Anat Cell Biol.
2013 Dec;46(4):229-234. 10.5115/acb.2013.46.4.229.
Adiponectin as a new paradigm for approaching Alzheimer's disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jelee@yuhs.ac
- 2BK21 Plus Project for Medical Sciences, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2046762
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2013.46.4.229
Abstract
- Adiponectin is an adipocytokine released by the adipose tissue and has multiple roles in the immune system and in the metabolic syndromes such as cardiovascular disease, Type 2 diabetes, obesity and also in the neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer's disease. Adiponectin regulates the sensitivity of insulin, fatty acid catabolism, glucose homeostasis and anti-inflammatory system through various mechanisms. Previous studies demonstrated that adiponectin modulates memory and cognitive impairment and contributes to the deregulated glucose metabolism and mitochondrial dysfunction observed in Alzheimer's disease. Here, we aim to summarize recent studies that suggest the potential correlation between adiponectin and Alzheimer's disease.
MeSH Terms
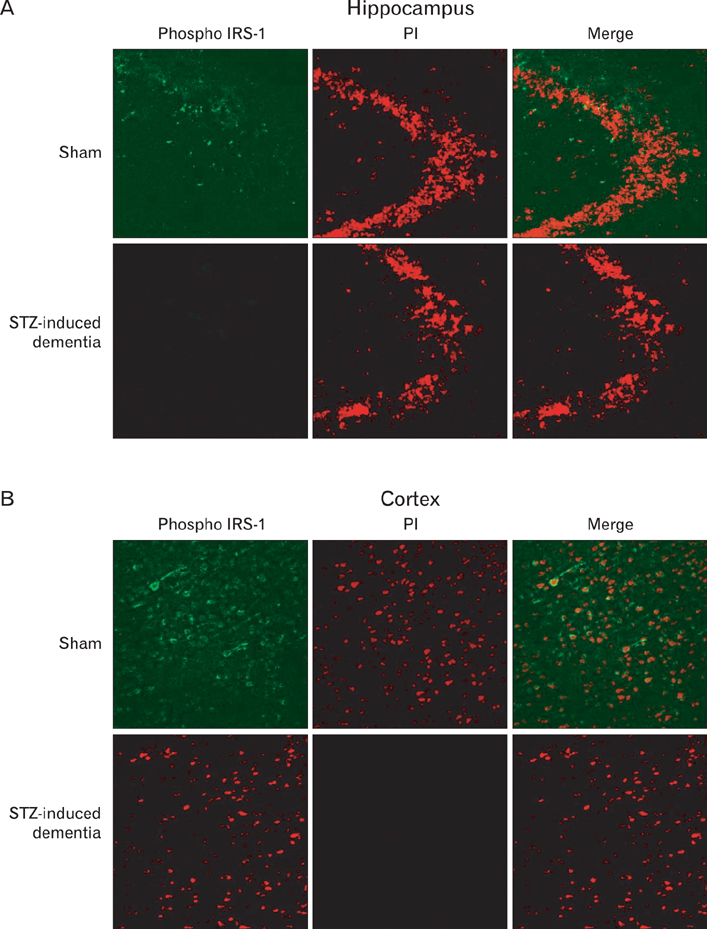
Figure
Reference
-
1. Spranger J, Verma S, Göhring I, Bobbert T, Seifert J, Sindler AL, Pfeiffer A, Hileman SM, Tschöp M, Banks WA. Adiponectin does not cross the blood-brain barrier but modifies cytokine expression of brain endothelial cells. Diabetes. 2006; 55:141–147.2. Kubota N, Yano W, Kubota T, Yamauchi T, Itoh S, Kumagai H, Kozono H, Takamoto I, Okamoto S, Shiuchi T, Suzuki R, Satoh H, Tsuchida A, Moroi M, Sugi K, Noda T, Ebinuma H, Ueta Y, Kondo T, Araki E, Ezaki O, Nagai R, Tobe K, Terauchi Y, Ueki K, Minokoshi Y, Kadowaki T. Adiponectin stimulates AMP-activated protein kinase in the hypothalamus and increases food intake. Cell Metab. 2007; 6:55–68.3. Psilopanagioti A, Papadaki H, Kranioti EF, Alexandrides TK, Varakis JN. Expression of adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in human pituitary gland and brain. Neuroendocrinology. 2009; 89:38–47.4. Calvani M, Scarfone A, Granato L, Mora EV, Nanni G, Castagneto M, Greco AV, Manco M, Mingrone G. Restoration of adiponectin pulsatility in severely obese subjects after weight loss. Diabetes. 2004; 53:939–947.5. Diniz BS, Teixeira AL, Campos AC, Miranda AS, Rocha NP, Talib LL, Gattaz WF, Forlenza OV. Reduced serum levels of adiponectin in elderly patients with major depression. J Psychiatr Res. 2012; 46:1081–1085.6. Zuliani G, Ranzini M, Guerra G, Rossi L, Munari MR, Zurlo A, Volpato S, Atti AR, Blè A, Fellin R. Plasma cytokines profile in older subjects with late onset Alzheimer's disease or vascular dementia. J Psychiatr Res. 2007; 41:686–693.7. Berg AH, Combs TP, Scherer PE. ACRP30/adiponectin: an adipokine regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 13:84–89.8. Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocr Rev. 2005; 26:439–451.9. Tsao TS, Lodish HF, Fruebis J. ACRP30, a new hormone controlling fat and glucose metabolism. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002; 440:213–221.10. Cai H, Cong WN, Ji S, Rothman S, Maudsley S, Martin B. Metabolic dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012; 9:5–17.11. Chen B, Liao WQ, Xu N, Xu H, Wen JY, Yu CA, Liu XY, Li CL, Zhao SM, Campbell W. Adiponectin protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through anti-inflammatory action. Brain Res. 2009; 1273:129–137.12. Jung TW, Lee JY, Shim WS, Kang ES, Kim JS, Ahn CW, Lee HC, Cha BS. Adiponectin protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against acetaldehyde-induced cytotoxicity. