Ann Lab Med.
2014 Sep;34(5):399-401. 10.3343/alm.2014.34.5.399.
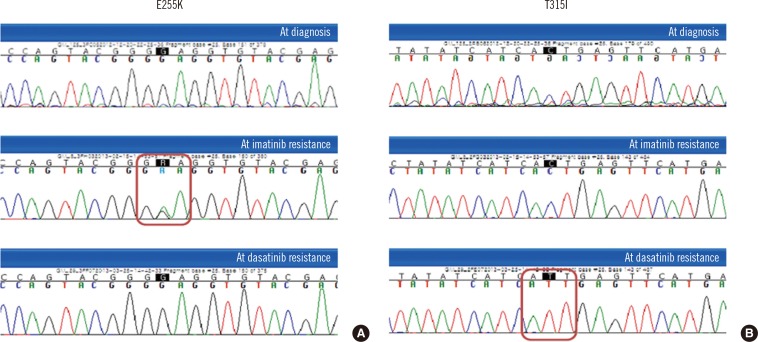
Rapid Sequential Gain of ABL1 Kinase Domain Mutations with a Complex Karyotype in the Progression of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Hematologic Oncology Clinic, Research Institute and Hospital, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Research Institute and Hospital, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. finekong@gmail.com
- 4Greencross Reference Laboratory, Yongin, Korea.
- KMID: 1791958
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2014.34.5.399
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Base Sequence
Benzamides/therapeutic use
Bone Marrow/pathology
Female
Fusion Proteins, bcr-abl/*genetics
Humans
Karyotyping
Leukemia, Myelogenous, Chronic, BCR-ABL Positive/drug therapy/*genetics
Middle Aged
Philadelphia Chromosome
Piperazines/therapeutic use
Protein Kinase Inhibitors/therapeutic use
Pyrimidines/therapeutic use
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Thiazoles/therapeutic use
Translocation, Genetic
Benzamides
Fusion Proteins, bcr-abl
Piperazines
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Pyrimidines
Thiazoles
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hochhaus A, O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Druker BJ, Branford S, Foroni L, et al. Six-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for the first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2009; 23:1054–1061. PMID: 19282833.
Article2. von Bubnoff N, Schneller F, Peschel C, Duyster J. BCR-ABL gene mutations in relation to clinical resistance of Philadelphia-chromosome-positive leukaemia to STI571: a prospective study. Lancet. 2002; 359:487–491. PMID: 11853795.
Article3. Hochhaus A, Kreil S, Corbin AS, La Rosée P, Müller MC, Lahaye T, et al. Molecular and chromosomal mechanisms of resistance to imatinib (STI571) therapy. Leukemia. 2002; 16:2190–2196.
Article4. Soverini S, Colarossi S, Gnani A, Castagnetti F, Rosti G, Bosi C, et al. Resistance to dasatinib in Philadelphia-positive leukemia patients and the presence or the selection of mutations at residues 315 and 317 in the BCR-ABL kinase domain. Haematologica. 2007; 92:401–404. PMID: 17339191.
Article5. Hughes T, Saglio G, Branford S, Soverini S, Kim DW, Müller MC, et al. Impact of baseline BCR-ABL mutations on response to nilotinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:4204–4210.
Article6. Müller MC, Cortes JE, Kim DW, Druker BJ, Erben P, Pasquini R, et al. Dasatinib treatment of chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: analysis of responses according to preexisting BCR-ABL mutations. Blood. 2009; 114:4944–4953.
Article7. Baccarani M, Cortes J, Pane F, Niederwieser D, Saglio G, Apperley J, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia: an update of concepts and management recommendations of European LeukemiaNet. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:6041–6051.
Article8. Sokal JE, Cox EB, Baccarani M, Tura S, Gomez GA, Robertson JE, et al. Prognostic discrimination in "good-risk" chronic granulocytic leukemia. Blood. 1984; 63:789–799. PMID: 6584184.
Article9. Hehlmann R, Ansari H, Hasford J, Heimpel H, Hossfeld DK, Kolb HJ, et al. German chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML)-Study Group. Comparative analysis of the impact of risk profile and of drug therapy on survival in CML using Sokal's index and a new score. Br J Haematol. 1997; 97:76–85.
Article10. Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N, Paquette R, Rao PN, et al. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science. 2001; 293:876–880.
Article11. Soverini S, Hochhaus A, Nicolini FE, Gruber F, Lange T, Saglio G, et al. BCR-ABL kinase domain mutation analysis in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2011; 118:1208–1215.
Article12. Ernst T, Gruber FX, Pelz-Ackermann O, Maier J, Pfirrmann M, Müller MC, et al. A co-operative evaluation of different methods of detecting BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia on second-line dasatinib or nilotinib therapy after failure of imatinib. Haematologica. 2009; 94:1227–1235.
Article13. Parker WT, Lawrence RM, Ho M, Irwin DL, Scott HS, Hughes TP, et al. Sensitive detection of BCR-ABL1 mutations in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia after imatinib resistance is predictive of outcome during subsequent therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:4250–4259.
Article14. Parker WT, Ho M, Scott HS, Hughes TP, Branford S. Poor response to second-line kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia patients with multiple low-level mutations, irrespective of their resistance profile. Blood. 2012; 119:2234–2238.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Novel Four-Way Translocation t(5;9;22;18)(q31;q34;q11.2;q21) in a Patient with Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
- Isolated monocytosis was the flag preceding abnormalities in other parameters of complete blood counts in chronic myeloid leukemia with e1a2 (minor, P190) BCR-ABL1 chimeric transcripts
- Genomic Profiling of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: Basic and Clinical Approach
- Clinical Resistance to the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Imatinib (STI571) and Detection of BCR-ABL Gene Mutations in Korean Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- A Case of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia with a 47,XYY Karyotype