Anat Cell Biol.
2020 Sep;53(3):330-341. 10.5115/acb.20.136.
Effect of caffeinated energy drinks on the structure of hippocampal cornu ammonis 1 and dentate gyrus of adult male albino rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
- KMID: 2507646
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.20.136
Abstract
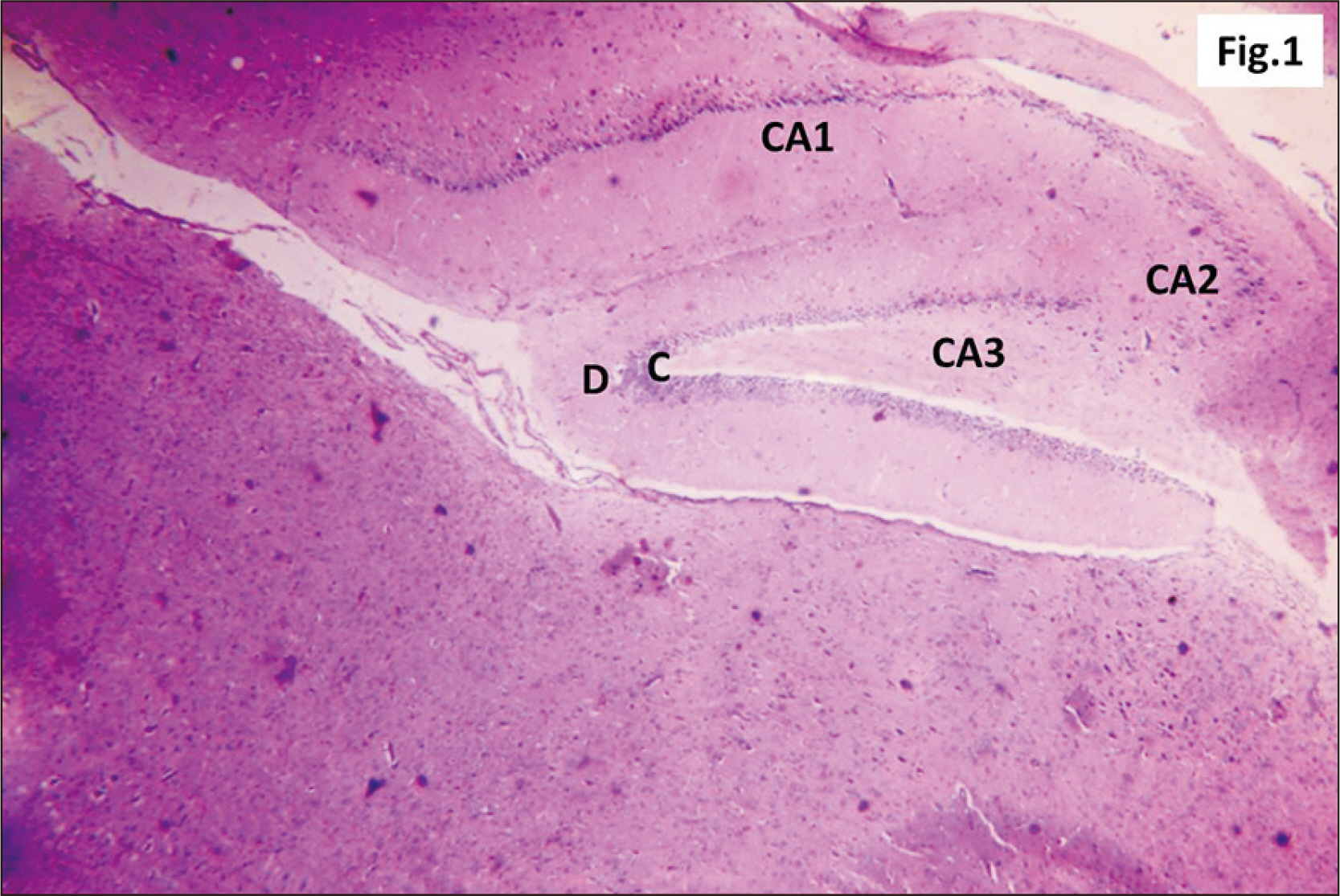
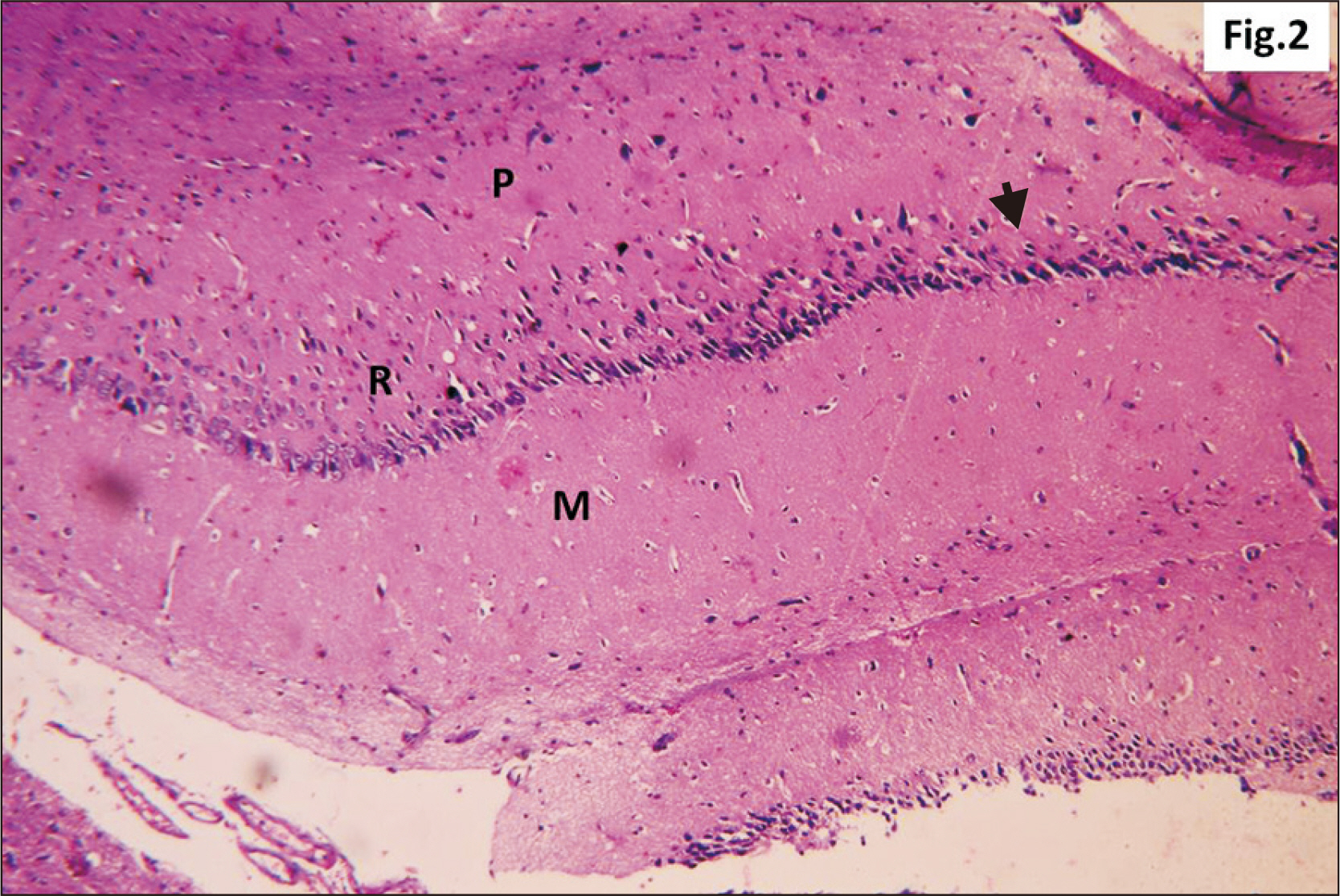
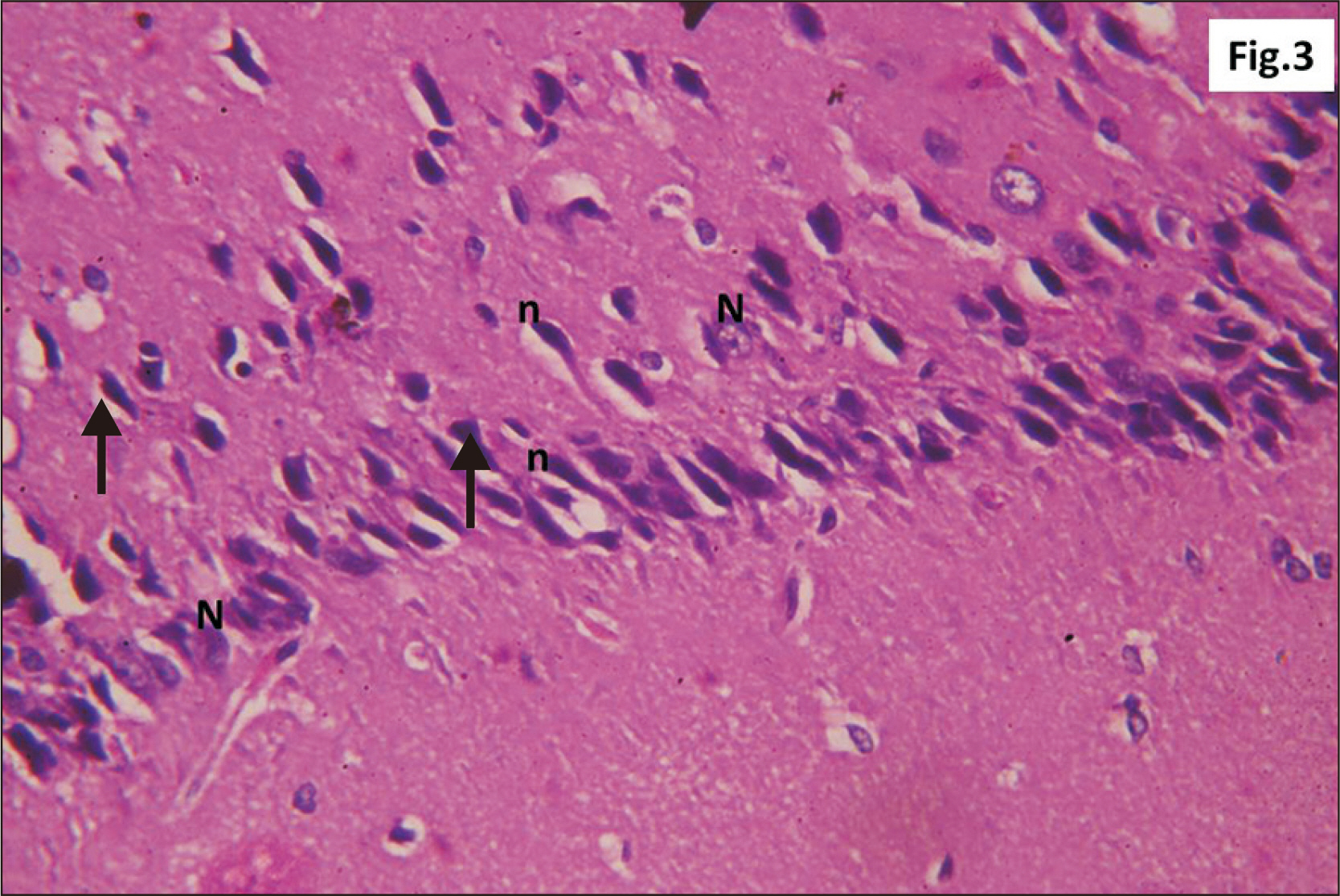
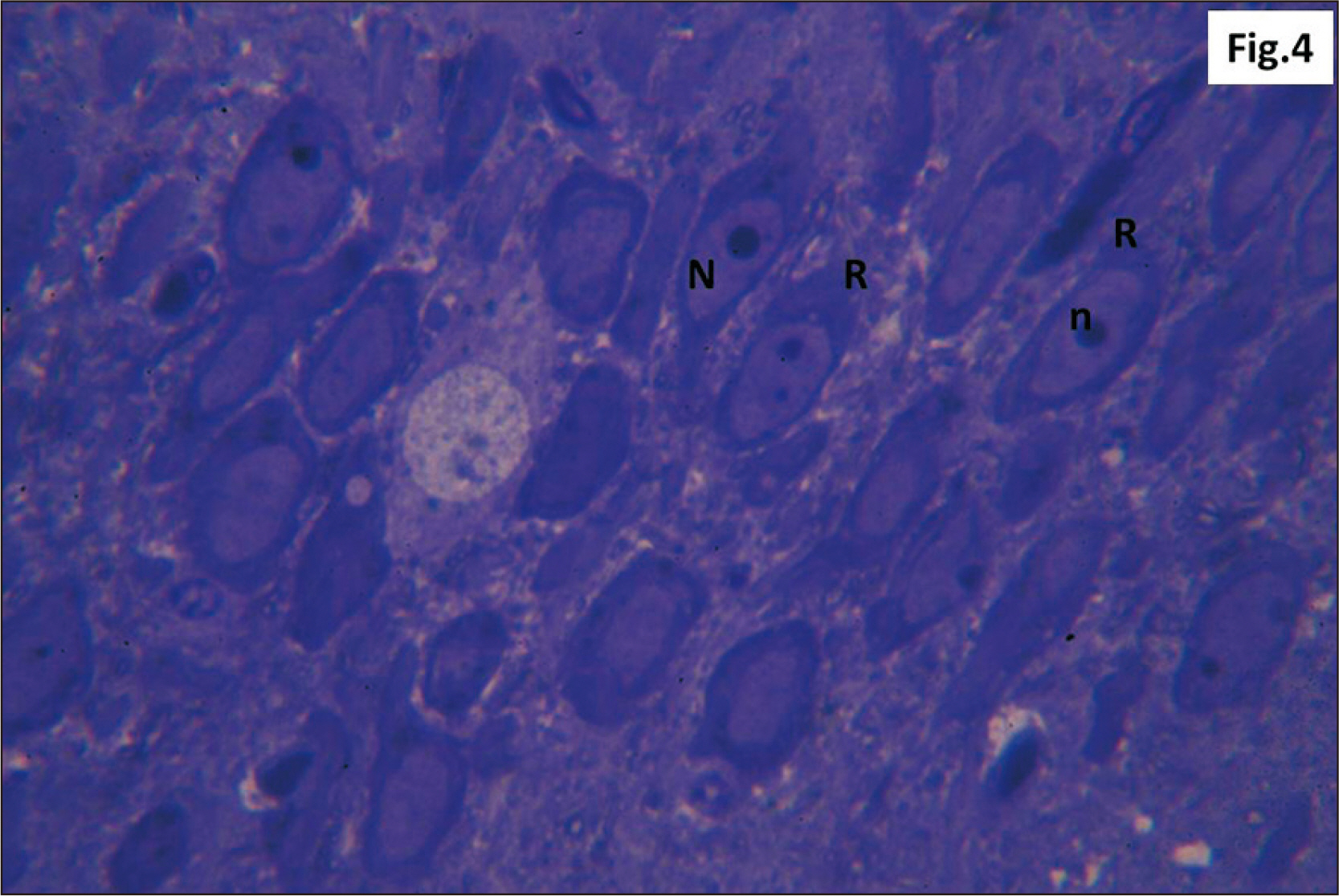
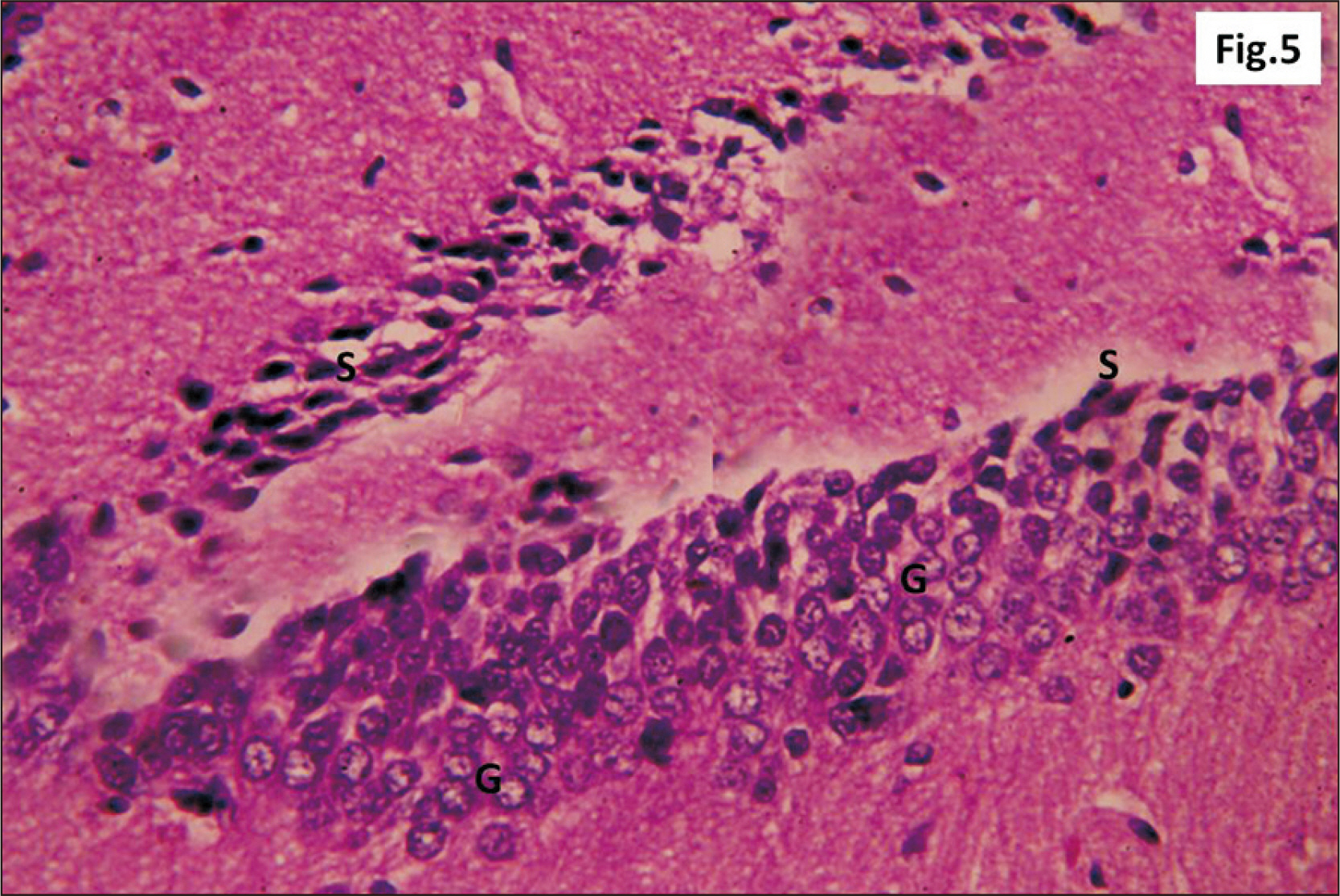
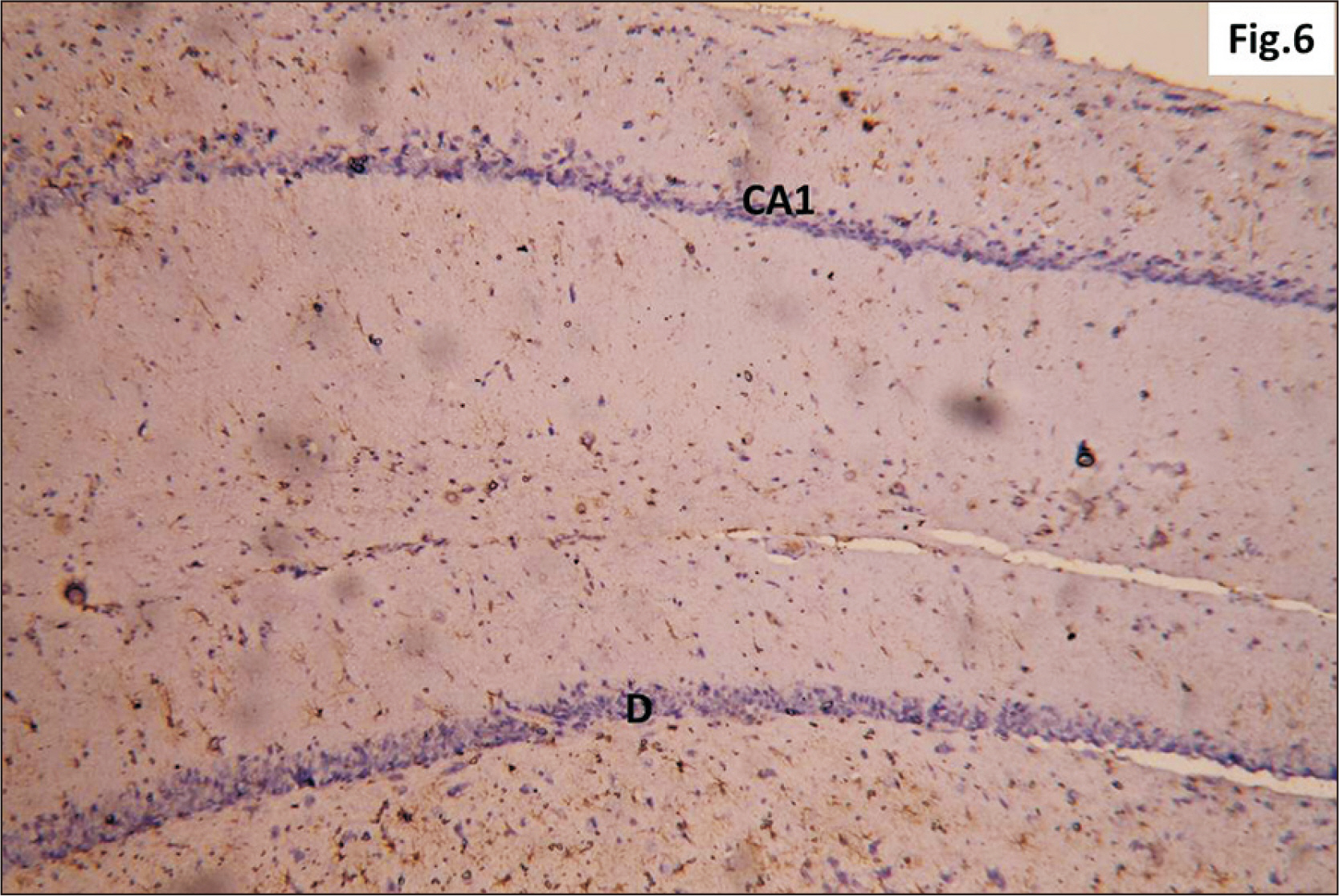
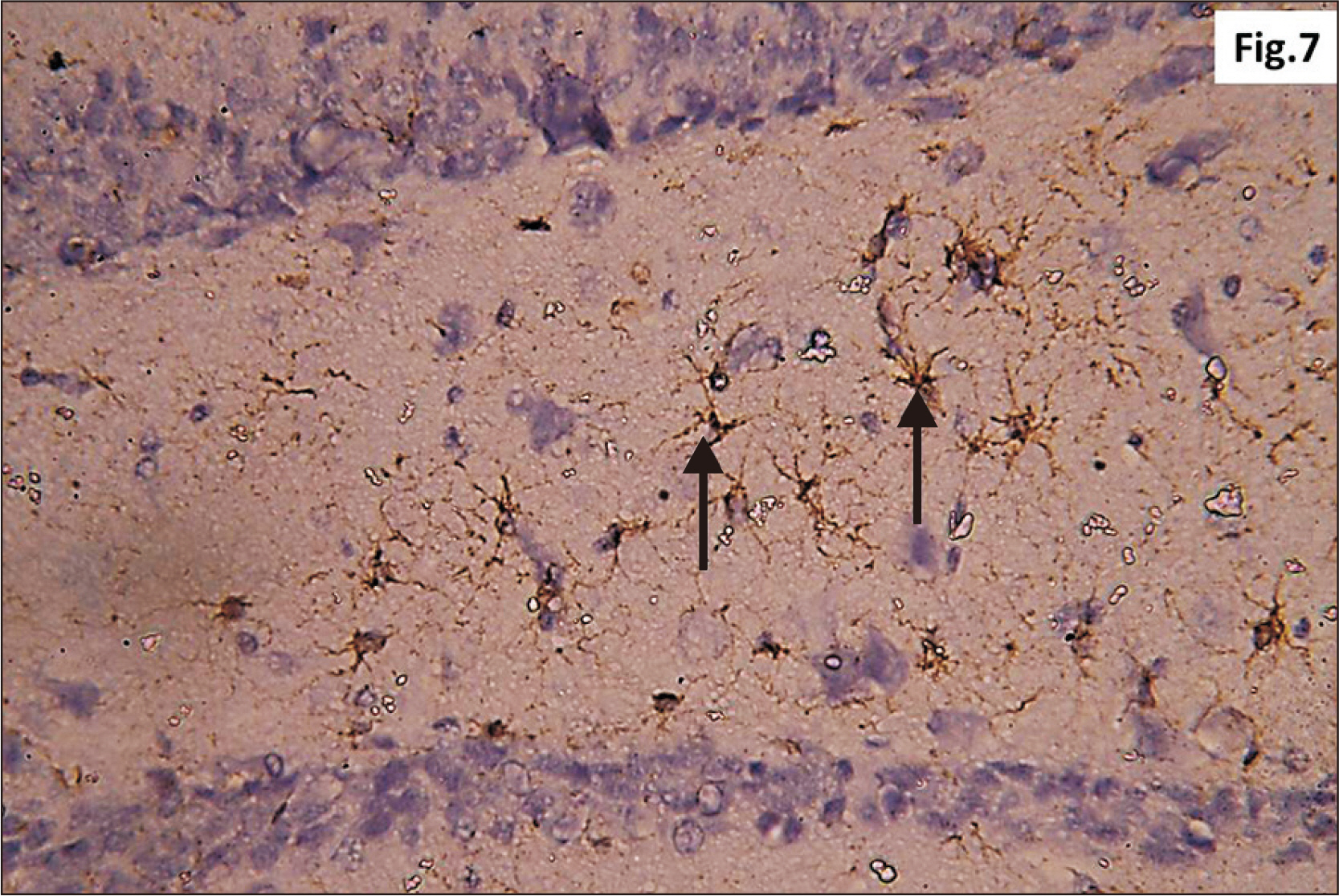
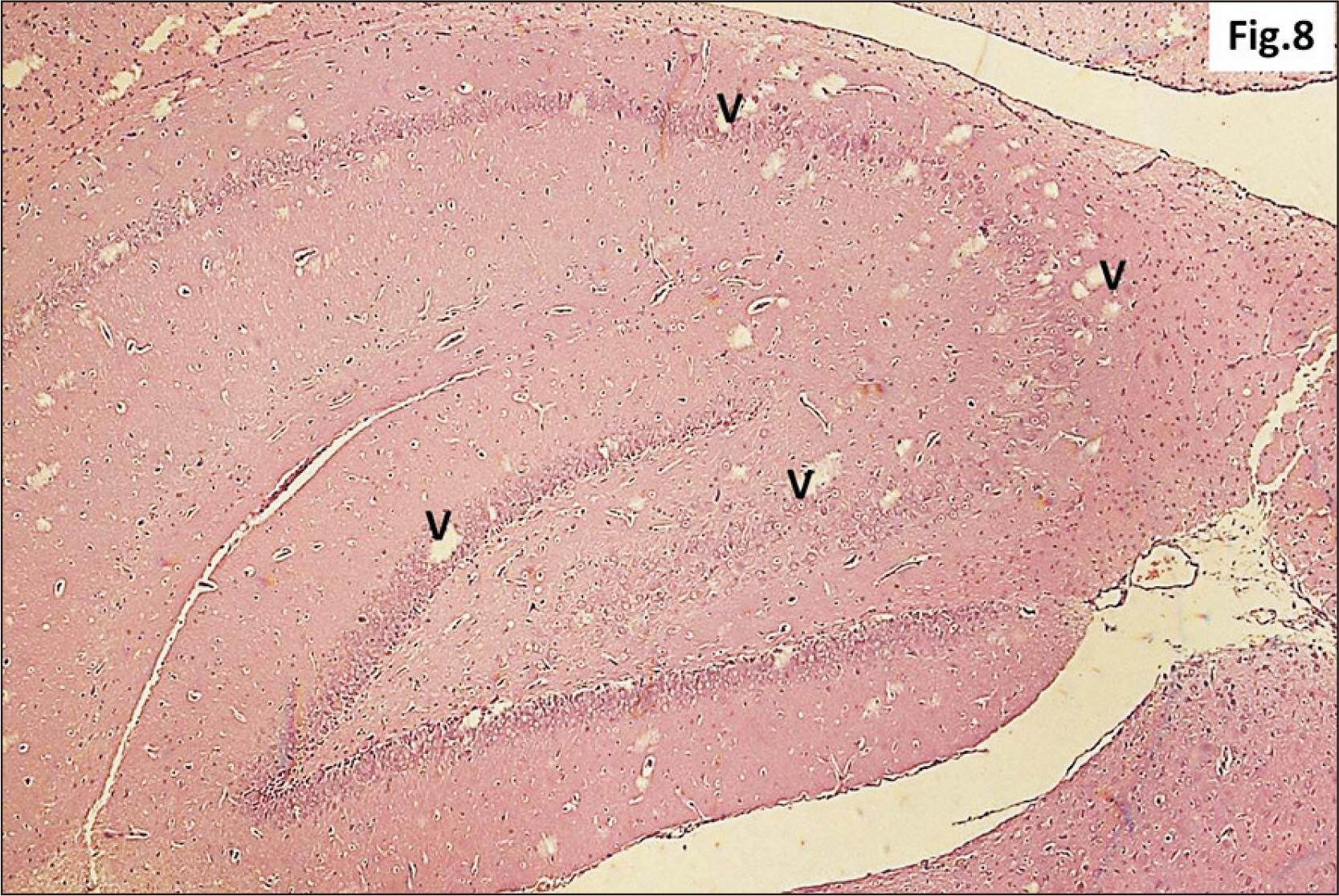
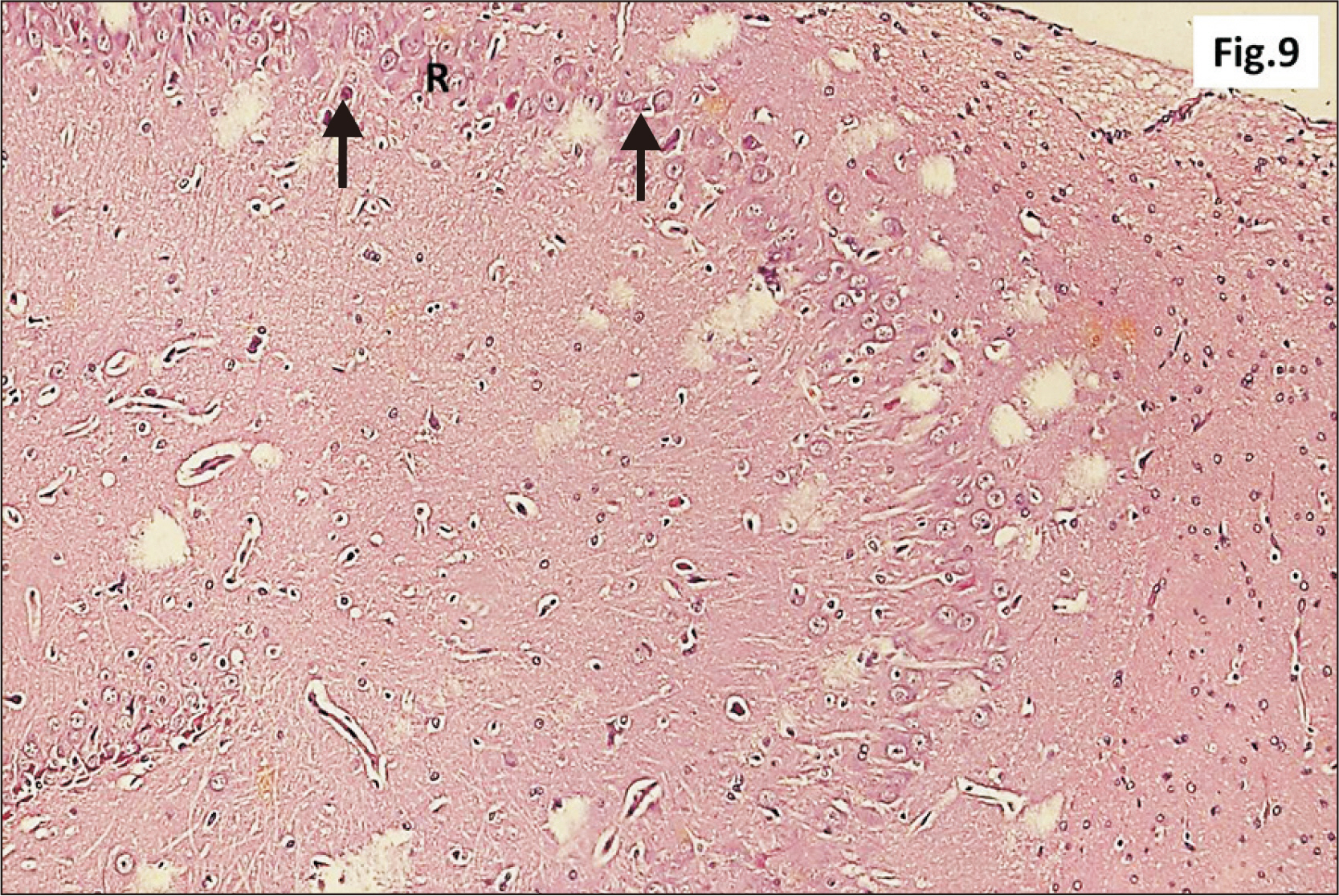
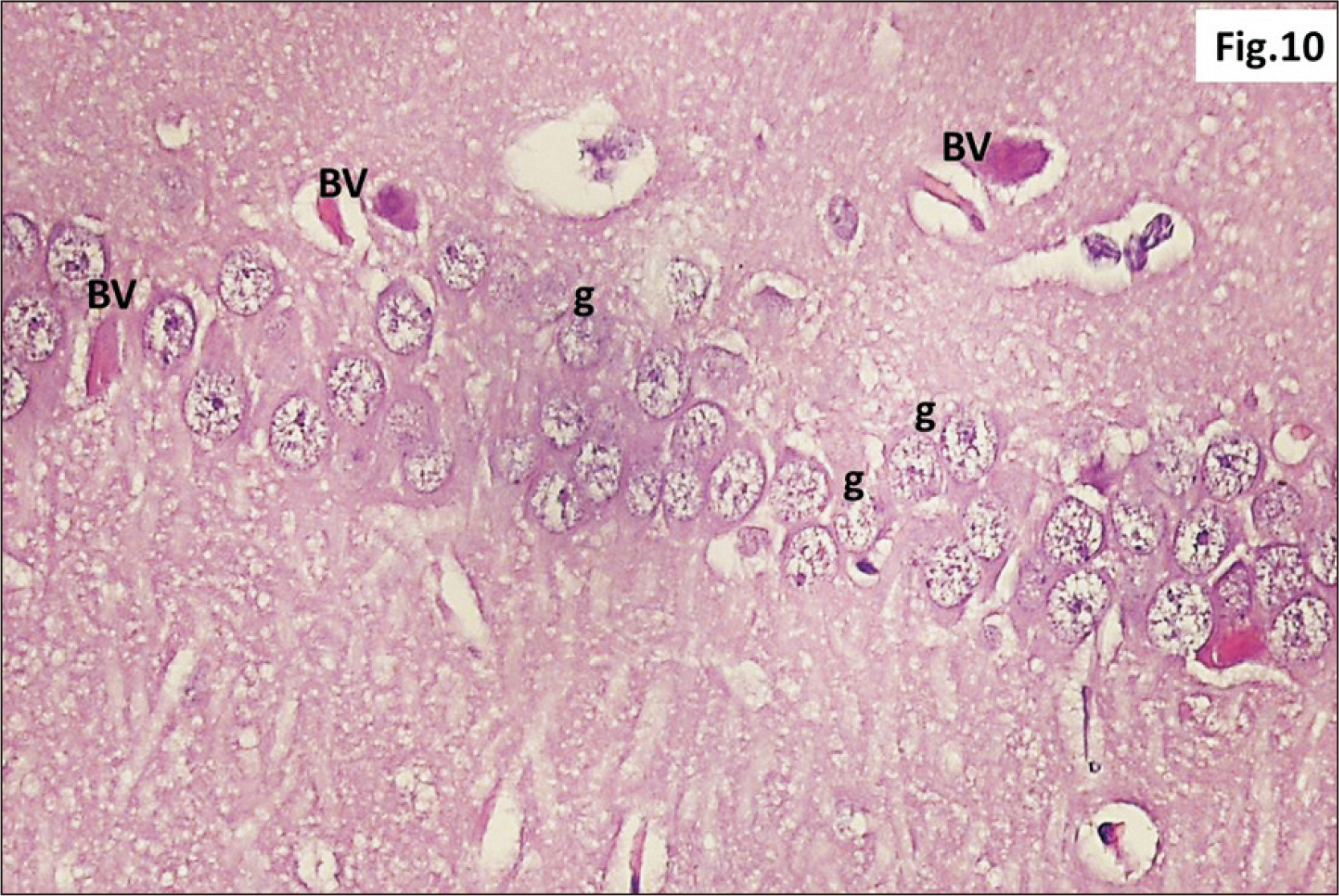
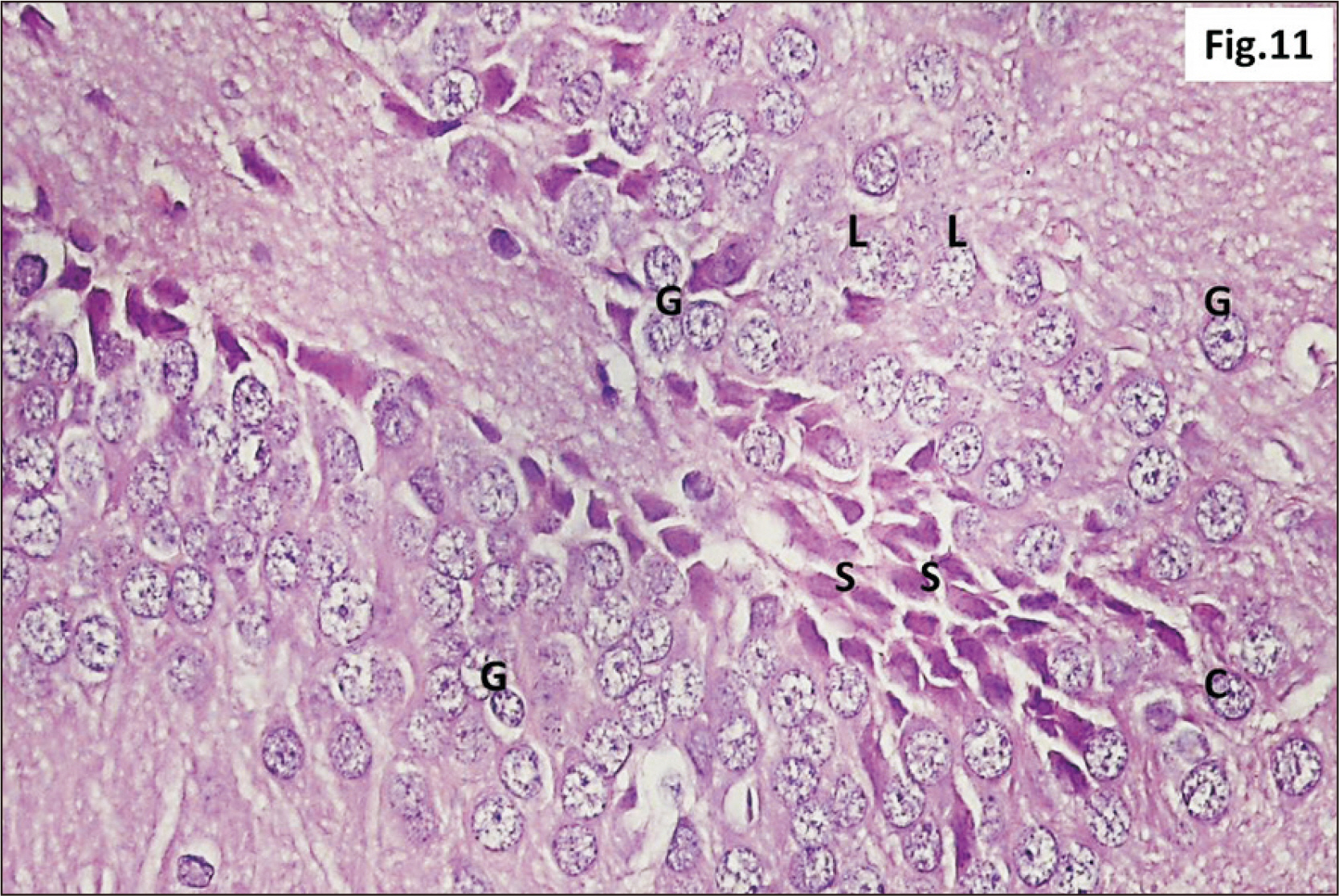
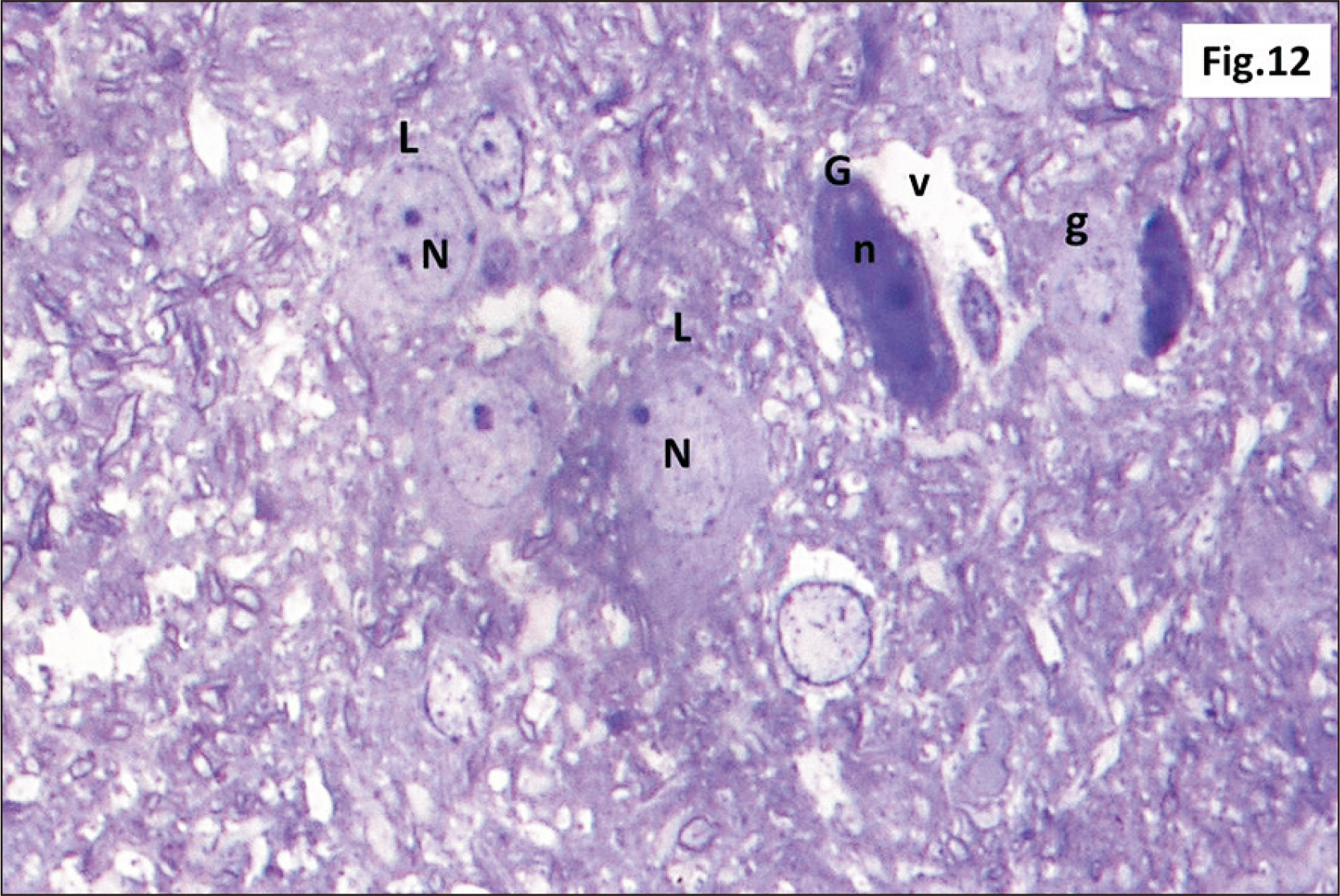
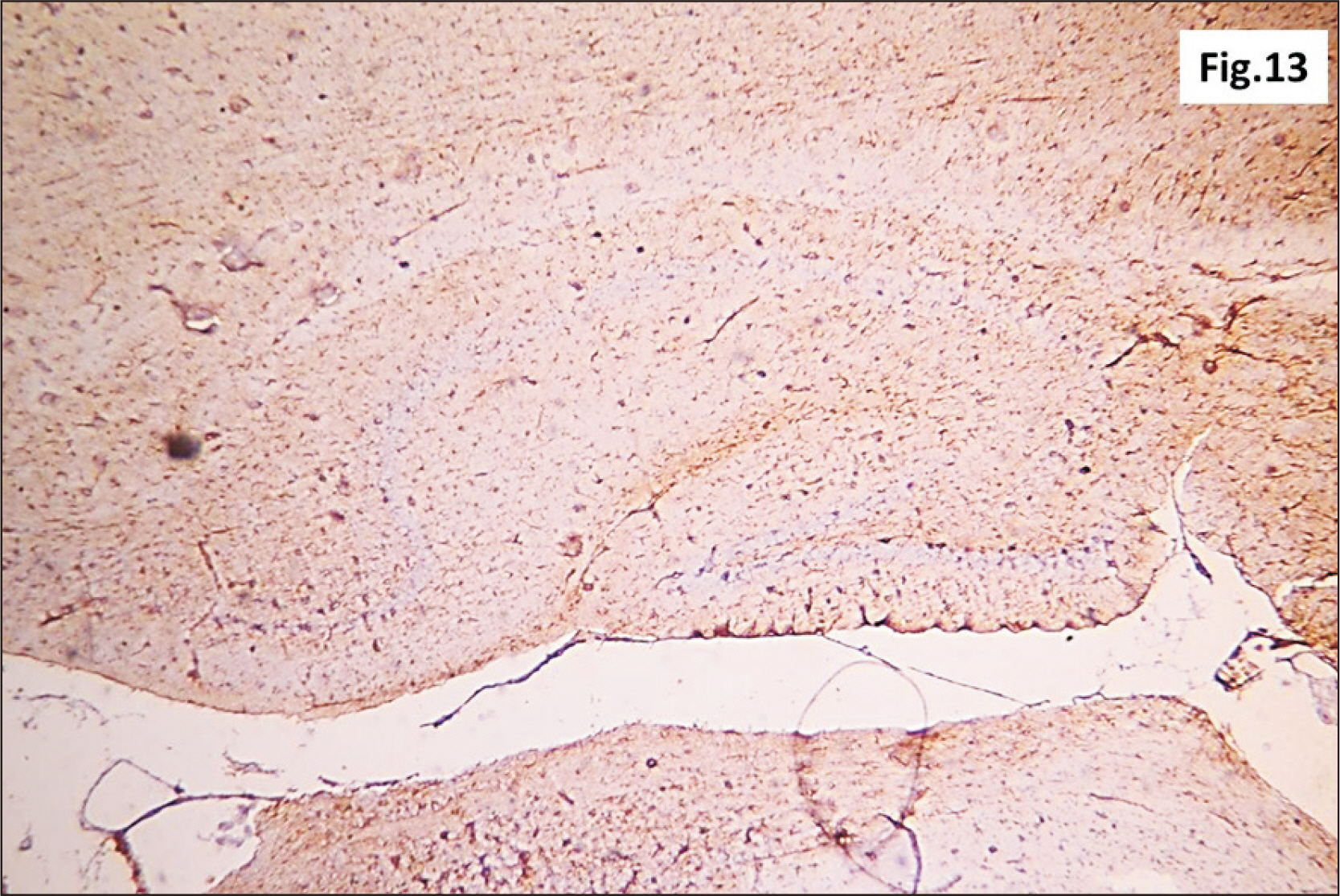
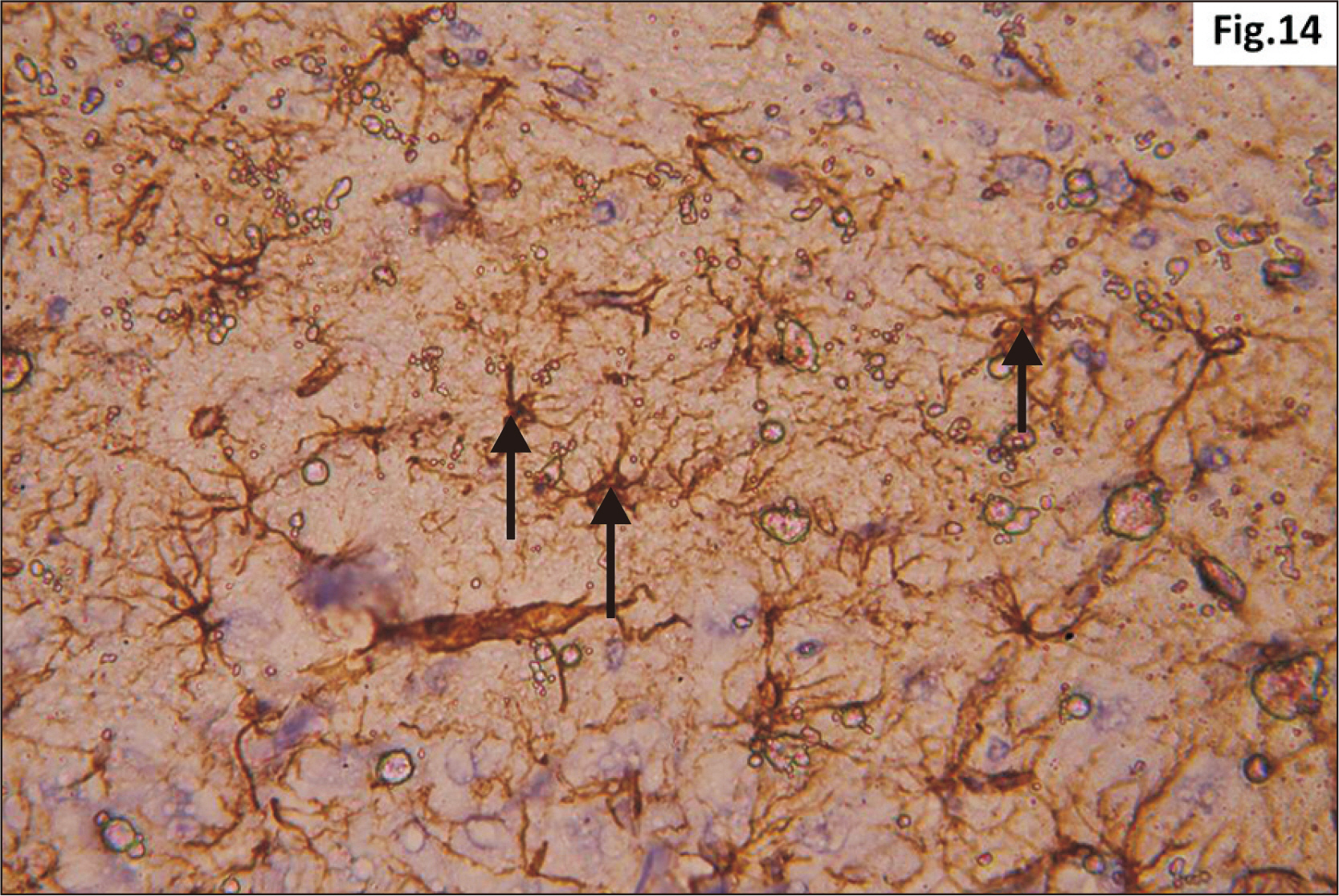
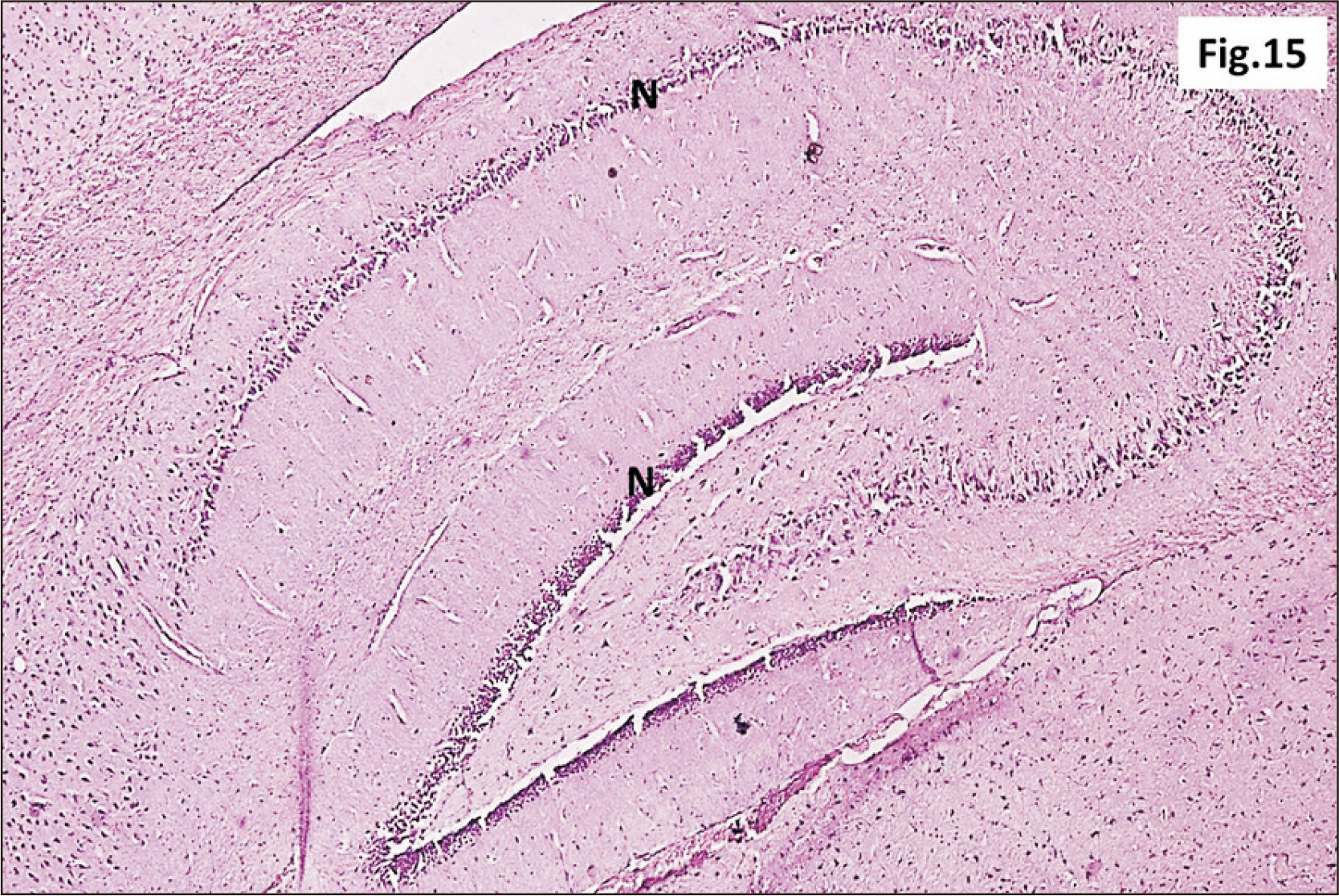
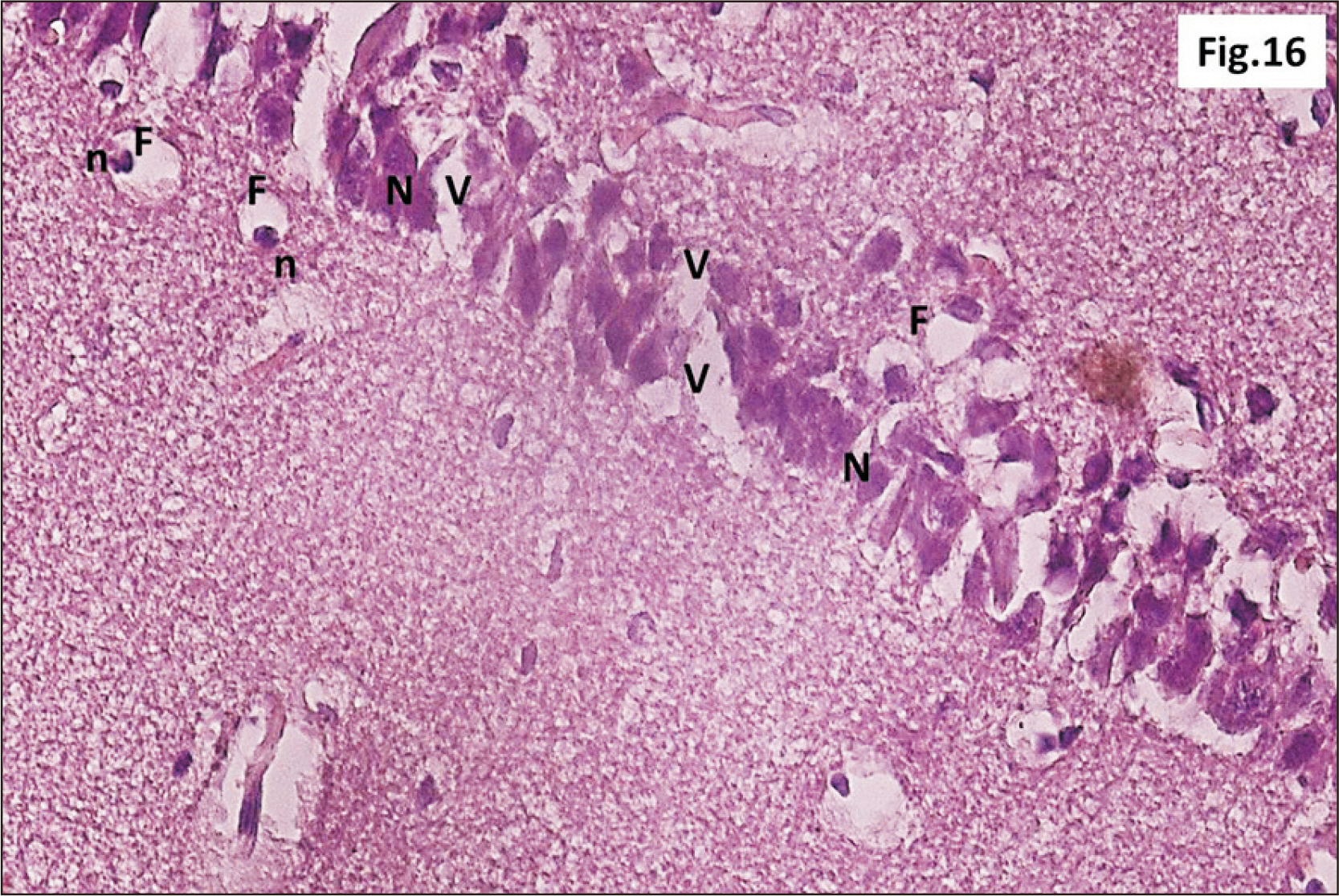
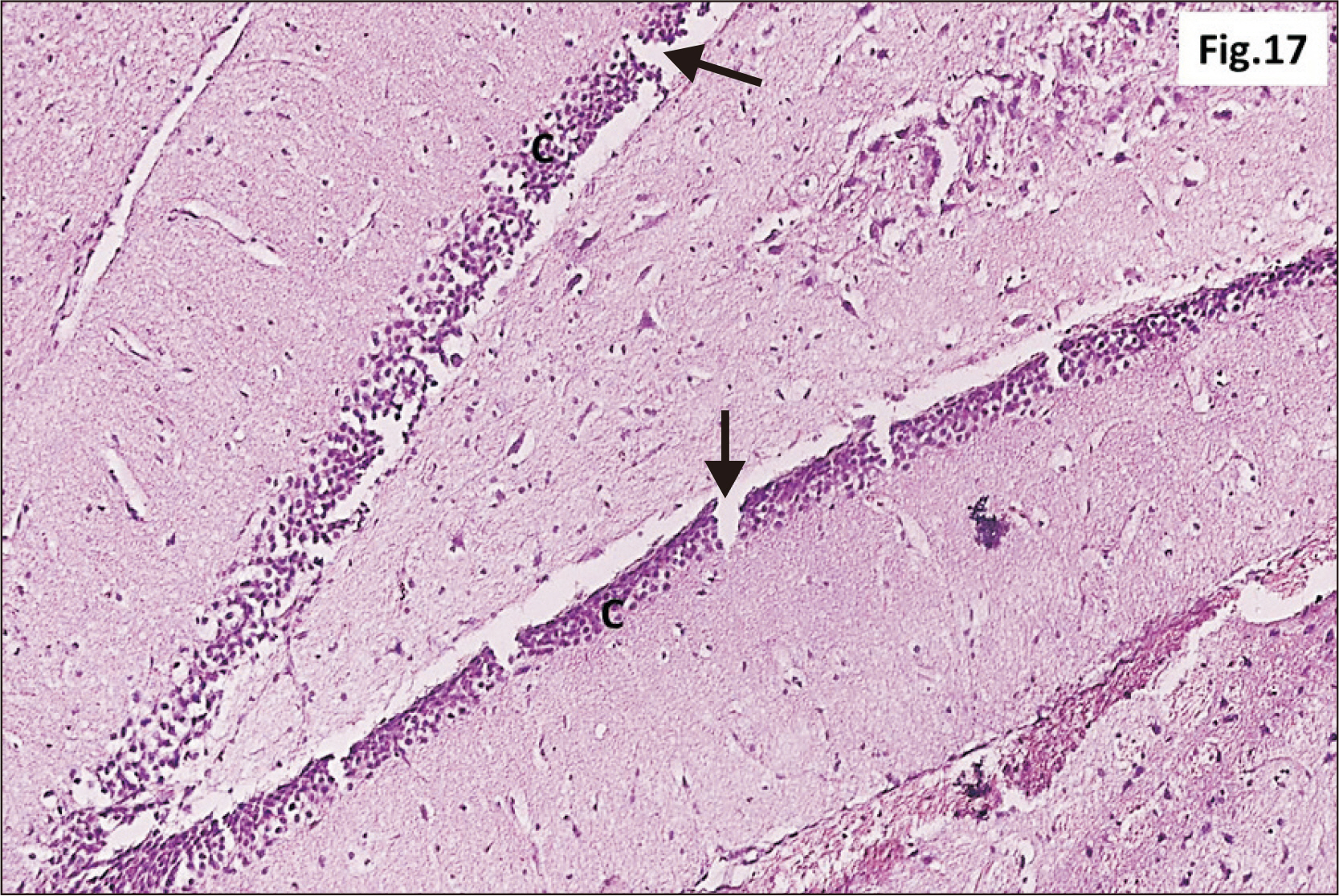
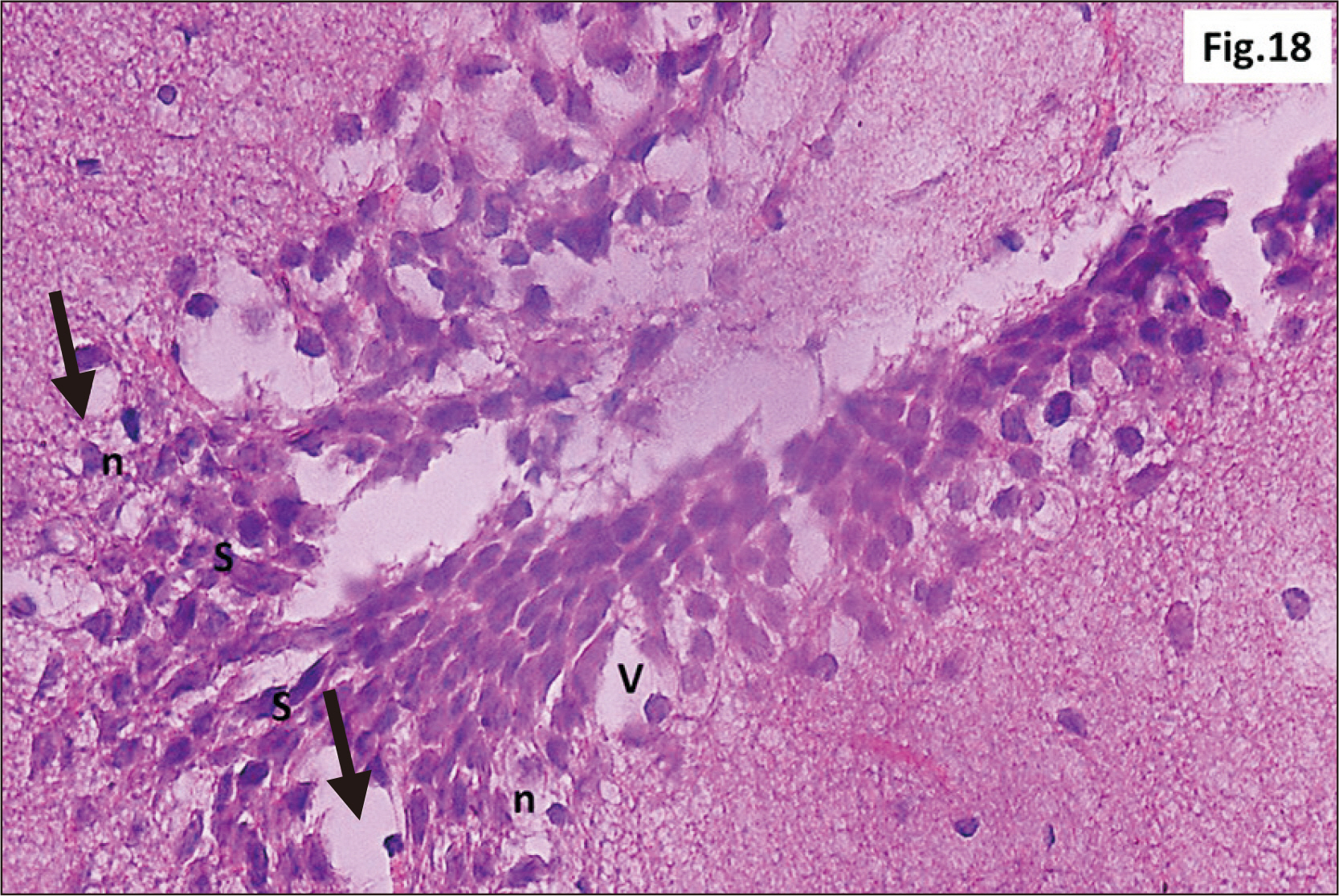
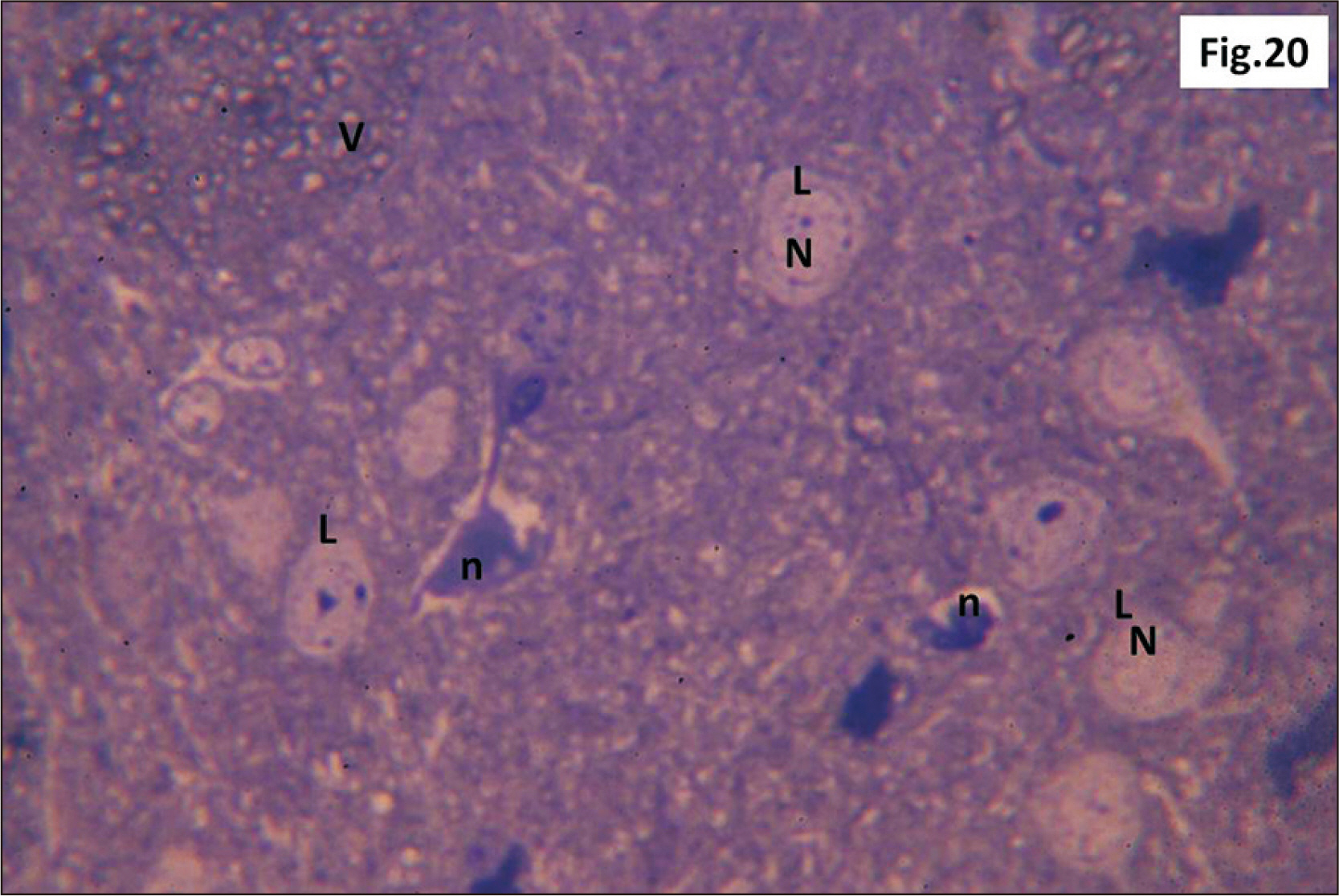
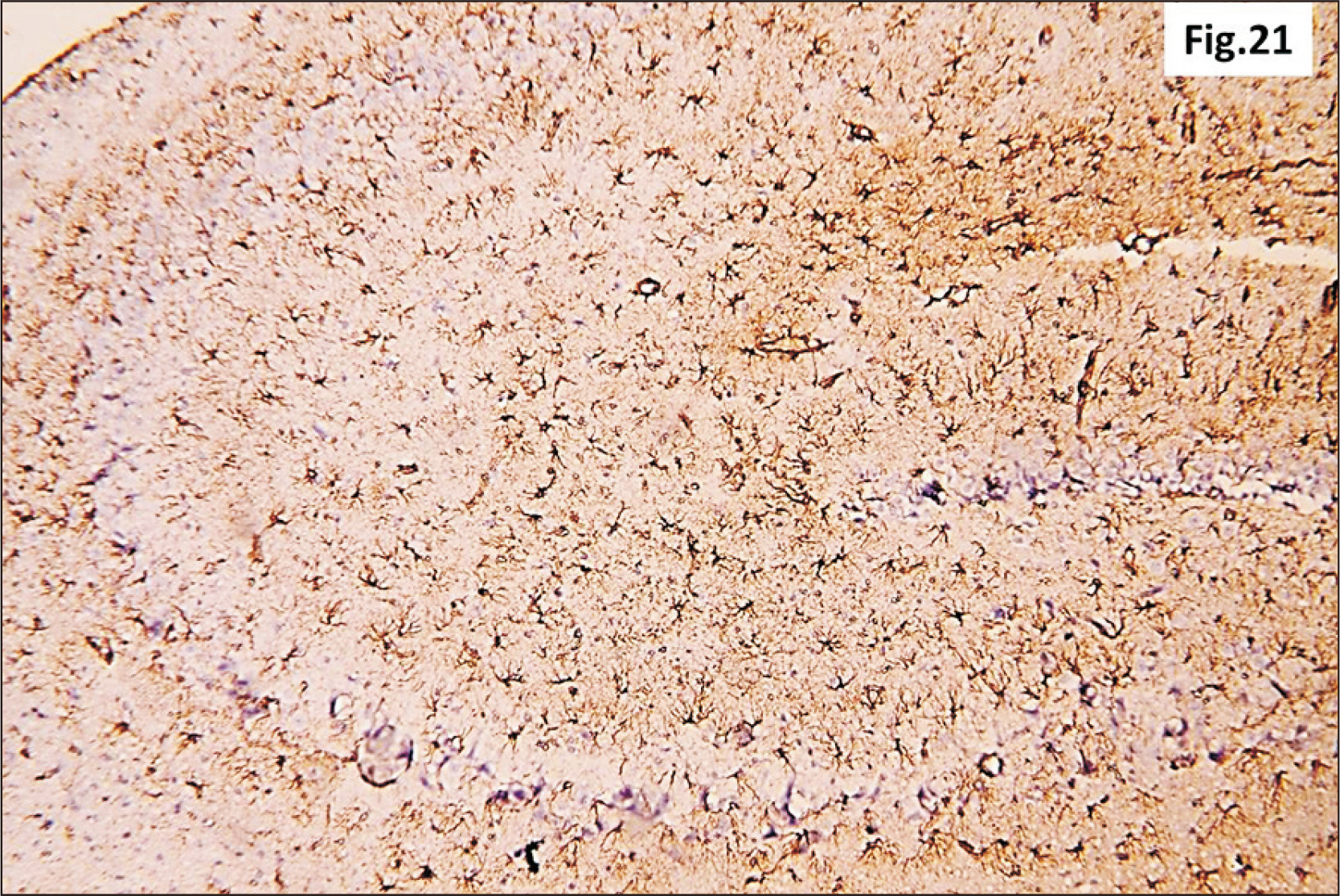
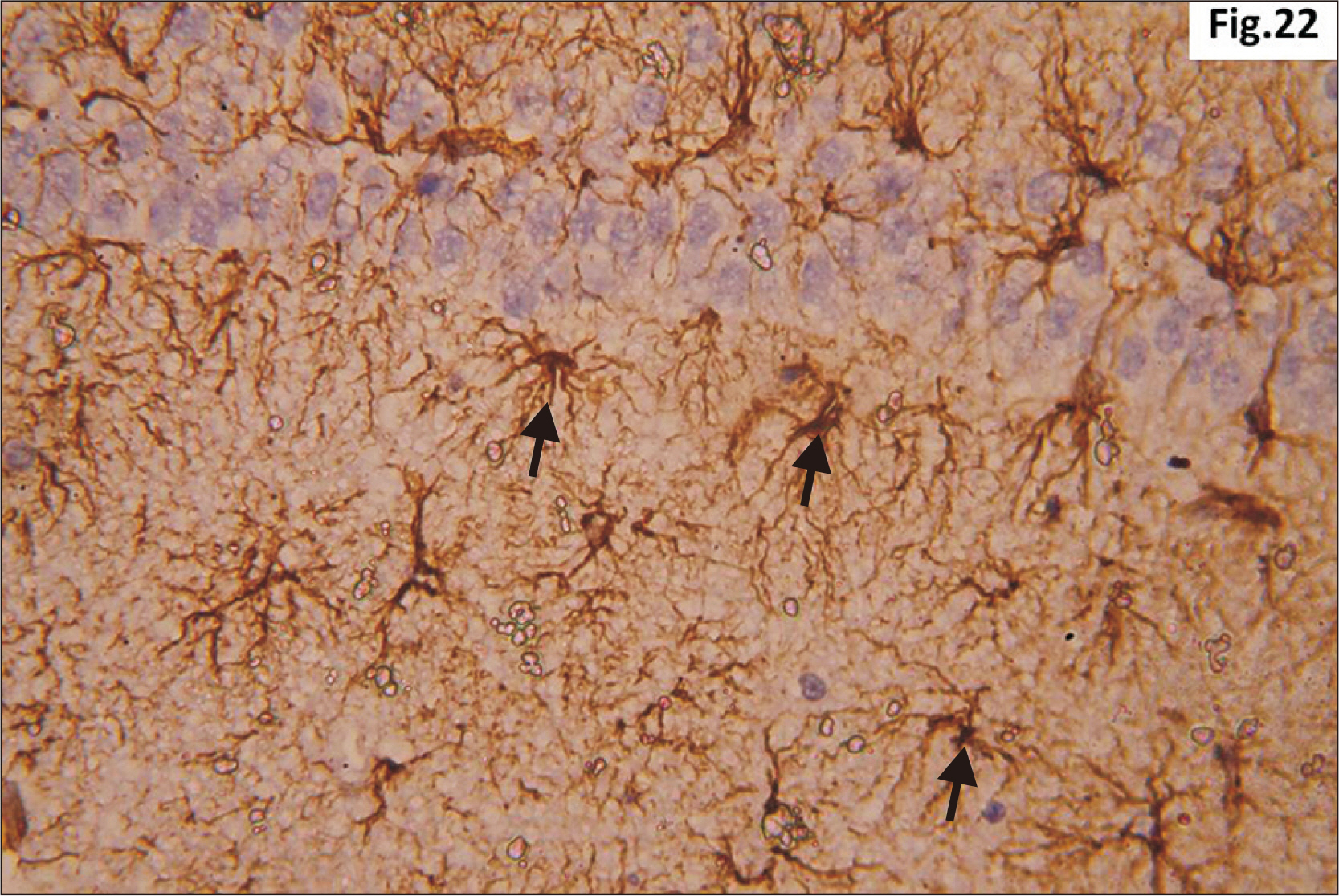
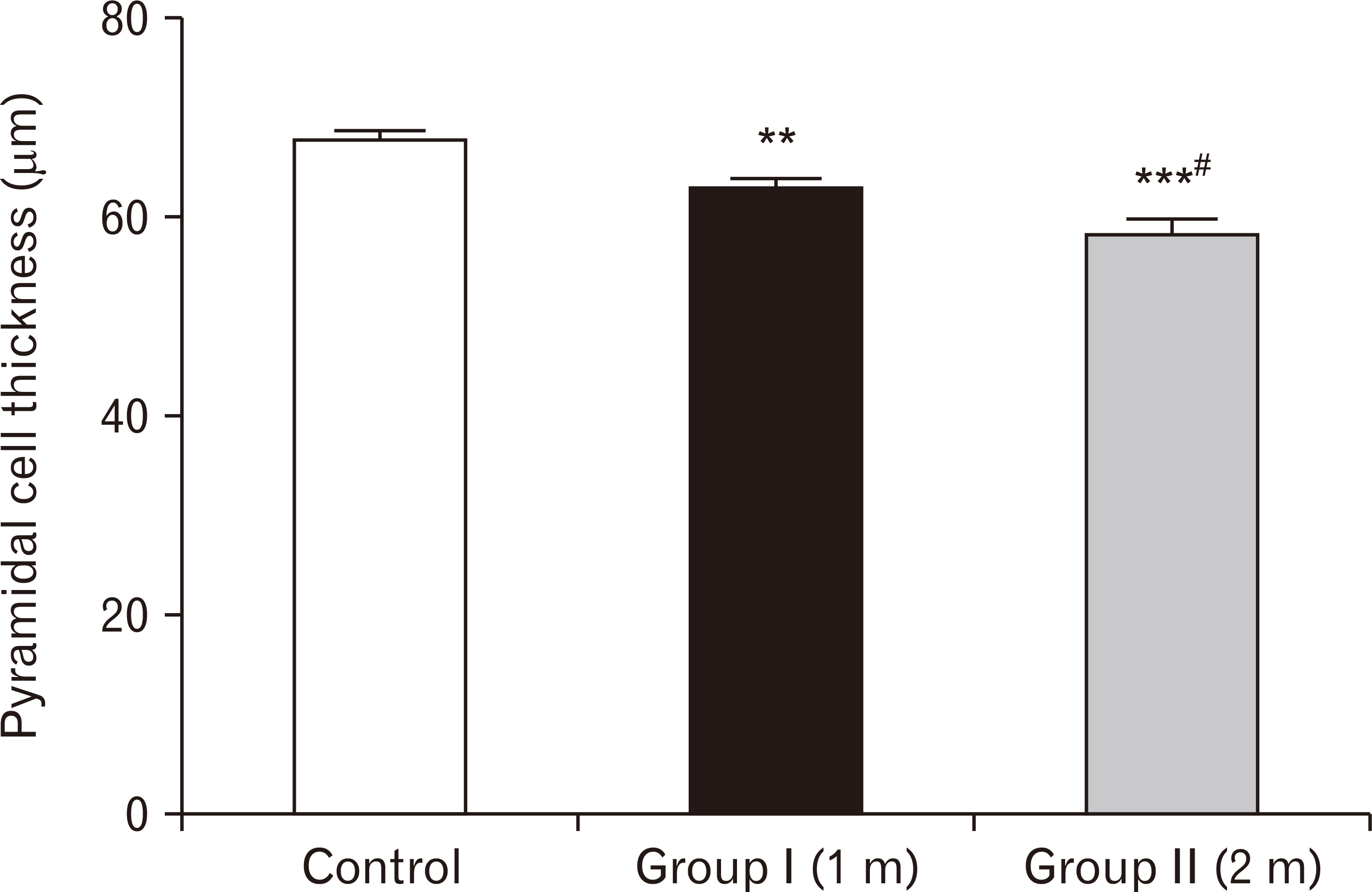
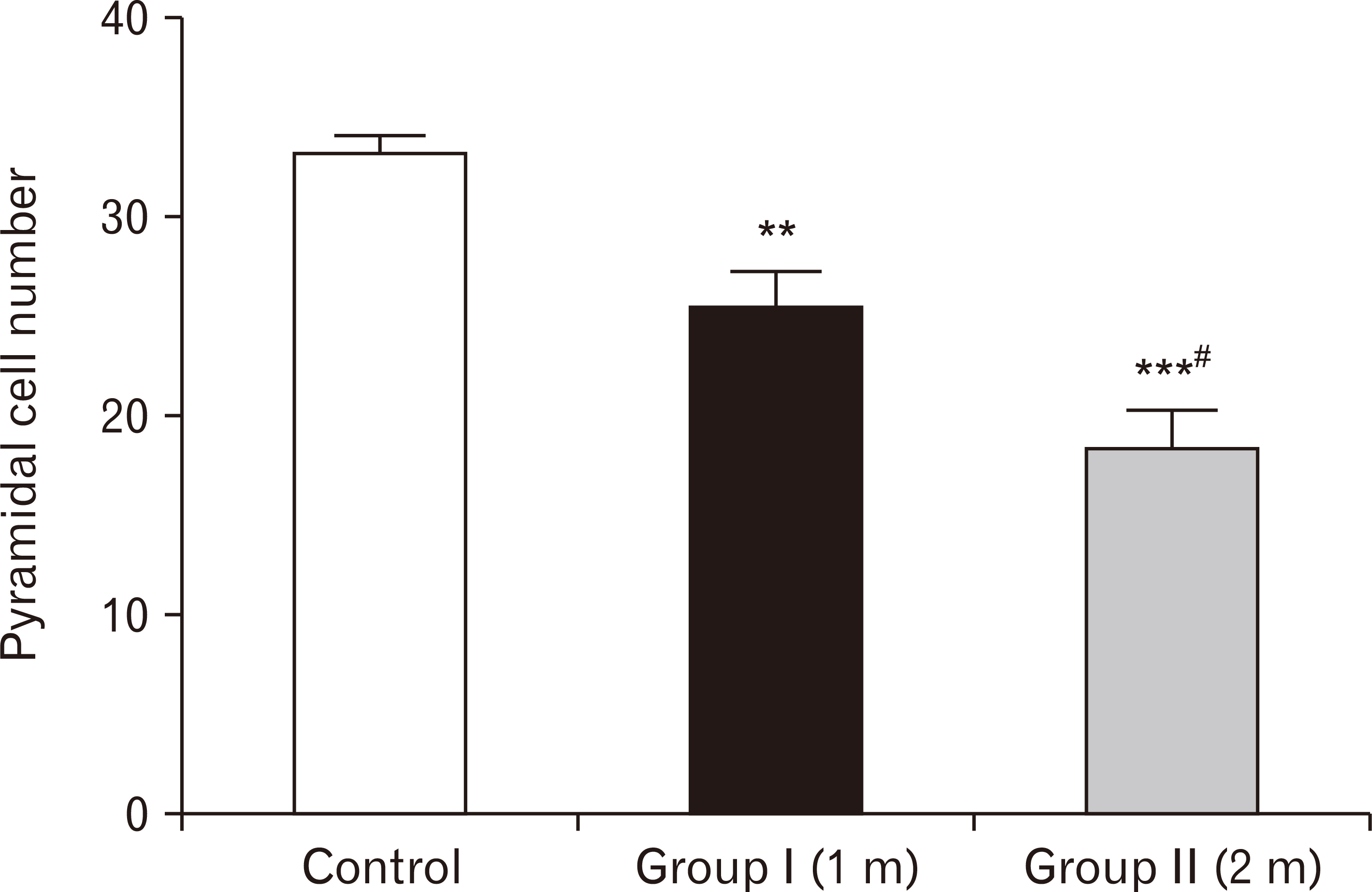
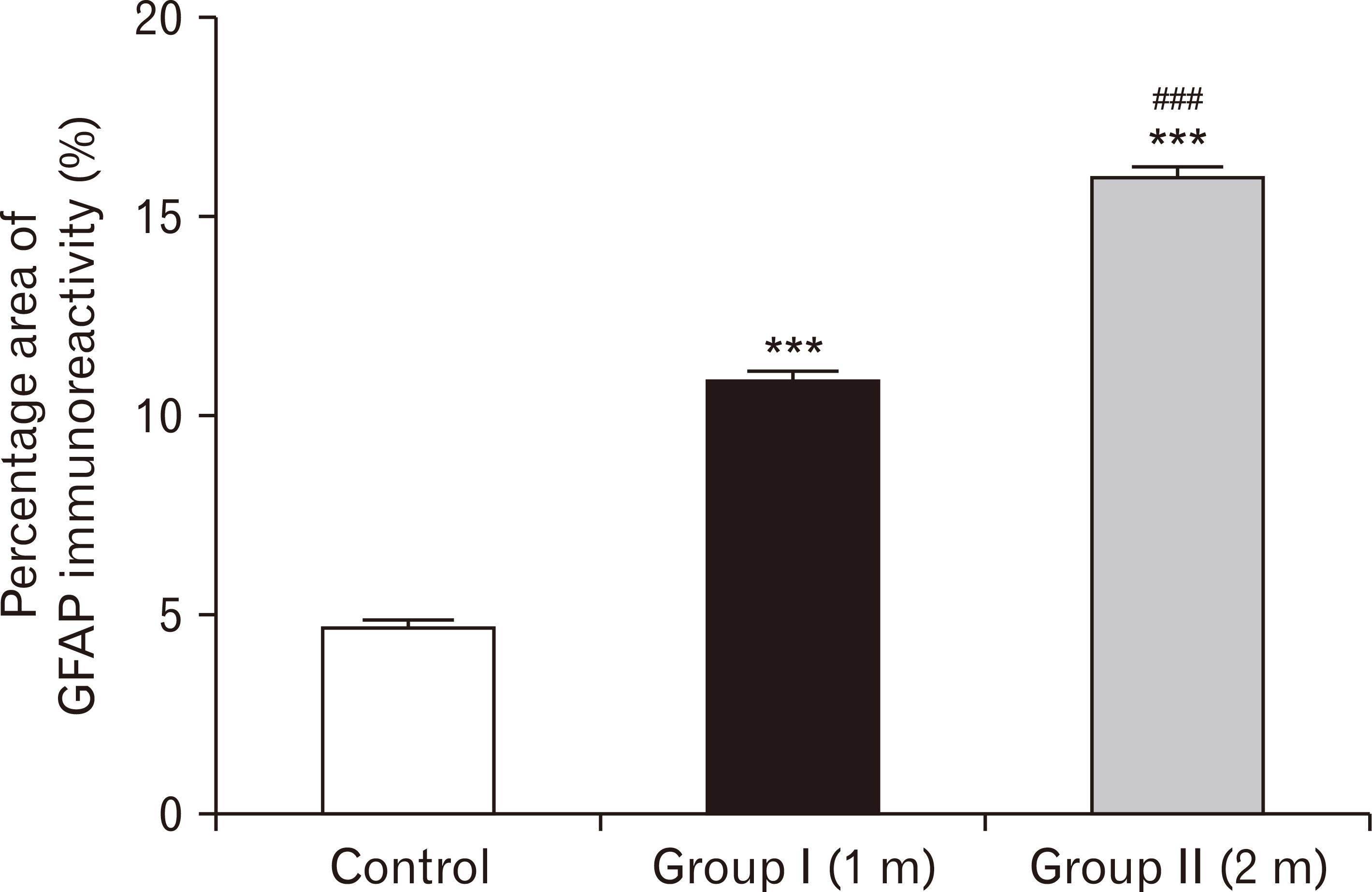
- Energy drinks are available worldwide and frequently consumed to increase energy level and compensate lack of sleep. Energy drinks consumers aim to improve their cognitive functions. Red Bull is the most popular energy drink consumed in Egypt. However, the link between the impact of energy drinks on the structure of hippocampal cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) and dentate gyrus (DG), a highly vulnerable brain regions to various insults, has not yet documented. To study the effect of energy drinks on structure of hippocampal CA1 and DG of adult male albino rats. Twenty one adult male albino rats were divided into three groups; group I control group, groups II and III received Red Bull, with a dose of 3.75 ml/kg/day orally using gastric tube for four and eight consecutive weeks respectively. At the end of the experiment, brains were dissected and hippocampal specimens were processed for histopathological and immunohistochemical studies. Histopathological examination of hippocampal sections in group II revealed vacuoles, decrease thickness of pyramidal cell layer with irregular dark or ghost nuclei. However, changes were more severe in group III with cracks in pyramidal cell layer, massive vacuolation and signet ring cells. Moreover, star shaped astrocytes and glial fibrillary acidic protein immuno-reactivity were more abundant in group III than in group II. Caffeinated energy drinks produced neurodegenerative changes and reactive astrocytosis in hippocampal CA1 and DG of adult male albino rats. These changes were duration-dependent being more severe in longer duration of intake.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Seifert SM, Schaechter JL, Hershorin ER, Lipshultz SE. 2011; Health effects of energy drinks on children, adolescents, and young adults. Pediatrics. 127:511–28. DOI: 10.1542/peds.2009-3592. PMID: 21321035.
Article2. Backer WS, Baeissa HM. 2014; Effect of different energy drinks on liver and heart enzymes in rats. Int J Biotechnol. 3:1–11.3. Mubarak R. 2012; Effect of Red Bull energy drink on rats' submandibular salivary glands (light and electron microscopic study). J Am Sci. 8:366–72.4. Abian P, Del Coso J, Salinero JJ, Gallo-Salazar C, Areces F, Ruiz-Vicente D, Lara B, Soriano L, Muñoz V, Abian-Vicen J. 2015; The ingestion of a caffeinated energy drink improves jump performance and activity patterns in elite badminton players. J Sports Sci. 33:1042–50. DOI: 10.1080/02640414.2014.981849. PMID: 25530454.
Article5. Prins PJ, Goss FL, Nagle EF, Beals K, Robertson RJ, Lovalekar MT, Welton GL. 2016; Energy drinks improve five-kilometer running performance in recreational endurance runners. J Strength Cond Res. 30:2979–90. DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001391. PMID: 26937774.
Article6. Campbell B, Wilborn C, La Bounty P, Taylor L, Nelson MT, Greenwood M, Ziegenfuss TN, Lopez HL, Hoffman JR, Stout JR, Schmitz S, Collins R, Kalman DS, Antonio J, Kreider RB. 2013; International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: energy drinks. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 10:1. DOI: 10.1186/1550-2783-10-1. PMID: 23281794. PMCID: PMC3538552.
Article7. Clauson KA, Shields KM, McQueen CE, Persad N. 2008; Safety issues associated with commercially available energy drinks. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 48:e55–63. quiz e64–7. DOI: 10.1331/JAPhA.2008.07055. PMID: 18595815. PMCID: PMC5660441.
Article8. Vivekanandarajah A, Ni S, Waked A. 2011; Acute hepatitis in a woman following excessive ingestion of an energy drink: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 5:227. DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-5-227. PMID: 21696583. PMCID: PMC3141691.
Article9. Attila S, Cakir B. 2011; Energy-drink consumption in college students and associated factors. Nutrition. 27:316–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2010.02.008. PMID: 20579846.
Article10. Grasser EK, Miles-Chan JL, Charrière N, Loonam CR, Dulloo AG, Montani JP. 2016; Energy drinks and their impact on the cardiovascular system: potential mechanisms. Adv Nutr. 7:950–60. DOI: 10.3945/an.116.012526. PMID: 27633110. PMCID: PMC5015039.
Article11. Bukhar HM, ElSawy NA, Header EA. 2012; Biological effect of high energy drink on normal and hyperglycemic rats. Pakistan J Nutr. 11:301–9. DOI: 10.3923/pjn.2012.301.309.12. Worthley MI, Prabhu A, De Sciscio P, Schultz C, Sanders P, Willoughby SR. 2010; Detrimental effects of energy drink consumption on platelet and endothelial function. Am J Med. 123:184–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.09.013. PMID: 20103032.
Article13. Ebuehi OA, Ajayl OE, Onyeulor AL, Awelimobor D. 2011; Effects of oral administration of energy drinks on blood chemistry, tissue histology and brain acetylcholine in rabbits. Nig Q J Hosp Med. 21:29–34. PMID: 21913538.14. Guilbeau JR. 2012; Health risks of energy drinks: what nurses and consumers need to know. Nurs Womens Health. 16:423–8. DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-486X.2012.01766.x. PMID: 23067287.
Article15. Buck R, Dixon J, Matjasich L, Petersen R. 2013. Energy drink consumption among adolescents and young adults: health effects and implications for practice. Westminster College;Salt Lake City:16. Tibrewal P, Dhillon R. 2011; Caffeine induced psychotic exacerbation. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 45:179–80. DOI: 10.3109/00048674.2010.529605. PMID: 21070185.
Article17. Ishak WW, Ugochukwu C, Bagot K, Khalili D, Zaky C. 2012; Energy drinks: psychological effects and impact on well-being and quality of life-a literature review. Innov Clin Neurosci. 9:25–34. PMID: 22347688. PMCID: PMC3280075.18. Andersen P, Morris R, Amaral D, Bliss T, O'Keefe J. 2007. The hippocampus book. Oxford University Press;New York: DOI: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195100273.001.0001.19. Mesulam MM. Mesulam MM, editor. 2000. Behavioral neuroanatomy: large-scale networks, association cortex, frontal syndromes, the limbic system, and the hemispheric specializations. Principles of behavioral and cognitive neurology. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press;New York: p. 1–120.20. Malinauskas BM, Aeby VG, Overton RF, Carpenter-Aeby T, Barber-Heidal K. 2007; A survey of energy drink consumption patterns among college students. Nutr J. 6:35. DOI: 10.1186/1475-2891-6-35. PMID: 17974021. PMCID: PMC5165673.
Article21. Hashish HA. 2014; Histopathologic effect of prenatal topiramate exposure on rat cerebral cortex and hippocampus. J Interdiscipl Histopathol. 2:61–8. DOI: 10.5455/jihp.20140130125547.
Article22. Huang TT, Zou Y, Corniola R. 2012; Oxidative stress and adult neurogenesis--effects of radiation and superoxide dismutase deficiency. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 23:738–44. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.04.003. PMID: 22521481. PMCID: PMC3410958.
Article23. Licht T, Kreisel T, Biala Y, Mohan S, Yaari Y, Anisimov A, Alitalo K, Keshet E. 2020; Age-dependent remarkable regenerative potential of the dentate gyrus provided by intrinsic stem cells. J Neurosci. 40:974–95. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1010-19.2019. PMID: 31959697. PMCID: PMC6989002.
Article24. Kassab AA, Tawfik SM. 2018; Effect of a caffeinated energy drink and its withdrawal on the submandibular salivary gland of adult male albino rats: a histological and immunohistochemical study. Egypt J Histol. 41:11–26. DOI: 10.21608/EJH.2018.7518.
Article25. Hamshari RGM. 2006. A study of the effect of khat on the offsprings of rabbits with special emphasis on its effect on the brain [Masters thesis]. Faculty of Medicine Ain Shams University;Cairo:26. Bancroft JD, Gamble M. 2002. Theory and practice of histological techniques. 5th ed. Churchill Livingstone;London:27. Graham L, Orenstein JM. 2007; Processing tissue and cells for transmission electron microscopy in diagnostic pathology and research. Nat Protoc. 2:2439–50. DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2007.304. PMID: 17947985. PMCID: PMC7086545.
Article28. Mahdy AA. 2014; Possible protective effect of ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol against damage induced by ionizing radiation in adult albino rat hippocampus. Egypt J Anat. 37:301–21.29. Gao Y, Bezchlibnyk YB, Sun X, Wang JF, McEwen BS, Young LT. 2006; Effects of restraint stress on the expression of proteins involved in synaptic vesicle exocytosis in the hippocampus. Neuroscience. 141:1139–48. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.04.066. PMID: 16757120.
Article30. Sawilowsky SS. 2005; Misconceptions leading to choosing the t test over the Wilcoxon Mann-Whitney test for shift in location parameter. J Mod Appl Stat Methods. 4:598–600. DOI: 10.22237/jmasm/1130804700.
Article31. Frane AV. 2015; Are per-family Type I error rates relevant in social and behavioral science? J Mod Appl Stat Methods. 14:12–23. DOI: 10.22237/jmasm/1430453040.
Article32. Bawazirand AE, Almehmadi MG. 2017; Effect of "Red Bull" energy drink on some neurotransmitters content and histological structure of cerebral cortex in male albino rats. Life Sci J. 14:63–73.33. Akande IS, Banjoko OA. 2011; Assessment of biochemical effect of "Power Horse" energy drink on hepatic, renal and histological functions in Sprague Dawley rats. Annu Res Rev Biol. 1:45–56.34. Blaise JH, Park JE, Bellas NJ, Gitchell TM, Phan V. 2018; Caffeine consumption disrupts hippocampal long-term potentiation in freely behaving rats. Physiol Rep. 6:e13632. DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13632. PMID: 29512310. PMCID: PMC5840440.
Article35. Huang ZL, Qu WM, Eguchi N, Chen JF, Schwarzschild MA, Fredholm BB, Urade Y, Hayaishi O. 2005; Adenosine A2A, but not A1, receptors mediate the arousal effect of caffeine. Nat Neurosci. 8:858–9. DOI: 10.1038/nn1491. PMID: 15965471.
Article36. Lazarus M, Shen HY, Cherasse Y, Qu WM, Huang ZL, Bass CE, Winsky-Sommerer R, Semba K, Fredholm BB, Boison D, Hayaishi O, Urade Y, Chen JF. 2011; Arousal effect of caffeine depends on adenosine A2A receptors in the shell of the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci. 31:10067–75. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6730-10.2011. PMID: 21734299. PMCID: PMC3153505.
Article37. Han ME, Park KH, Baek SY, Kim BS, Kim JB, Kim HJ, Oh SO. 2007; Inhibitory effects of caffeine on hippocampal neurogenesis and function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 356:976–80. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.03.086. PMID: 17400186.
Article38. Arikkath J. 2012; Molecular mechanisms of dendrite morphogenesis. Front Cell Neurosci. 6:61. DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2012.00061. PMID: 23293584.
Article39. Lin YC, Koleske AJ. 2010; Mechanisms of synapse and dendrite maintenance and their disruption in psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 33:349–78. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-060909-153204. PMID: 20367247. PMCID: PMC3063389.
Article40. Abo El-Khair DM, El-Safti Fel-N, Nooh HZ, El-Mehi AE. 2014; A comparative study on the effect of high cholesterol diet on the hippocampal CA1 area of adult and aged rats. Anat Cell Biol. 47:117–26. DOI: 10.5115/acb.2014.47.2.117. PMID: 24987548. PMCID: PMC4076418.
Article41. Díaz A, Treviño S, Guevara J, Muñoz-Arenas G, Brambila E, Espinosa B, Moreno-Rodríguez A, Lopez-Lopez G, Peña-Rosas U, Venegas B, Handal-Silva A, Morán-Perales JL, Flores G, Aguilar-Alonso P. 2016; Energy drink administration in combination with alcohol causes an inflammatory response and oxidative stress in the hippocampus and temporal cortex of rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:8725354. DOI: 10.1155/2016/8725354. PMID: 27069534. PMCID: PMC4812470.
Article42. Al-Shaar L, Vercammen K, Lu C, Richardson S, Tamez M, Mattei J. 2017; Health effects and public health concerns of energy drink consumption in the United States: a mini-review. Front Public Health. 5:225. DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2017.00225. PMID: 28913331. PMCID: PMC5583516.
Article43. Al-Basher GI, Aljabal H, Almeer RS, Allam AA, Mahmoud AM. 2018; Perinatal exposure to energy drink induces oxidative damage in the liver, kidney and brain, and behavioral alterations in mice offspring. Biomed Pharmacother. 102:798–811. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.139. PMID: 29605768.
Article44. Zeidán-Chuliá F, Gelain DP, Kolling EA, Rybarczyk-Filho JL, Ambrosi P, Terra SR, Pires AS, da Rocha JB, Behr GA, Moreira JC. 2013; Major components of energy drinks (caffeine, taurine, and guarana) exert cytotoxic effects on human neuronal SH-SY5Y cells by decreasing reactive oxygen species production. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:791795. DOI: 10.1155/2013/791795. PMID: 23766861. PMCID: PMC3674721.
Article45. Maiti P, Manna J, Dunbar GL. 2017; Current understanding of the molecular mechanisms in Parkinson's disease: targets for potential treatments. Transl Neurodegener. 6:28. DOI: 10.1186/s40035-017-0099-z. PMID: 29090092.
Article46. Li Q, Xing S, Chen Y, Liao Q, Li Q, Liu Y, He S, Feng F, Chen Y, Zhang J, Liu W, Guo Q, Sun Y, Sun H. 2020; Reasonably activating Nrf2: a long-term, effective and controllable strategy for neurodegenerative diseases. Eur J Med Chem. 185:111862. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111862. PMID: 31735576.
Article47. Vallés SL, Blanco AM, Pascual M, Guerri C. 2004; Chronic ethanol treatment enhances inflammatory mediators and cell death in the brain and in astrocytes. Brain Pathol. 14:365–71. DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2004.tb00079.x. PMID: 15605983.
Article48. Kang SH, Lee YA, Won SJ, Rhee KH, Gwag BJ. 2002; Caffeine-induced neuronal death in neonatal rat brain and cortical cell cultures. Neuroreport. 13:1945–50. DOI: 10.1097/00001756-200210280-00023. PMID: 12395097.
Article49. Bi F, Huang C, Tong J, Qiu G, Huang B, Wu Q, Li F, Xu Z, Bowser R, Xia XG, Zhou H. 2013; Reactive astrocytes secrete lcn2 to promote neuron death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 110:4069–74. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1218497110. PMID: 23431168. PMCID: PMC3593910.
Article50. Li K, Li J, Zheng J, Qin S. 2019; Reactive astrocytes in neurodegenerative diseases. Aging Dis. 10:664–75. DOI: 10.14336/AD.2018.0720. PMID: 31165009.
Article51. Spanswick SC, Sutherland RJ. 2010; Object/context-specific memory deficits associated with loss of hippocampal granule cells after adrenalectomy in rats. Learn Mem. 17:241–5. DOI: 10.1101/lm.1746710. PMID: 20410060. PMCID: PMC2893217.
Article52. Gebril HM, Rose RM, Gesese R, Emond MP, Huo Y, Aronica E, Boison D. 2020; Adenosine kinase inhibition promotes proliferation of neural stem cells after traumatic brain injury. Brain Commun. 2:fcaa017. DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcaa017. PMID: 32322821. PMCID: PMC7158236.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differential expression levels of synaptophysin through developmental stages in hippocampal region of mouse brain
- A comparative study on the effect of high cholesterol diet on the hippocampal CA1 area of adult and aged rats
- Developmental Hypothyroidism Influences the Development of the Entorhinal-Dentate Gyrus Pathway of Rat Offspring
- Neurogenesis and Psychiatry: Focusing on Mood Disorders
- Protective Effect of Shenqi-wan on Traumatic Brain Injury-induced Delayed Apoptosis in Rat Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus