Anat Cell Biol.
2014 Jun;47(2):117-126. 10.5115/acb.2014.47.2.117.
A comparative study on the effect of high cholesterol diet on the hippocampal CA1 area of adult and aged rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy and Embryology, Faculty of Medicine, Menoufia University, Menoufia, Egypt. hanaa_noh_10@yahoo.com
- KMID: 1882582
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2014.47.2.117
Abstract
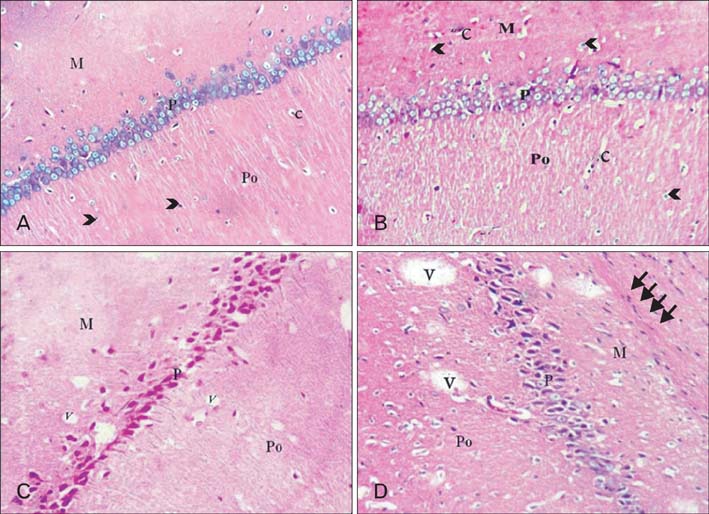
- Dementia is one of the most important problems nowadays. Aging is associated with learning and memory impairments. Diet rich in cholesterol has been shown to be detrimental to cognitive performance. This work was carried out to compare the effect of high cholesterol diet on the hippocampus of adult and aged male albino rats. Twenty adult and twenty aged male rats were used in this study. According to age, the rats were randomly subdivided into balanced and high cholesterol diet fed groups. The diet was 15 g/rat/day for adult rats and 20 g/rat/day for aged rats for eight weeks. Serial coronal sections of hippocampus and blood samples were taken from each rat. For diet effect evaluation, Clinical, biochemical, histological, immunohistochemical, and morphometric assessments were done. In compare to a balanced diet fed rat, examination of Cornu Ammonis 1 (CA 1) area in the hippocampus of the high cholesterol diet adult rats showed degeneration, a significant decrease of the pyramidal cells, attenuation and/or thickening of small blood vessels, apparent increase of astrocytes and apparent decrease of Nissl's granules content. Moreover, the high cholesterol diet aged rats showed aggravation of senility changes of the hippocampus together with Alzheimer like pathological changes. In conclusion, the high cholesterol diet has a significant detrimental effect on the hippocampus and aging might pronounce this effect. So, we should direct our attention to limit cholesterol intake in our food to maintain a healthy life style for a successful aging.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of caffeinated energy drinks on the structure of hippocampal cornu ammonis 1 and dentate gyrus of adult male albino rats
Sherif A. Kamar, Hany W. Abdel Malak, Shereen Adel Saad
Anat Cell Biol. 2020;53(3):330-341. doi: 10.5115/acb.20.136.
Reference
-
1. Wimo A, Prince M. The global economic impact of dementia. A conceptual framework. Alzheimer's disease international [Internet]. NHS Choices;2010. cited 2013 May 29. Available from: http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Dementia/Pages/Causes.aspx.2. Kahn DA, Gwyther LP, Frances A. Agitation in older persons with dementia, expert consensus guideline series. A guide for families and caregivers [Internet]. Alzheimer's Outreach;cited 2014 May 16. Available from: http://www.zarcrom.com/users/alzheimers/.3. Pearce JM. Ammon's horn and the hippocampus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001; 71:351.4. Mills SE. Histology for pathologists. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2007. p. 274–319.5. Driscoll I, Sutherland RJ. The aging hippocampus: navigating between rat and human experiments. Rev Neurosci. 2005; 16:87–121.6. Elias PK, Elias MF, D'Agostino RB, Sullivan LM, Wolf PA. Serum cholesterol and cognitive performance in the Framingham Heart Study. Psychosom Med. 2005; 67:24–30.7. Ando K, Higami Y, Tsuchiya T, Kanematsu T, Shimokawa I. Impact of aging and life-long calorie restriction on expression of apoptosis-related genes in male F344 rat liver. Microsc Res Tech. 2002; 59:293–300.8. Abdel Tawab SM, Nada HF, Mohammed SA, Bahaa ES. Histological and immunohistochemical study on the effect of hypo and hypercaloric diet on the structure of hippocampus of male albino rat. Egypt J Histol. 2008; 31:103–114.9. Granholm AC, Bimonte-Nelson HA, Moore AB, Nelson ME, Freeman LR, Sambamurti K. Effects of a saturated fat and high cholesterol diet on memory and hippocampal morphology in the middle-aged rat. J Alzheimers Dis. 2008; 14:133–145.10. Carol JV. Calculating percent increase and decrease. A conceptual framework [Internet]. Honolulu: Atlantic International University;c2004-2013. cited 2013 May 30. Available from: http://www.onemathematicalcat.org/algebra_book/online_problems/calc_percent_inc_dec.htm.11. Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972; 18:499–502.12. Rifai N, Bachori KP, Alber S. Lipids, lipoprotein and apolipoprotein. In : Aldrich JE, editor. Tiez Fundamental of Clinical Chemistry. 5th ed. Pennsylvania: W.B. Saunder Co.;2001. p. 484–489.13. Kiernan JA. Histological and histochemical methods: theory and practice. 3rd ed. Oxford: Linacre House, Jordan Hill;1999.14. Drury RA. Wallington EA. Carleton's histological techniques. 5th ed. New York: Oxford University Press;1980.15. Bancroft JD, Gamble M. Theory and practice of histological techniques. 5th ed. London: Churchill Livingstone;2002.16. Mostafa H, Anwar M, Ahmed S, Yahia N. Effect of vincamine on age related structural changes in the frontal cortex and the hippocampus of male albino rat [dissertation]. Cairo: Ain Shams University;2006. 188.17. Hashem HE, Elmasry SM, Eladl MA. Dentate gyrus in aged male albino rats (histological and Tau-immunohistochemical study). Egypt J Histol. 2010; 33:659–670.18. von Bohlen und Halbach O, Zacher C, Gass P, Unsicker K. Age-related alterations in hippocampal spines and deficiencies in spatial memory in mice. J Neurosci Res. 2006; 83:525–531.19. Riddle DR, Sonntag WE, Lichtenwalner RJ. Microvascular plasticity in aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2003; 2:149–168.20. Franciosi S, Gama Sosa MA, English DF, Oler E, Oung T, Janssen WG, De Gasperi R, Schmeidler J, Dickstein DL, Schmitz C, Gandy S, Hof PR, Buxbaum JD, Elder GA. Novel cerebrovascular pathology in mice fed a high cholesterol diet. Mol Neurodegener. 2009; 4:42.21. Mohamed GF, Ahmed MA, Omar SM. Light and electron microscopic study on the effect of caffeine on blood brain barrier integrity in a rabbit model of Alzheimer's disease. Egypt J Histol. 2010; 33:467–478.22. Dickson DW, Weller RO. Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. 2nd ed. New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell;2011. p. 62–91.23. Rahman SM, Van Dam AM, Schultzberg M, Crisby M. High cholesterol diet results in increased expression of interleukin-6 and caspase-1 in the brain of apolipoprotein E knockout and wild type mice. J Neuroimmunol. 2005; 169:59–67.24. Li L, Cao D, Garber DW, Kim H, Fukuchi K. Association of aortic atherosclerosis with cerebral beta-amyloidosis and learning deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 2003; 163:2155–2164.25. Rosenblum WI. Neuropathology mini-course for residents. Dementias [Internet]. Richmond: VCU Department of Pathology;2007. cited 2013 May 25. Available from: http://www.pathology.vcu.edu/education/WirSelfInst/dementias.html.26. Causes of dementia: a conceptual framework [Internet]. NHS Choices;2012. cited 2013 May 29. Available from: http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Dementia/Pages/Causes.aspx.27. Iseki E, Togo T, Suzuki K, Katsuse O, Marui W, de Silva R, Lees A, Yamamoto T, Kosaka K. Dementia with Lewy bodies from the perspective of tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2003; 105:265–270.28. Ha S, Furukawa R, Stramiello M, Wagner JJ, Fechheimer M. Transgenic mouse model for the formation of Hirano bodies. BMC Neurosci. 2011; 12:97.29. Gómez-Isla T, Hollister R, West H, Mui S, Growdon JH, Petersen RC, Parisi JE, Hyman BT. Neuronal loss correlates with but exceeds neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1997; 41:17–24.30. Park SH, Kim JH, Choi KH, Jang YJ, Bae SS, Choi BT, Shin HK. Hypercholesterolemia accelerates amyloid beta-induced cognitive deficits. Int J Mol Med. 2013; 31:577–582.31. Sparks DL, Scheff SW, Hunsaker JC 3rd, Liu H, Landers T, Gross DR. Induction of Alzheimer-like beta-amyloid immunoreactivity in the brains of rabbits with dietary cholesterol. Exp Neurol. 1994; 126:88–94.32. Refolo LM, Malester B, LaFrancois J, Bryant-Thomas T, Wang R, Tint GS, Sambamurti K, Duff K, Pappolla MA. Hypercholesterolemia accelerates the Alzheimer's amyloid pathology in a transgenic mouse model. Neurobiol Dis. 2000; 7:321–331.33. Levin-Allerhand JA, Lominska CE, Smith JD. Increased amyloid-levels in APPSWE transgenic mice treated chronically with a physiological high-fat high-cholesterol diet. J Nutr Health Aging. 2002; 6:315–319.34. Shie FS, Jin LW, Cook DG, Leverenz JB, LeBoeuf RC. Diet-induced hypercholesterolemia enhances brain A beta accumulation in transgenic mice. Neuroreport. 2002; 13:455–459.35. Ghribi O. Potential mechanisms linking cholesterol to Alzheimer's disease-like pathology in rabbit brain, hippocampal organotypic slices, and skeletal muscle. J Alzheimers Dis. 2008; 15:673–684.36. Simons M, Keller P, Dichgans J, Schulz JB. Cholesterol and Alzheimer's disease: is there a link. Neurology. 2001; 57:1089–1093.37. Yoon SY, Park JS, Choi JE, Choi JM, Lee WJ, Kim SW, Kim DH. Rosiglitazone reduces tau phosphorylation via JNK inhibition in the hippocampus of rats with type 2 diabetes and tau transfected SH-SY5Y cells. Neurobiol Dis. 2010; 40:449–455.38. Kim DH, Huh JW, Jang M, Suh JH, Kim TW, Park JS, Yoon SY. Sitagliptin increases tau phosphorylation in the hippocampus of rats with type 2 diabetes and in primary neuron cultures. Neurobiol Dis. 2012; 46:52–58.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A TUNEL and Electron Microscopic Study on the Delayed Neuronal Death of Rat CA1 Pyramidal Neurons after MCAO
- Temporal changes in mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and phosphorylated-mTOR expressions in the hippocampal CA1 region of rat with vascular dementia
- Effects of N-acetylcystein on changes in parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the hippocampus after carbon monoxide poisoning
- Effect of caffeinated energy drinks on the structure of hippocampal cornu ammonis 1 and dentate gyrus of adult male albino rats
- Effect of Ginsenosides on the Lipid Distribution in Rat Tissues