Korean J Hematol.
2005 Jun;40(2):82-92. 10.5045/kjh.2005.40.2.82.
Clinical Resistance to the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Imatinib (STI571) and Detection of BCR-ABL Gene Mutations in Korean Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ejseo@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2252342
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2005.40.2.82
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Imatinib mesylate, the tyrosine kinase activity of the BCR-ABL fusion gene, induces a remarkable remission in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients. However, resistance to imatinib has been observed in a significant proportion of subjects, with the point mutations of the BCR-ABL kinase domain clinically identified as a possible mechanism. The aim of this study was to investigate clinical resistance to imatinib in Korean CML patients, and search for the point mutation of the BCR-ABL gene.
METHODS
The clinical data and cytogenetic results of thirty two CML patients, who were treated with imatinib, between Jan. 2002 and Aug. 2003, were evaluated. Mutational analyses for the point mutations of the BCR-ABL kinase domain in clinically resistant patients were tested using RT-PCR and direct sequencing methods.
RESULTS
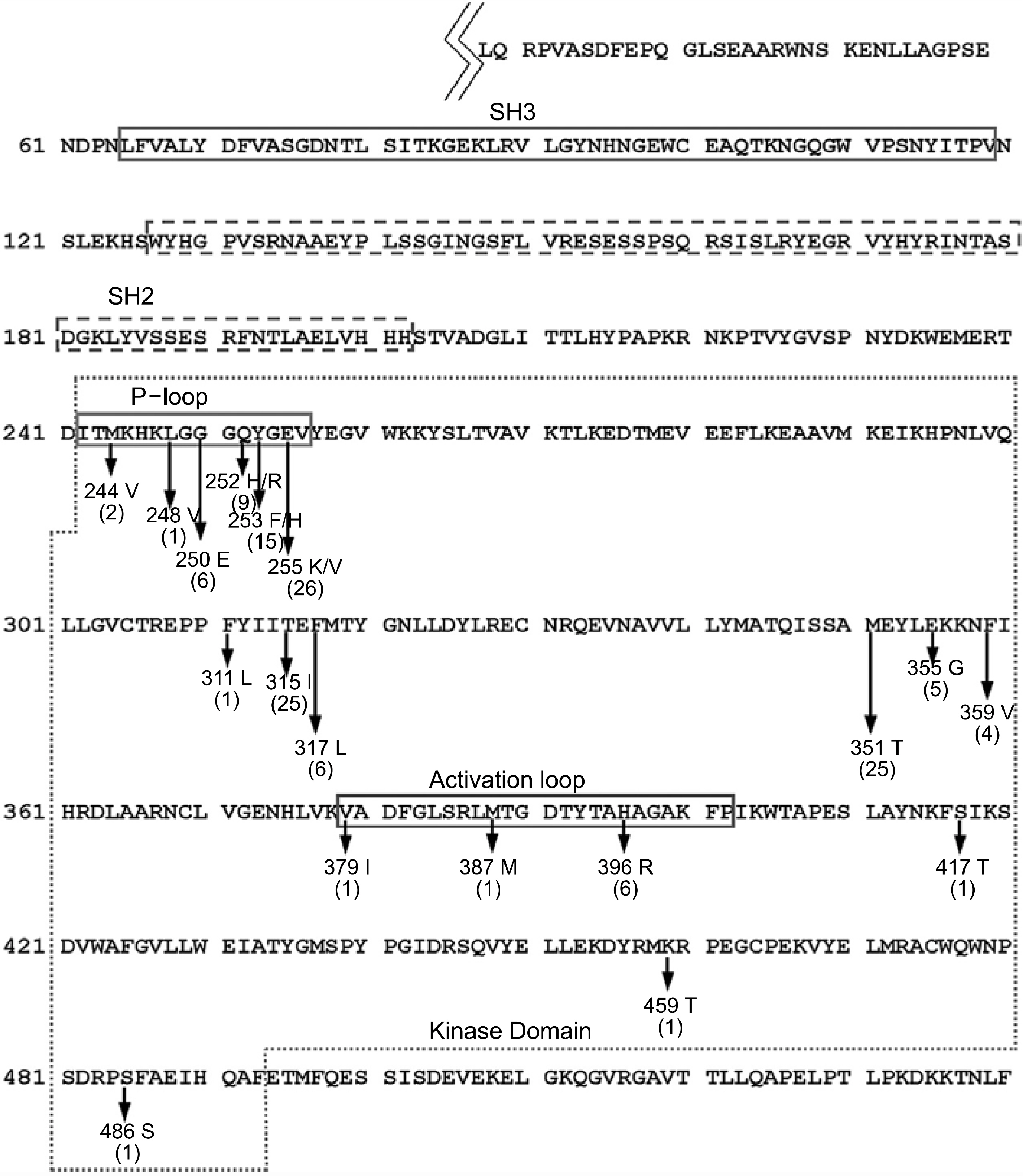
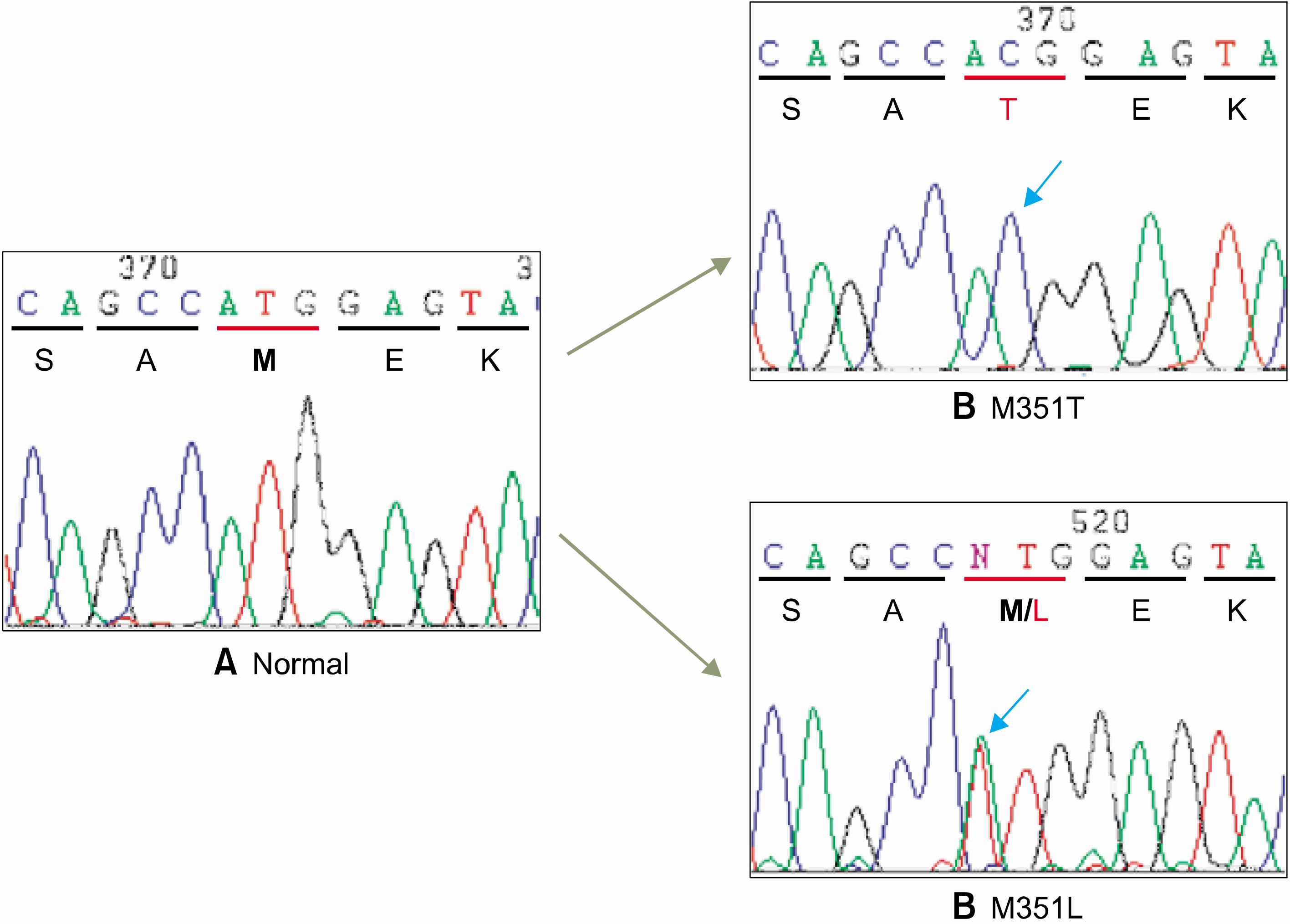
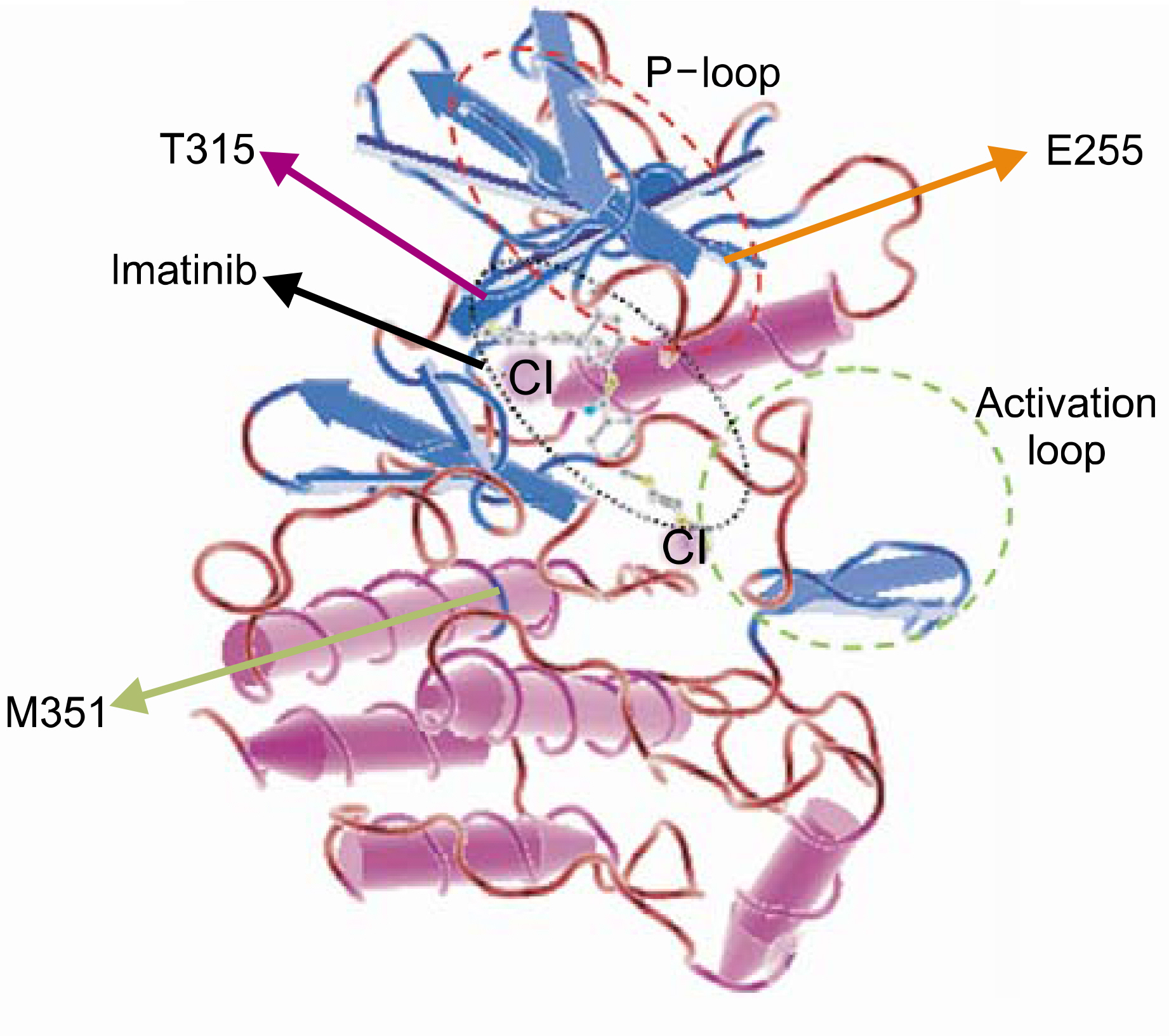
Complete hematological remission was obtained in all CML patients with a chronic phase and in 4 of 6 CML with accelerated or blast crisis. However, 4 patients (2 in the chronic phase and 2 with blast crisis) relapsed to blast crisis following continued treatment. A major cytogenetic response was observed in 67% of the chronic phase patients, but in 2, the Philadelphia chromosomes reemerged in a follow-up chromosome study. Mutational analyses showed point mutations in the 351st amino acid of the BCR-ABL kinase domain in 2 patients: M351T, which has previously been reported in many studies, and a novel substitution, M351L.
CONCLUSION
The frequency of imatinib resistance in Koreans was similar to that found in well-controlled western studies. Point mutations of the BCR-ABL kinase domain were detected in two patients. Further studies, with more sensitive methods and a greater number of patients will help reveal other mechanisms of imatinib resistance and establish more effective treatment plans.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Sawyers CL. Chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999; 340:1330–40.
Article2). Druker BJ. Perspectives on the development of a molecularly targeted agent. Cancer Cell. 2002; 1:31–6.
Article3). Druker BJ, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, et al. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat Med. 1996; 2:561–6.
Article4). Buchdunger E, Zimmermann J, Mett H, et al. Inhibition of the Abl protein-tyrosine kinase in vitro and in vivo by a 2-phenylaminopyrimidine derivative. Cancer Res. 1996; 56:100–4.5). Kantarjian H, Sawyers C, Hochhaus A, et al. International STI571 CML Study Group: Hematologic and cytogenetic responses to imatinib mesylate in chronic myelogenous leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:645–52.6). Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Kantarjian H, et al. Activity of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the Philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:1038–42.
Article7). Talpaz M, Silver RT, Druker BJ, et al. Imatinib induces durable hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia: results of a phase 2 study. Blood. 2002; 99:1928–37.
Article8). von Bubnoff N, Peschel C, Duyster J. Resistance of Philadelphia-chromosome positive leukemia towards the kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571, Glivec): a targeted oncoprotein strikes back. Leukemia. 2003; 17:829–38.
Article9). Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, et al. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science. 2001; 293:876–80.
Article10). Barthe C, Gharbi M, Lagarde V, et al. Mutation in the ATP-binding site of BCR-ABL in a patient with chronic myeloid leukaemia with increasing resitance to STI571. Br J Haematol. 2002; 119:109–11.11). Branford S, Rudzki Z, Walsh S, et al. High frequency of point mutations clustered within the adenosine triphosphate-binding region of BCR/ABL in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia or Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia who develop imatinib (STI571) resistance. Blood. 2002; 99:3472–5.
Article12). von Bubnoff N, Schneller F, Peschel C, Duyster J. BCR-ABL gene mutations in relation to clinical resistance of Philadelphia-chromosome positive leukemia to STI-571: a prospective study. Lancet. 2002; 359:487–91.13). Hochhaus A, Kreil S, Corbin AS, et al. Molecular and chromosomal mechanisms of resistance to imatinib (STI571) therapy. Leukemia. 2002; 16:2190–6.
Article14). Roche-Lestienne C, Soenen-Cornu V, Gradel-Duflos N, et al. Several types of mutations of the Abl gene can be found in chronic myeloid leukemia patients resistant to STI571, and they can pre-exist to the onset of treatment. Blood. 2002; 100:1014–8.
Article15). Shah NP, Nicoll JM, Nagar B, et al. Multiple BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations confer polyclonal resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571) in chronic phase and blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2002; 2:117–25.
Article16). Branford S, Rudzki Z, Walsh S, et al. Detection of BCR-ABL mutaitons in patients with CML treated with imatinib is virtually always accompanied by clinical resistance, and mutations in the ATP phosphate-binding loop (P-loop) are associated with a poor prognosis. Blood. 2003; 102:276–83.17). Schindler T, Bornmann W, Pellicena P, Miller WT, Clarkson B, Kuriyan J. Structural mechanism for STI-571 inhibition of Abelson tyrosine kinase. Science. 2000; 289:1938–42.
Article18). Nagar B, Hantschel O, Young MA, et al. Structural basis of the autoinhibition of c-Abl tyrosine kinase. Cell. 2003; 112:859–71.19). Gambacorti-Passerini CB, Gunby RH, Piazza R, Gali-etta A, Rostagno R, Scapozza L. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to imatinib in Philadelphia-chromosome-positive leukaemias. Lancet Oncol. 2003; 4:75–85.
Article20). Azam M, Latek RR, Daley GQ. Mechanisms of auto-inhibition and STI-571/Imatinib resistance revealed by mutagenesis of BCR-ABL. Cell. 2003; 112:831–43.
Article21). Cobin AS, La Rosee P, Stoffergen EP, Druker BJ, Deininger MW. Several Bcr-Abl kinase domain mutants associated with imatinib mesylate resistance remain sensitive to imatinib. Blood. 2003; 101:4611–4.22). Shannon KM. Resistance in the land of molecular cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell. 2002; 2:99–102.
Article23). Kreuzer KA, le Coutre P, Landt O, et al. Preexistence and evolution of imatinib mesylate-resistant clones in chronic myelogenous leukemia detected by a PNA-based PCR clamping technique. Ann Hematol. 2003; 82:284–9.
Article24). Marktel S, Marin D, Foot N, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase responding to imatinib: the occurrence of additional abnormalities predicts disease progression. Haematologica. 2003; 88:260–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- A Case of Drug Eruption with Localized ExfoliativeDermatitis Induced by Imatinib Mesylate
- A Case of Drug Eruption with Periorbital Edema and Exfoliative Dermatitis Induced by Imatinib Mesylate (STI571, Gleevec(TM))
- Detection of single nucleotide insertion of BCR/ABL region in imatinib-resistant human myelogenous leukemia SR-1 cells
- Imatinib Mesylate is Effective for Patients Not Only with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia, but Also Rheumatoid Arthritis