J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2005 Jan;30(1):1-6. 10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.001.
Effects of Enterococcus faecalis sonicated extracts on IL-2, IL-4 and TGF-beta1 production from human lymphocytes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Korea. limss@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1986990
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.001
Abstract
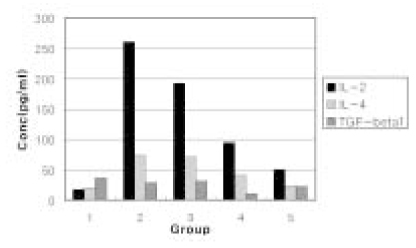
- In order to examine the immunoresponse of host cells to Enterococcus faecalis, this in vitro study monitored the production of Interleukin-2 (IL-2), Interleukin-4 (IL-4) and Transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) in human lymphocytes. Lymphocytes were activated with PHA in the presence or abscence of sonicated extracts of E. Faecalis (SEF) and further incubated for 72 hours. The level of each cytokine was measured by ELISA. Data were analyzed with Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney U test (P < 0.05). PHA-activated group did exhibit higher level of IL-2 and IL-4 than untreated control group. The levels of expression of both cytokines were significantly decreased following the treatment of high (25 microg/ml) and medium concentration (12.5 microg/ml) of SEF (P <0 .05) than those of PHA activated group. But low concentration (5 microg/ml) of SEF showed the similar level of IL-2 and IL-4 production as those of PHA activated group. TGF-beta1 was unaffected by SEF treatment. These results suggested that E. faecalis may suppress IL-2 and IL-4 production by lymphocytes and this could be one of possible factors why E. faecalis are found frequently in the teeth with failed endodontic treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls. In vitro SEM study
Saad Al-Nazhan, Alaa Al-Sulaiman, Fellwa Al-Rasheed, Fatimah Alnajjar, Bander Al-Abdulwahab, Abdulhakeem Al-Badah
Restor Dent Endod. 2014;39(4):258-264. doi: 10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.258.
Reference
-
1. Kakehashi S, et al. The effects of surgical exposures of dental pulps in germ-free and conventional laboratory rat. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1965. 20:340–349.
Article2. Sundqvist G, et al. Microbiologic analysis of the teeth with failed endodontic treatment and the outcome of conservative re-treatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998. 85:86–93.
Article3. Dahlen G, et al. Identification and antimicrobial susceptibility of enterococci isolated from the root canal. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2000. 15:309–312.
Article4. Orstavik D, Haapasalo M. Disinfection by endodontic irrigants and dressings of experimentally infected dentinal tubules. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1990. 6:142–149.
Article5. Love RM. Enterococcus faecalis - a mechanism for its role in endodontic failure. Int Endod J. 2001. 34:399–405.6. Evans M, et al. Mechanisms involved in the resistance of Enterococcus faecalis to calcium hydroxide. Int Endod J. 2002. 35:221–228.
Article7. Yoshida H, et al. Effect of sonicated material from Fusobacterium nucleatum on the functional capacity of accessory cells derived from dental pulp. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1995. 10:208–212.
Article8. Kurita-Ochiai T, et al. Immunosuppressive effect induced by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: effect on immunoglobulin production and lymphokine synthesis. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1992. 7:338–343.
Article9. Trowbridge H. Inflammation; A review of the process. 1997. 5th edition. Quintessence Publishing Co;79–90.10. Hahn CL, et al. A study of T and B cells in pulpal pathosis. J Endod. 1989. 15:20–26.
Article11. Rauschenberger CR, et al. Detection of human IL-2 in normal and inflamed dental pulps. J Endod. 1997. 23:366–370.
Article12. Kawashima N, Stashenko P. Expression of bone-resorptive and regulatory cytokines in murine periapical inflammation. Arch Oral Biol. 1999. 44:55–66.
Article13. Walker KF, et al. Cytokine expression in periapical granulation tissue as assessed by immunohistochemistry. Eur J Oral Sci. 2000. 108:195–201.
Article14. Kim SA, Lim SS. T lymphocyte subpopulations and interleukin-2, interferon-gamma, and interleukin-4 in rat pulpitis experimentally induced by specific bacteria. J Endod. 2002. 28:202–205.
Article15. Wahl SM. Transforming growth factor beta in inflammation : a cause and a cure. J Clin Immunol. 1992. 12:61–74.
Article16. Wahl SM. Transforming growth factor β; the good, the bad, and the ugly. J Exp Med. 1994. 180:1587–1590.17. Shenker BJ, et al. Suppression of human lymphocyte responses by oral spirochetes: a monocyte-dependent phenomenon. J Immunol. 1984. 132:2039–2045.18. Reiner NE. Parasite accessory cell interactions in murine heishmaniasis. I. Evasion and stimulus-dependent suppression of the macrophage interleukin-1 response by Leishmania donovani. J Immunol. 1987. 138:1919–1925.19. Shenker BJ, Slots J. Immunomodulatory effects of Bacteroides products on in vitro human lymphocyte functions. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1989. 4:24–29.
Article20. Ko HJ, Lim SS. Production of macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils stimulated with Porphyromonas endodontalis lipopolysaccharide. J Endod. 2002. 28:754–757.
Article21. Shenker BJ, et al. Immunosuppressive effects of Prevotella intermedia on In vitro Human lymphocyte activation. Infect Immun. 1991. 59:4583–4589.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of Treponema denticola immunoinhibitory protein on cytokine expression in T cells
- Effect of sonicated extracts of Enterococcus faecalis on the production of matrix metalloproteinase-8 by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils
- Changes of Interleukin-12 and Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 before and after Antipsychotic Treatments in Schizophrenic Patients
- Transforming Growth Factor-beta1(TGF-beta1) Synthesis of Human Peritoneal Mesothelial Cell
- Impact of Circulating TGF-beta and IL-10 on T Cell Cytokines in Patients with Asthma and Tuberculosis