Korean J Urol.
2010 Aug;51(8):511-517. 10.4111/kju.2010.51.8.511.
Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling: Implications in Urology
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urologic Oncology and Dean and Betty Gallo Prostate Cancer Center, The Cancer Institute of New Jersey, Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ, USA. kimiy@umdnj.edu
- 2Department of Urology, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1997017
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2010.51.8.511
Abstract
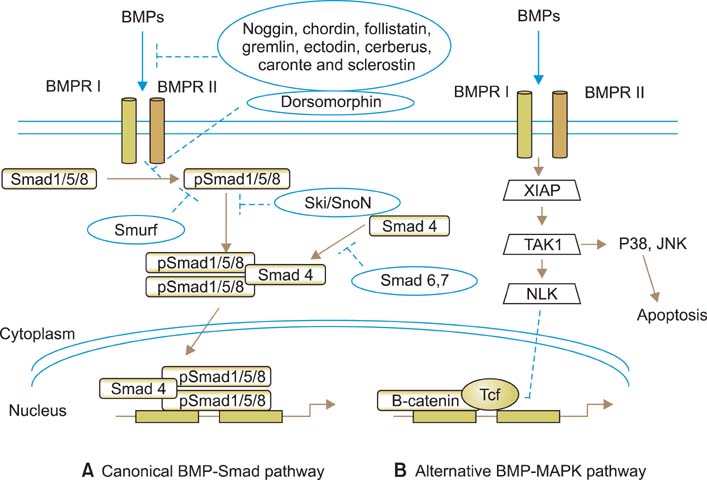
- The bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), as members of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) superfamily, not only control bone formation, but also regulate multiple key steps during embryonic development and differentiation. Furthermore, BMPs play critical roles in maintaining the homeostasis of the cardiovascular, pulmonary, reproductive, urogenital, and nervous systems in adult life. Like all members of the TGF-beta superfamily, BMP signaling is mediated through a heteromeric complex of type I and type II transmembrane serine/threonine kinase receptors. The subsequent signal transduction cascade includes either the canonical Smad-dependent or non-canonical Smad-independent pathways. Reflecting the critical function of BMPs, BMP signaling is tightly regulated at multiple steps by various mechanisms including extracellular endogenous antagonists, neutralizing antibodies/extracellular soluble receptor domains, small molecule inhibitors, cytoplasmic inhibitory Smads, and transcriptional co-repressors. Recently, dorsomorphin, the first small molecule inhibitor of BMP signaling, was identified and suggested as a useful tool for dissecting the mechanisms of signaling pathways and for developing novel therapeutics for diverse human diseases that are related to the BMP signaling pathways. In this article, we discuss various mechanisms involved in regulating BMP signaling pathways and their implications for urology.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins
Co-Repressor Proteins
Cytoplasm
Embryonic Development
Female
Homeostasis
Humans
Nervous System
Osteogenesis
Phosphotransferases
Pregnancy
Pyrazoles
Pyrimidines
Signal Transduction
Transforming Growth Factor beta
Transforming Growth Factors
Urology
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins
Co-Repressor Proteins
Phosphotransferases
Pyrazoles
Pyrimidines
Transforming Growth Factor beta
Transforming Growth Factors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Massague J. TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998. 67:753–791.2. Wozney JM, Rosen V, Celeste AJ, Mitsock LM, Whitters MJ, Kriz RW, et al. Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science. 1988. 242:1528–1534.3. Balemans W, Van Hul W. Extracellular regulation of BMP signaling in vertebrates: a cocktail of modulators. Dev Biol. 2002. 250:231–250.4. Chen D, Zhao M, Mundy GR. Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors. 2004. 22:233–241.5. Cunningham NS, Paralkar V, Reddi AH. Osteogenin and recombinant bone morphogenetic protein 2B are chemotactic for human monocytes and stimulate transforming growth factor beta 1 mRNA expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. 89:11740–11744.6. Yamashita H, ten Dijke P, Huylebroeck D, Sampath TK, Andries M, Smith JC, et al. Osteogenic protein-1 binds to activin type II receptors and induces certain activin-like effects. J Cell Biol. 1995. 130:217–226.7. Zhao GQ. Consequences of knocking out BMP signaling in the mouse. Genesis. 2003. 35:43–56.8. Goumans MJ, Mummery C. Functional analysis of the TGFbeta receptor/Smad pathway through gene ablation in mice. Int J Dev Biol. 2000. 44:253–265.9. Billings PC, Fiori JL, Bentwood JL, O'Connell MP, Jiao X, Nussbaum B, et al. Dysregulated BMP signaling and enhanced osteogenic differentiation of connective tissue progenitor cells from patients with fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP). J Bone Miner Res. 2008. 23:305–313.10. Haramis AP, Begthel H, van den Born M, van Es J, Jonkheer S, Offerhaus GJ, et al. De novo crypt formation and juvenile polyposis on BMP inhibition in mouse intestine. Science. 2004. 303:1684–1686.11. Yu PB, Beppu H, Kawai N, Li E, Bloch KD. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type II receptor deletion reveals BMP ligand-specific gain of signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2005. 280:24443–24450.12. Hardwick JC, Kodach LL, Offerhaus GJ, van den Brink GR. Bone morphogenetic protein signalling in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008. 8:806–812.13. Theriault BL, Shepherd TG, Mujoomdar ML, Nachtigal MW. BMP4 induces EMT and Rho GTPase activation in human ovarian cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2007. 28:1153–1162.14. Kraunz KS, Nelson HH, Liu M, Wiencke JK, Kelsey KT. Interaction between the bone morphogenetic proteins and Ras/MAP-kinase signalling pathways in lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2005. 93:949–952.15. Hsu MY, Rovinsky S, Penmatcha S, Herlyn M, Muirhead D. Bone morphogenetic proteins in melanoma: angel or devil? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2005. 24:251–263.16. Tseng YH, Kokkotou E, Schulz TJ, Huang TL, Winnay JN, Taniguchi CM, et al. New role of bone morphogenetic protein 7 in brown adipogenesis and energy expenditure. Nature. 2008. 454:1000–1004.17. Gesta S, Tseng YH, Kahn CR. Developmental origin of fat: tracking obesity to its source. Cell. 2007. 131:242–256.18. Sebald W, Nickel J, Zhang JL, Mueller TD. Molecular recognition in bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)/receptor interaction. Biol Chem. 2004. 385:697–710.19. Miyazono K, Kusanagi K, Inoue H. Divergence and convergence of TGF-beta/BMP signaling. J Cell Physiol. 2001. 187:265–276.20. Nohe A, Keating E, Knaus P, Petersen NO. Signal transduction of bone morphogenetic protein receptors. Cell Signal. 2004. 16:291–299.21. Ito H, Akiyama H, Shigeno C, Nakamura T. Noggin and bone morphogenetic protein-4 coordinately regulate the progression of chondrogenic differentiation in mouse clonal EC cells, ATDC5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. 260:240–244.22. Zhu W, Kim J, Cheng C, Rawlins BA, Boachie-Adjei O, Crystal RG, et al. Noggin regulation of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) 2/7 heterodimer activity in vitro. Bone. 2006. 39:61–71.23. Yu PB, Hong CC, Sachidanandan C, Babitt JL, Deng DY, Hoyng SA, et al. Dorsomorphin inhibits BMP signals required for embryogenesis and iron metabolism. Nat Chem Biol. 2008. 4:33–41.24. ten Dijke P, Yamashita H, Ichijo H, Franzen P, Laiho M, Miyazono K, et al. Characterization of type I receptors for transforming growth factor-beta and activin. Science. 1994. 264:101–104.25. Rosenzweig BL, Imamura T, Okadome T, Cox GN, Yamashita H, ten Dijke P, et al. Cloning and characterization of a human type II receptor for bone morphogenetic proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. 92:7632–7636.26. Derynck R, Zhang Y, Feng XH. Smads: transcriptional activators of TGF-beta responses. Cell. 1998. 95:737–740.27. Nohe A, Hassel S, Ehrlich M, Neubauer F, Sebald W, Henis YI, et al. The mode of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor oligomerization determines different BMP-2 signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:5330–5338.28. Hassel S, Schmitt S, Hartung A, Roth M, Nohe A, Petersen N, et al. Initiation of Smad-dependent and Smad-independent signaling via distinct BMP-receptor complexes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003. 85:A Suppl 3. 44–51.29. Canalis E, Economides AN, Gazzerro E. Bone morphogenetic proteins, their antagonists, and the skeleton. Endocr Rev. 2003. 24:218–235.30. Larrain J, Bachiller D, Lu B, Agius E, Piccolo S, De Robertis EM. BMP-binding modules in chordin: a model for signalling regulation in the extracellular space. Development. 2000. 127:821–830.31. Miyazono K. Positive and negative regulation of TGF-beta signaling. J Cell Sci. 2000. 113:1101–1109.32. Stottmann RW, Anderson RM, Klingensmith J. The BMP antagonists Chordin and Noggin have essential but redundant roles in mouse mandibular outgrowth. Dev Biol. 2001. 240:457–473.33. Piccolo S, Agius E, Leyns L, Bhattacharyya S, Grunz H, Bouwmeester T, et al. The head inducer Cerberus is a multifunctional antagonist of Nodal, BMP and Wnt signals. Nature. 1999. 397:707–710.34. Yokouchi Y, Vogan KJ, Pearse RV 2nd, Tabin CJ. Antagonistic signaling by Caronte, a novel Cerberus-related gene, establishes left-right asymmetric gene expression. Cell. 1999. 98:573–583.35. Capdevila J, Johnson RL. Endogenous and ectopic expression of noggin suggests a conserved mechanism for regulation of BMP function during limb and somite patterning. Dev Biol. 1998. 197:205–217.36. Zhang D, Ferguson CM, O'Keefe RJ, Puzas JE, Rosier RN, Reynolds PR. A role for the BMP antagonist chordin in endochondral ossification. J Bone Miner Res. 2002. 17:293–300.37. Tardif G, Pelletier JP, Boileau C, Martel-Pelletier J. The BMP antagonists follistatin and gremlin in normal and early osteoarthritic cartilage: an immunohistochemical study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009. 17:263–270.38. Michos O, Panman L, Vintersten K, Beier K, Zeller R, Zuniga A. Gremlin-mediated BMP antagonism induces the epithelial-mesenchymal feedback signaling controlling metanephric kidney and limb organogenesis. Development. 2004. 131:3401–3410.39. Khokha MK, Hsu D, Brunet LJ, Dionne MS, Harland RM. Gremlin is the BMP antagonist required for maintenance of Shh and Fgf signals during limb patterning. Nat Genet. 2003. 34:303–307.40. Zimmerman LB, De Jesus-Escobar JM, Harland RM. The Spemann organizer signal noggin binds and inactivates bone morphogenetic protein 4. Cell. 1996. 86:599–606.41. Hsu DR, Economides AN, Wang X, Eimon PM, Harland RM. The Xenopus dorsalizing factor Gremlin identifies a novel family of secreted proteins that antagonize BMP activities. Mol Cell. 1998. 1:673–683.42. Haudenschild DR, Palmer SM, Moseley TA, You Z, Reddi AH. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-6 signaling and BMP antagonist noggin in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2004. 64:8276–8284.43. Tezval M, Tezval H, Dresing K, Stuermer EK, Blaschke M, Stuermer KM, et al. Differentiation dependent expression of urocortin's mRNA and peptide in human osteoprogenitor cells: influence of BMP-2, TGF-beta-1 and dexamethasone. J Mol Histol. 2009. 40:331–341.44. Hanyu A, Ishidou Y, Ebisawa T, Shimanuki T, Imamura T, Miyazono K. The N domain of Smad7 is essential for specific inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Cell Biol. 2001. 155:1017–1027.45. Zhu HT, Kavsak P, Abdollah S, Wrana JL, Thomsen GH. A SMAD ubiquitin ligase targets the BMP pathway and affects embryonic pattern formation. Nature. 1999. 400:687–693.46. Hata A, Lagna G, Massague J, Hemmati-Brivanlou A. Smad6 inhibits BMP/Smad1 signaling by specifically competing with the Smad4 tumor suppressor. Gene Dev. 1998. 12:186–197.47. Zwijsen A, Verschueren K, Huylebroeck D. New intracellular components of bone morphogenetic protein/Smad signaling cascades. FEBS Lett. 2003. 546:133–139.48. Dudley AT, Robertson EJ. Overlapping expression domains of bone morphogenetic protein family members potentially account for limited tissue defects in BMP7 deficient embryos. Dev Dyn. 1997. 208:349–362.49. Godin RE, Robertson EJ, Dudley AT. Role of BMP family members during kidney development. Int J Dev Biol. 1999. 43:405–411.50. Dudley AT, Lyons KM, Robertson EJ. A requirement for bone morphogenetic protein-7 during development of the mammalian kidney and eye. Genes Dev. 1995. 9:2795–2807.51. Mitu G, Hirschberg R. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 (BMP7) in chronic kidney disease. Front Biosci. 2008. 13:4726–4739.52. Kim IY, Lee DH, Lee DK, Kim BC, Kim HT, Leach FS, et al. Decreased expression of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor type II correlates with insensitivity to BMP-6 in human renal cell carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. 9:6046–6051.53. Basic-Jukic N, Radic-Antolic M, Hudolin T, Coric M, Zadro R, Pasini J, et al. Immunolocalization and mRNA expression of bone morphogenetic protein-6 in human clear cell renal carcinoma. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2009. 32:445–450.54. Blish KR, Wang W, Willingham MC, Du W, Birse CE, Krishnan SR, et al. A human bone morphogenetic protein antagonist is down-regulated in renal cancer. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. 19:457–464.55. Kim IY, Lee DH, Lee DK, Kim WJ, Kim MM, Morton RA, et al. Restoration of bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II expression leads to a decreased rate of tumor growth in bladder transitional cell carcinoma cell line TSU-Pr1. Cancer Res. 2004. 64:7355–7360.56. Bentley H, Hamdy FC, Hart KA, Seid JM, Williams JL, Johnstone D, et al. Expression of bone morphogenetic proteins in human prostatic adenocarcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Br J Cancer. 1992. 66:1159–1163.57. Hamdy FC, Autzen P, Robinson MC, Horne CH, Neal DE, Robson CN. Immunolocalization and messenger RNA expression of bone morphogenetic protein-6 in human benign and malignant prostatic tissue. Cancer Res. 1997. 57:4427–4431.58. Masuda H, Fukabori Y, Nakano K, Takezawa Y, CSuzuki T, Yamanaka H. Increased expression of bone morphogenetic protein-7 in bone metastatic prostate cancer. Prostate. 2003. 54:268–274.59. Yuen HF, Chan YP, Cheung WL, Wong YC, Wang X, Chan KW. The prognostic significance of BMP-6 signaling in prostate cancer. Mod Pathol. 2008. 21:1436–1443.60. Masuda H, Fukabori Y, Nakano K, Shimizu N, Yamanaka H. Expression of bone morphogenetic protein-7 (BMP-7) in human prostate. Prostate. 2004. 59:101–106.61. Buijs JT, Rentsch CA, van der Horst G, van Overveld PG, Wetterwald A, Schwaninger R, et al. BMP7, a putative regulator of epithelial homeostasis in the human prostate, is a potent inhibitor of prostate cancer bone metastasis in vivo. Am J Pathol. 2007. 171:1047–1057.62. Kim IY, Lee DH, Ahn HJ, Tokunaga H, Song W, Devereaux LM, et al. Expression of bone morphogenetic protein receptors type-IA, -IB and -II correlates with tumor grade in human prostate cancer tissues. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:2840–2844.63. Sugimoto H, Yang C, LeBleu VS, Soubasakos MA, Giraldo M, Zeisberg M, et al. BMP-7 functions as a novel hormone to facilitate liver regeneration. FASEB J. 2007. 21:256–264.64. Souza TA, Chen X, Guo Y, Sava P, Zhang J, Hill JJ, et al. Proteomic identification and functional validation of activins and bone morphogenetic protein 11 as candidate novel muscle mass regulators. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. 22:2689–2702.65. Natsume T, Tomita S, Iemura S, Kinto N, Yamaguchi A, Ueno N. Interaction between soluble type I receptor for bone morphogenetic protein and bone morphogenetic protein-4. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:11535–11540.66. Inman GJ, Nicolas FJ, Callahan JF, Harling JD, Gaster LM, Reith AD, et al. SB-431542 is a potent and specific inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta superfamily type I activin receptor-like kinase (ALK) receptors ALK4, ALK5, and ALK7. Mol Pharmacol. 2002. 62:65–74.67. Halder SK, Beauchamp RD, Datta PK. A specific inhibitor of TGF-beta receptor kinase, SB-431542, as a potent antitumor agent for human cancers. Neoplasia. 2005. 7:509–521.68. Lee GT, Hong JH, Mueller TJ, Watson JA, Kwak C, Sheen YY, et al. Effect of IN-1130, a small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor/activin receptor-like kinase-5, on prostate cancer cells. J Urol. 2008. 180:2660–2667.69. Hao J, Daleo MA, Murphy CK, Yu PB, Ho JN, Hu J, et al. Dorsomorphin, a selective small molecule inhibitor of BMP signaling, promotes cardiomyogenesis in embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 2008. 3:e2904.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Response of Human Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells to Bone Morphogenetic Proteins, and the Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptors
- Purification of porcine bone morphogenetic protein
- The experimental study on the effect of pulsating electromagnetic fields in the osteoinduction induced by bone morphogenetic protein
- Effect of composite of bone morphogenetic protein and plaster of paris on healing of bone defect in the rat tibia
- Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Desensitizes MC3T3-E1 Osteoblastic Cells to Estrogen Through Transcriptional Downregulation of Estrogen Receptor 1