Ann Surg Treat Res.
2014 Oct;87(4):167-173. 10.4174/astr.2014.87.4.167.
Anticancer effect of silibinin on the xenograft model using MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. gilbak73@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1882820
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2014.87.4.167
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study is to know whether silibinin has an anticancer effect on triple negative breast cancer xenograft model using MDA-MB-468 cells.
METHODS
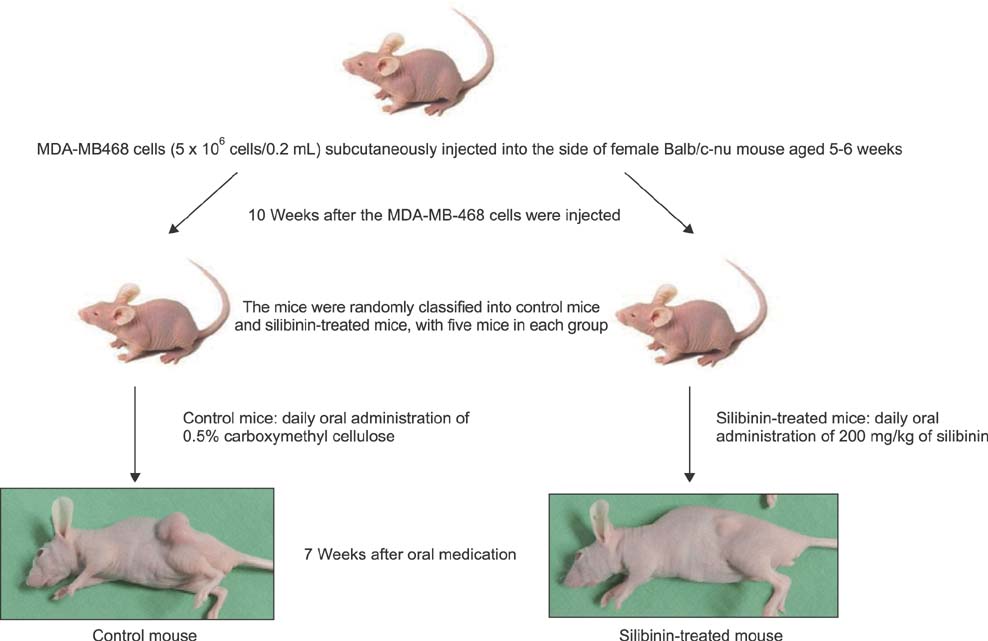
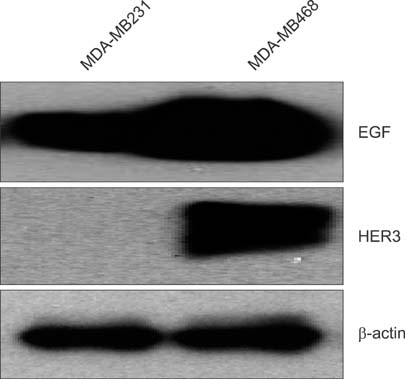
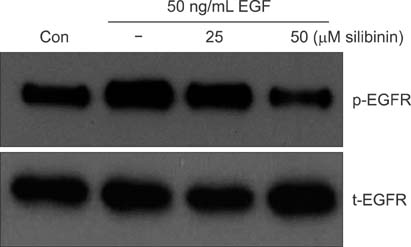
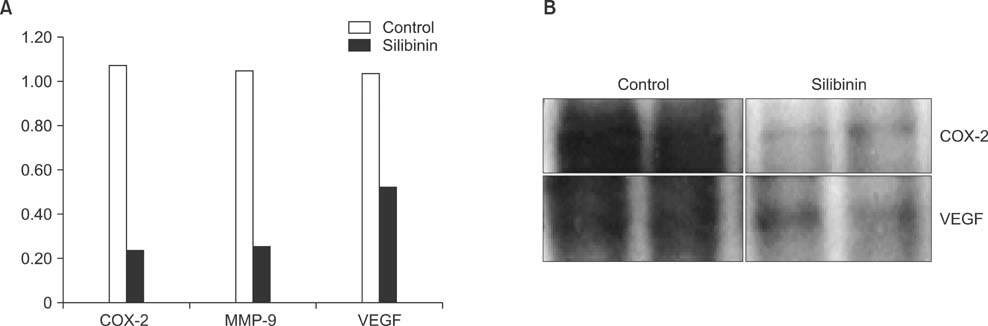
To establish the xenograft model, we injected the MDA-MB-468 cells into female Balb/c-nude mice. After establishing a xenograft model, oral silibinin was administered to the tested mice in the way of 200 mg/kg for 45 days. The difference of mean tumor volume between silibinin fed mice and control mice was analyzed. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) phosphorylation in MDA-MB-468 cells was analyzed by Western blotting. The expression of VEGF, COX-2, and MMP-9 genes in tumor tissue was analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
RESULTS
In the xenograft model using MDA-MB-468 cells, we found that oral administration of silibinin significantly suppressed the tumor volume (silibinin treated mice vs. control mice; 230.3 +/- 61.6 mm3 vs. 435.7 +/- 93.5 mm3, P < 0.001). The phosphorylation of EGFR in MDA-MB-468 cells was inhibited by treatment with 50 microg/mL of silibinin. In real time-PCR analysis of tumor tissue obtained from sacrificed mice, the gene expression of MMP-9, VEGF, and COX-2 was 51.8%-80% smaller in silibinin group than that of control group and we can also verify the similar result using Western blotting analysis.