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006; 72:616–623.13. Jeon BT, Shin HJ, Kim JB, Kim YK, Lee DH, Kim KH, Kim HJ, Kang SS, Cho GJ, Choi WS, Roh GS. Adiponectin protects hippocampal neurons against kainic acid-induced excitotoxicity. Brain Res Rev. 2009; 61:81–88.14. Qi Y, Takahashi N, Hileman SM, Patel HR, Berg AH, Pajvani UB, Scherer PE, Ahima RS. Adiponectin acts in the brain to decrease body weight. Nat Med. 2004; 10:524–529.15. Reaven GM. Insulin resistance and human disease: a short history. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 1998; 9:387–406.16. Kusminski CM, McTernan PG, Schraw T, Kos K, O'Hare JP, Ahima R, Kumar S, Scherer PE. Adiponectin complexes in human cerebrospinal fluid: distinct complex distribution from serum. Diabetologia. 2007; 50:634–642.17. Kos K, Harte AL, da Silva NF, Tonchev A, Chaldakov G, James S, Snead DR, Hoggart B, O'Hare JP, McTernan PG, Kumar S. Adiponectin and resistin in human cerebrospinal fluid and expression of adiponectin receptors in the human hypothalamus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:1129–1136.18. Ebinuma H, Miida T, Yamauchi T, Hada Y, Hara K, Kubota N, Kadowaki T. Improved ELISA for selective measurement of adiponectin multimers and identification of adiponectin in human cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem. 2007; 53:1541–1544.19. Une K, Takei YA, Tomita N, Asamura T, Ohrui T, Furukawa K, Arai H. Adiponectin in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid in MCI and Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurol. 2011; 18:1006–1009.20. Dzielińska Z, Januszewicz A, Wiecek A, Demkow M, Makowiecka-Cieśla M, Prejbisz A, Kadziela J, Mielniczuk R, Florczak E, Janas J, Januszewicz M, Ruzyłło W. Decreased plasma concentration of a novel anti-inflammatory protein--adiponectin--in hypertensive men with coronary artery disease. Thromb Res. 2003; 110:365–369.21. Ouchi N, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Walsh K. Obesity, adiponectin and vascular inflammatory disease. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2003; 14:561–566.22. Gulcelik NE, Halil M, Ariogul S, Usman A. Adipocytokines and aging: adiponectin and leptin. Minerva Endocrinol. 2013; 38:203–210.23. Yokota T, Oritani K, Takahashi I, Ishikawa J, Matsuyama A, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Tenner AJ, Tomiyama Y, Matsuzawa Y. Adiponectin, a new member of the family of soluble defense collagens, negatively regulates the growth of myelomonocytic progenitors and the functions of macrophages. Blood. 2000; 96:1723–1732.24. Wolf AM, Wolf D, Rumpold H, Enrich B, Tilg H. Adiponectin induces the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-1RA in human leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 323:630–635.25. Steen E, Terry BM, Rivera EJ, Cannon JL, Neely TR, Tavares R, Xu XJ, Wands JR, de la Monte SM. Impaired insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease: is this type 3 diabetes? J Alzheimers Dis. 2005; 7:63–80.26. Rivera EJ, Goldin A, Fulmer N, Tavares R, Wands JR, de la Monte SM. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and function deteriorate with progression of Alzheimer's disease: link to brain reductions in acetylcholine. J Alzheimers Dis. 2005; 8:247–268.27. Vingtdeux V, Davies P, Dickson DW, Marambaud P. AMPK is abnormally activated in tangle- and pre-tangle-bearing neurons in Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies. Acta Neuropathol. 2011; 121:337–349.28. Ceddia RB, Somwar R, Maida A, Fang X, Bikopoulos G, Sweeney G. Globular adiponectin increases GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake but reduces glycogen synthesis in rat skeletal muscle cells. Diabetologia. 2005; 48:132–139.29. Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Terauchi Y, Kubota N, Hara K, Mori Y, Ide T, Murakami K, Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Ezaki O, Akanuma Y, Gavrilova O, Vinson C, Reitman ML, Kagechika H, Shudo K, Yoda M, Nakano Y, Tobe K, Nagai R, Kimura S, Tomita M, Froguel P, Kadowaki T. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med. 2001; 7:941–946.30. Kubota N, Terauchi Y, Yamauchi T, Kubota T, Moroi M, Matsui J, Eto K, Yamashita T, Kamon J, Satoh H, Yano W, Froguel P, Nagai R, Kimura S, Kadowaki T, Noda T. Disruption of adiponectin causes insulin resistance and neointimal formation. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:25863–25866.31. Hu E, Liang P, Spiegelman BM. AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:10697–10703.32. Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE, Tataranni PA. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:1930–1935.33. Statnick MA, Beavers LS, Conner LJ, Corominola H, Johnson D, Hammond CD, Rafaeloff-Phail R, Seng T, Suter TM, Sluka JP, Ravussin E, Gadski RA, Caro JF. Decreased expression of apM1 in omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue of humans with type 2 diabetes. Int J Exp Diabetes Res. 2000; 1:81–88.34. Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, Iwahashi H, Kuriyama H, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Nishida M, Kihara S, Sakai N, Nakajima T, Hasegawa K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa Y. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000; 20:1595–1599.35. Craft S, Asthana S, Newcomer JW, Wilkinson CW, Matos IT, Baker LD, Cherrier M, Lofgreen C, Latendresse S, Petrova A, Plymate S, Raskind M, Grimwood K, Veith RC. Enhancement of memory in Alzheimer disease with insulin and somatostatin, but not glucose. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999; 56:1135–1140.36. Park CR, Seeley RJ, Craft S, Woods SC. Intracerebroventricular insulin enhances memory in a passive-avoidance task. Physiol Behav. 2000; 68:509–514.37. van der Heide LP, Ramakers GM, Smidt MP. Insulin signaling in the central nervous system: learning to survive. Prog Neurobiol. 2006; 79:205–221.38. Plum L, Schubert M, Brüning JC. The role of insulin receptor signaling in the brain. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 16:59–65.39. Wang YT, Salter MW. Regulation of NMDA receptors by tyrosine kinases and phosphatases. Nature. 1994; 369:233–235.40. van der Heide LP, Kamal A, Artola A, Gispen WH, Ramakers GM. Insulin modulates hippocampal activity-dependent synaptic plasticity in a N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor and phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase-dependent manner. J Neurochem. 2005; 94:1158–1166.41. Hotamisligil GS, Peraldi P, Budavari A, Ellis R, White MF, Spiegelman BM. IRS-1-mediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-alpha- and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Science. 1996; 271:665–668.42. Winer S, Chan Y, Paltser G, Truong D, Tsui H, Bahrami J, Dorfman R, Wang Y, Zielenski J, Mastronardi F, Maezawa Y, Drucker DJ, Engleman E, Winer D, Dosch HM. Normalization of obesity-associated insulin resistance through immunotherapy. Nat Med. 2009; 15:921–929.43. Nishimura S, Manabe I, Nagasaki M, Eto K, Yamashita H, Ohsugi M, Otsu M, Hara K, Ueki K, Sugiura S, Yoshimura K, Kadowaki T, Nagai R. CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat Med. 2009; 15:914–920.44. Semple RK, Halberg NH, Burling K, Soos MA, Schraw T, Luan J, Cochran EK, Dunger DB, Wareham NJ, Scherer PE, Gorden P, O'Rahilly S. Paradoxical elevation of high-molecular weight adiponectin in acquired extreme insulin resistance due to insulin receptor antibodies. Diabetes. 2007; 56:1712–1717.45. Ahima RS, Qi Y, Singhal NS, Jackson MB, Scherer PE. Brain adipocytokine action and metabolic regulation. Diabetes. 2006; 55:Suppl 2. S145–S154.46. Hivert MF, Sullivan LM, Fox CS, Nathan DM, D'Agostino RB Sr, Wilson PW, Meigs JB. Associations of adiponectin, resistin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93:3165–3172.47. Forlenza OV, Diniz BS, Talib LL, Mendonça VA, Ojopi EB, Gattaz WF, Teixeira AL. Increased serum IL-1beta level in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2009; 28:507–512.48. Diniz BS, Teixeira AL, Ojopi EB, Talib LL, Mendonça VA, Gattaz WF, Forlenza OV. Higher serum sTNFR1 level predicts conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010; 22:1305–1311.49. Poehlman ET, Dvorak RV. Energy expenditure in Alzheimer's disease. J Nutr Health Aging. 1998; 2:115–118.50. Giordano V, Peluso G, Iannuccelli M, Benatti P, Nicolai R, Calvani M. Systemic and brain metabolic dysfunction as a new paradigm for approaching Alzheimer's dementia. Neurochem Res. 2007; 32:555–567.51. Yan Z, Feng J. Alzheimer's disease: interactions between cholinergic functions and beta-amyloid. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2004; 1:241–248.52. Craft S, Asthana S, Schellenberg G, Cherrier M, Baker LD, Newcomer J, Plymate S, Latendresse S, Petrova A, Raskind M, Peskind E, Lofgreen C, Grimwood K. Insulin metabolism in Alzheimer's disease differs according to apolipoprotein E genotype and gender. Neuroendocrinology. 1999; 70:146–152.53. Kern W, Peters A, Fruehwald-Schultes B, Deininger E, Born J, Fehm HL. Improving influence of insulin on cognitive functions in humans. Neuroendocrinology. 2001; 74:270–280.54. Moreira PI, Duarte AI, Santos MS, Rego AC, Oliveira CR. An integrative view of the role of oxidative stress, mitochondria and insulin in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009; 16:741–761.55. Bonda DJ, Wang X, Perry G, Nunomura A, Tabaton M, Zhu X, Smith MA. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease: a possibility for prevention. Neuropharmacology. 2010; 59:290–294.56. Praticò D, Uryu K, Leight S, Trojanoswki JQ, Lee VM. Increased lipid peroxidation precedes amyloid plaque formation in an animal model of Alzheimer amyloidosis. J Neurosci. 2001; 21:4183–4187.57. Chan KH, Lam KS, Cheng OY, Kwan JS, Ho PW, Cheng KK, Chung SK, Ho JW, Guo VY, Xu A. Adiponectin is protective against oxidative stress induced cytotoxicity in amyloid-beta neurotoxicity. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e52354.58. Reger MA, Watson GS, Green PS, Wilkinson CW, Baker LD, Cholerton B, Fishel MA, Plymate SR, Breitner JC, DeGroodt W, Mehta P, Craft S. Intranasal insulin improves cognition and modulates beta-amyloid in early AD. Neurology. 2008; 70:440–448.59. Oh DK, Ciaraldi T, Henry RR. Adiponectin in health and disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007; 9:282–289.60. Deepa SS, Dong LQ. APPL1: role in adiponectin signaling and beyond. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 296:E22–E36.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Memorials of Alois Alzheimer (June 14, 1864~December 19, 1915) and Historical Background of Alzheimer's Disease
- Significance of Non-Alzheimer Dementia
- Metabolism-Centric Overview of the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease
- The Role of Plasma Adiponectin and Polymorphism of Adiponectin Gene in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Interrelationship between Plasma Adiponectin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease