daily Mortality during the Spring of 2002, in Seoul, Korea
- Effect of the Asian Dust Events on Respiratory Disease During the Spring