CONCLUSION
We verified that silibinin had anticancer effect on xenograft model of MDA-MB-468 cells in the way of preventing the phosphorylation of EGFR and eventually suppressed the production of COX-2, VEGF, and MMP-9 expression. Finally, the tumor volume of xenograft models was decreased after administration of Silibinin.
MeSH Terms
-
Administration, Oral
Animals
Blotting, Western
Breast Neoplasms*
Female
Gene Expression
Heterografts*
Humans
Mice
Phosphorylation
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Triple Negative Breast Neoplasms
Tumor Burden
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001; 98:10869–10874.2. Reis-Filho JS, Natrajan R, Vatcheva R, Lambros MB, Marchio C, Mahler-Araujo B, et al. Is acinic cell carcinoma a variant of secretory carcinoma? A FISH study using ETV6 'split apart' probes. Histopathology. 2008; 52:840–846.3. Mereish KA, Bunner DL, Ragland DR, Creasia DA. Protection against microcystin-LR-induced hepatotoxicity by Silymarin: biochemistry, histopathology, and lethality. Pharm Res. 1991; 8:273–277.4. Singh RP, Deep G, Chittezhath M, Kaur M, Dwyer-Nield LD, Malkinson AM, et al. Effect of silibinin on the growth and progression of primary lung tumors in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006; 98:846–855.5. Jiang C, Agarwal R, Lu J. Anti-angiogenic potential of a cancer chemopreventive flavonoid antioxidant, silymarin: inhibition of key attributes of vascular endothelial cells and angiogenic cytokine secretion by cancer epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000; 276:371–378.6. Kaur M, Velmurugan B, Tyagi A, Deep G, Katiyar S, Agarwal C, et al. Silibinin suppresses growth and induces apoptotic death of human colorectal carcinoma LoVo cells in culture and tumor xenograft. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009; 8:2366–2374.7. Singh RP, Raina K, Sharma G, Agarwal R. Silibinin inhibits established prostate tumor growth, progression, invasion, and metastasis and suppresses tumor angiogenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate model mice. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:7773–7780.8. Kim S, Choi JH, Lim HI, Lee SK, Kim WW, Kim JS, et al. Silibinin prevents TPA-induced MMP-9 expression and VEGF secretion by inactivation of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 2009; 16:573–580.9. Kim S, Kim SH, Hur SM, Lee SK, Kim WW, Kim JS, et al. Silibinin prevents TPA-induced MMP-9 expression by down-regulation of COX-2 in human breast cancer cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009; 126:252–257.10. Bhatia N, Zhao J, Wolf DM, Agarwal R. Inhibition of human carcinoma cell growth and DNA synthesis by silibinin, an active constituent of milk thistle: comparison with silymarin. Cancer Lett. 1999; 147:77–84.11. Kim S, Lee HS, Lee SK, Kim SH, Hur SM, Kim JS, et al. 12-O-Tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced growth arrest is increased by silibinin by the down-regulation of cyclin B1 and cdc2 and the up-regulation of p21 expression in MDA-MB231 human breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 2010; 17:1127–1132.12. Kim S, Han J, Kim JS, Kim JH, Choe JH, Yang JH, et al. Silibinin suppresses EGFR ligand-induced CD44 expression through inhibition of EGFR activity in breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2011; 31:3767–3773.13. Singh RP, Tyagi A, Sharma G, Mohan S, Agarwal R. Oral silibinin inhibits in vivo human bladder tumor xenograft growth involving down-regulation of survivin. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:300–308.14. Chang HR, Chen PN, Yang SF, Sun YS, Wu SW, Hung TW, et al. Silibinin inhibits the invasion and migration of renal carcinoma 786-O cells in vitro, inhibits the growth of xenografts in vivo and enhances chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil and paclitaxel. Mol Carcinog. 2011; 50:811–823.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Daurisoline Inhibits Progression of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Regulating the γγ-Secretase/Notch Axis
- Docetaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles to increase pharmacological sensitivity in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Potentiation of the Anticancer Effects by Combining Docetaxel with Ku-0063794 against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
- Effect of Curcumin on Cancer Invasion and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Activity in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cell
- Action and Signaling of Lysophosphatidylethanolamine in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells