Dieckol Attenuates Microglia-mediated Neuronal Cell Death via ERK, Akt and NADPH Oxidase-mediated Pathways
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju 690-756, Korea. syeun@jejunu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pharmacology, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju 690-756, Korea.
- 3BotaMedi Inc. 307 Jeju Bio-industry Center, Jeju 690-121, Korea.
- 4Department of Nanobiomedical Science & BK21 PLUS NBM Global Research Center for Regenerative Medicine and Department of Pharmacology, Dankook University, Cheonan 330-951, Korea.
- 5Department of Pharmacology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu 700-842, Korea.
- KMID: 1791422
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.3.219
Abstract
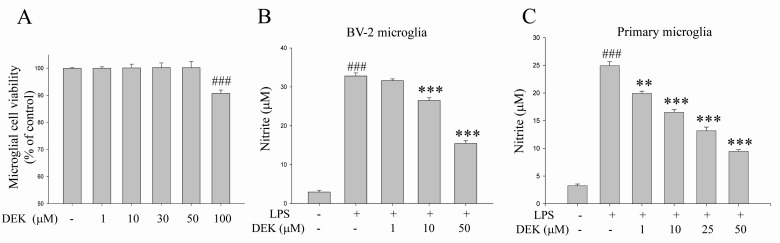
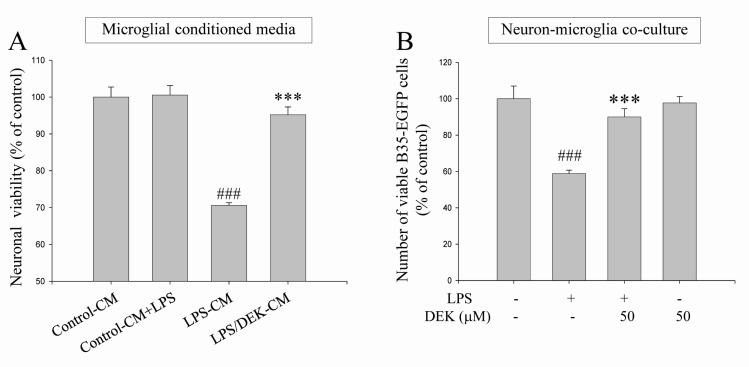
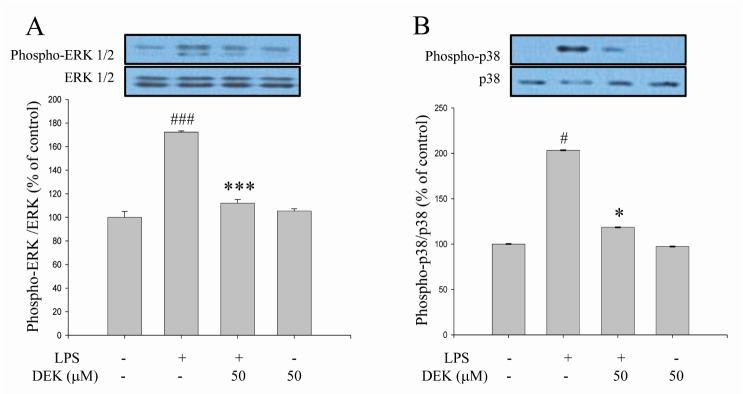
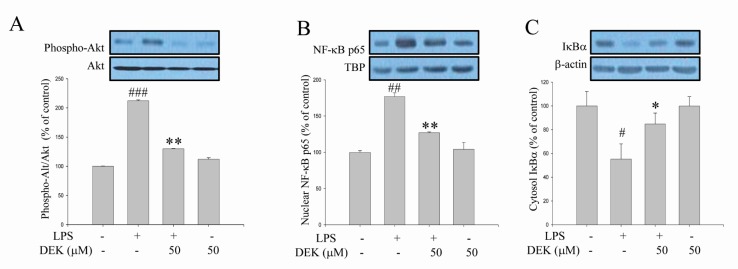
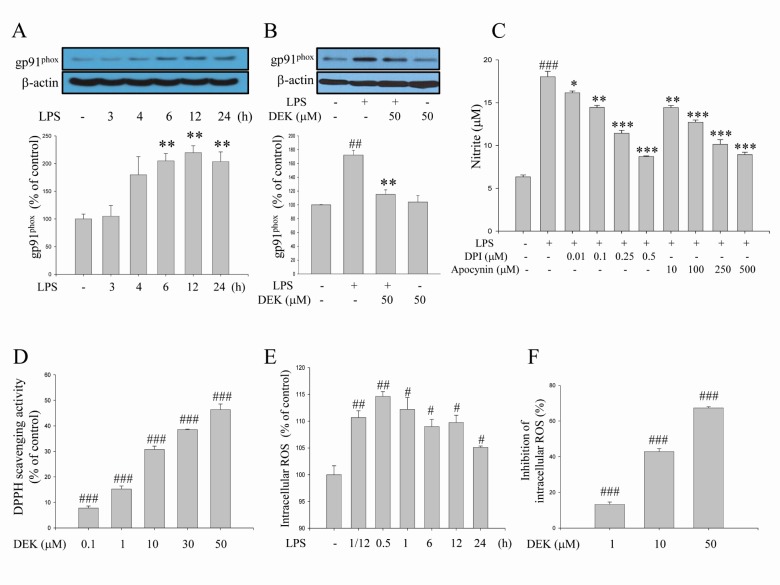
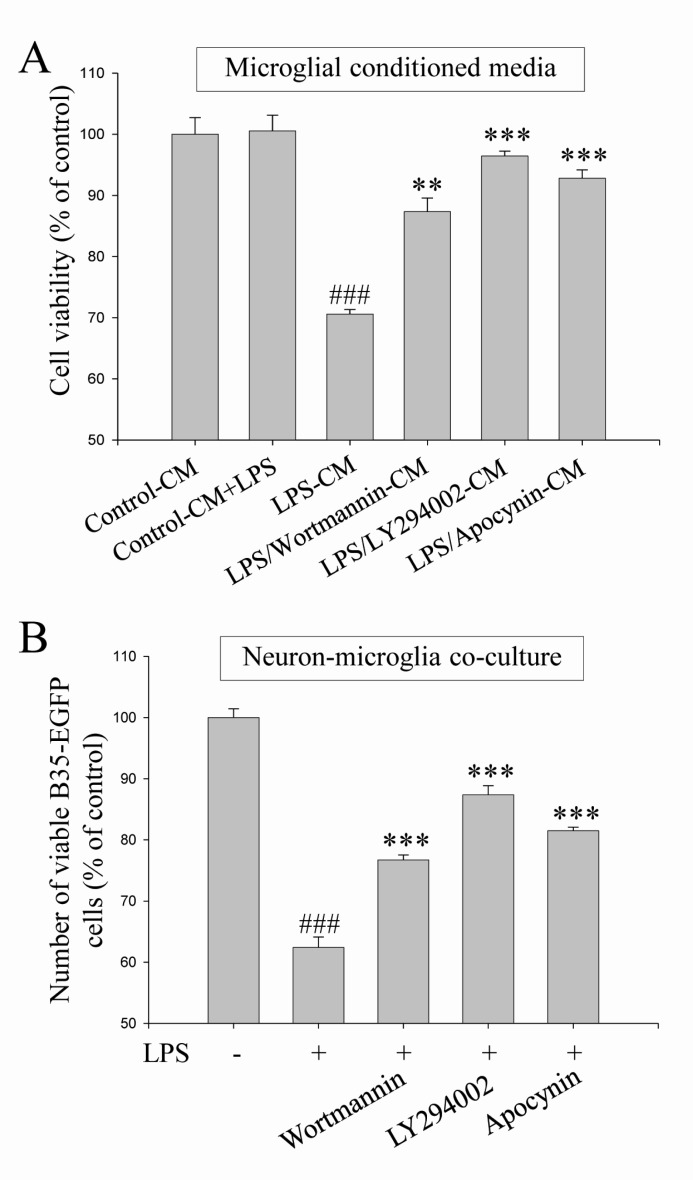
- Excessive microglial activation and subsequent neuroinflammation lead to synaptic loss and dysfunction as well as neuronal cell death, which are involved in the pathogenesis and progression of several neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, the regulation of microglial activation has been evaluated as effective therapeutic strategies. Although dieckol (DEK), one of the phlorotannins isolated from marine brown alga Ecklonia cava, has been previously reported to inhibit microglial activation, the molecular mechanism is still unclear. Therefore, we investigated here molecular mechanism of DEK via extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), Akt and nicotinamide adenine dinuclelotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase-mediated pathways. In addition, the neuroprotective mechanism of DEK was investigated in microglia-mediated neurotoxicity models such as neuron-microglia co-culture and microglial conditioned media system. Our results demonstrated that treatment of anti-oxidant DEK potently suppressed phosphorylation of ERK in lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 1 microg/ml)-stimulated BV-2 microglia. In addition, DEK markedly attenuated Akt phosphorylation and increased expression of gp91(phox), which is the catalytic component of NADPH oxidase complex responsible for microglial reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Finally, DEK significantly attenuated neuronal cell death that is induced by treatment of microglial conditioned media containing neurotoxic secretary molecules. These neuroprotective effects of DEK were also confirmed in a neuron-microglia co-culture system using enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)-transfected B35 neuroblastoma cell line. Taken together, these results suggest that DEK suppresses excessive microglial activation and microglia-mediated neuronal cell death via downregulation of ERK, Akt and NADPH oxidase-mediated pathways.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenine
Cell Death*
Cell Line
Coculture Techniques
Culture Media, Conditioned
Down-Regulation
Microglia
NADP*
NADPH Oxidase
Neuroblastoma
Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurons*
Neuroprotective Agents
Niacinamide
Phosphorylation
Phosphotransferases
Reactive Oxygen Species
Adenine
Culture Media, Conditioned
NADP
NADPH Oxidase
Neuroprotective Agents
Niacinamide
Phosphotransferases
Reactive Oxygen Species
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Neuroprotective mechanisms of dieckol against glutamate toxicity through reactive oxygen species scavenging and nuclear factor-like 2/heme oxygenase-1 pathway
Yanji Cui, Khulan Amarsanaa, Ji Hyung Lee, Jong-Kook Rhim, Jung Mi Kwon, Seong-Ho Kim, Joo Min Park, Sung-Cherl Jung, Su-Yong Eun
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;23(2):121-130. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2019.23.2.121.CRM1 inhibitor S109 suppresses cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest in renal cancer cells
Xuejiao Liu, Yulong Chong, Huize Liu, Yan Han, Mingshan Niu
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;20(2):161-168. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.2.161.Nobiletin attenuates neurotoxic mitochondrial calcium overload through K+ influx and ΔΨm across mitochondrial inner membrane
Ji Hyung Lee, Khulan Amarsanaa, Jinji Wu, Sang-Chan Jeon, Yanji Cui, Sung-Cherl Jung, Deok-Bae Park, Se-Jae Kim, Sang-Heon Han, Hyun-Wook Kim, Im Joo Rhyu, Su-Yong Eun
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;22(3):311-319. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.3.311.
Reference
-
1. Aschner M, Allen JW, Kimelberg HK, LoPachin RM, Streit WJ. Glial cells in neurotoxicity development. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1999; 39:151–173. PMID: 10331080.
Article2. Cui Y, Wu J, Jung SC, Park DB, Maeng YH, Hong JY, Kim SJ, Lee SR, Kim SJ, Kim SJ, Eun SY. Anti-neuroinflammatory activity of nobiletin on suppression of microglial activation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010; 33:1814–1821. PMID: 21048305.
Article3. Ock J, Han HS, Hong SH, Lee SY, Han YM, Kwon BM, Suk K. Obovatol attenuates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation by modulating redox regulation. Br J Pharmacol. 2010; 159:1646–1662. PMID: 20397299.
Article4. Lee JW, Cheong IY, Kim HS, Lee JJ, Lee YS, Kwon YS, Kim MJ, Lee HJ, Kim SS, Chun W. Anti-inflammatory activity of 1-docosanoyl cafferate isolated from rhus verniciflua in LPSstimulated BV2 microglial cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011; 15:9–15. PMID: 21461235.5. Chéret C, Gervais A, Lelli A, Colin C, Amar L, Ravassard P, Mallet J, Cumano A, Krause KH, Mallat M. Neurotoxic activation of microglia is promoted by a nox1-dependent NADPH oxidase. J Neurosci. 2008; 28:12039–12051. PMID: 19005069.6. Cooney SJ, Bermudez-Sabogal SL, Byrnes KR. Cellular and temporal expression of NADPH oxidase (NOX) isotypes after brain injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2013; 10:155. PMID: 24344836.
Article8. DeLeo FR, Quinn MT. Assembly of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase: molecular interaction of oxidase proteins. J Leukoc Biol. 1996; 60:677–691. PMID: 8975869.
Article9. Oh YT, Lee JY, Lee J, Kim H, Yoon KS, Choe W, Kang I. Oleic acid reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of iNOS and COX-2 in BV2 murine microglial cells: possible involvement of reactive oxygen species, p38 MAPK, and IKK/NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Neurosci Lett. 2009; 464:93–97. PMID: 19699266.10. Sun HN, Kim SU, Lee MS, Kim SK, Kim JM, Yim M, Yu DY, Lee DS. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase-dependent activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal pathways is required for lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial phagocytosis. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008; 31:1711–1715. PMID: 18758064.
Article11. Zhang L, Wu C, Zhao S, Yuan D, Lian G, Wang X, Wang L, Yang J. Demethoxycurcumin, a natural derivative of curcumin attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory responses through down-regulation of intracellular ROS-related MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathways in N9 microglia induced by lipopolysaccharide. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010; 10:331–338. PMID: 20018257.12. Kim AR, Shin TS, Lee MS, Park JY, Park KE, Yoon NY, Kim JS, Choi JS, Jang BC, Byun DS, Park NK, Kim HR. Isolation and identification of phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. J Agric Food Chem. 2009; 57:3483–3489. PMID: 19338274.
Article13. Ryu B, Li Y, Qian ZJ, Kim MM, Kim SK. Differentiation of human osteosarcoma cells by isolated phlorotannins is subtly linked to COX-2, iNOS, MMPs, and MAPK signaling: implication for chronic articular disease. Chem Biol Interact. 2009; 179:192–201. PMID: 19330880.
Article14. Jung WK, Heo SJ, Jeon YJ, Lee CM, Park YM, Byun HG, Choi YH, Park SG, Choi IW. Inhibitory effects and molecular mechanism of dieckol isolated from marine brown alga on COX-2 and iNOS in microglial cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2009; 57:4439–4446. PMID: 19408937.
Article15. Li Y, Qian ZJ, Ryu B, Lee SH, Kim MM, Kim SK. Chemical components and its antioxidant properties in vitro: an edible marine brown alga, Ecklonia cava. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009; 17:1963–1973. PMID: 19201199.
Article16. Eun SY, Hong YH, Kim EH, Jeon H, Suh YH, Lee JE, Jo C, Jo SA, Kim J. Glutamate receptor-mediated regulation of c-fos expression in cultured microglia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 325:320–327. PMID: 15522236.
Article17. Bocchini V, Mazzolla R, Barluzzi R, Blasi E, Sick P, Kettenmann H. An immortalized cell line expresses properties of activated microglial cells. J Neurosci Res. 1992; 31:616–621. PMID: 1578513.
Article18. Breyer A, Elstner M, Gillessen T, Weiser D, Elstner E. Glutamate-induced cell death in neuronal HT22 cells is attenuated by extracts from St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum L.). Phytomedicine. 2007; 14:250–255. PMID: 17346956.
Article19. Maher P, Davis JB. The role of monoamine metabolism in oxidative glutamate toxicity. J Neurosci. 1996; 16:6394–6401. PMID: 8815918.
Article20. Schubert D, Heinemann S, Carlisle W, Tarikas H, Kimes B, Patrick J, Steinbach JH, Culp W, Brandt BL. Clonal cell lines from the rat central nervous system. Nature. 1974; 249:224–227. PMID: 4151463.
Article21. Cui Y, Wu J, Jung SC, Kim GO, Kyeong Ko R, Lee HJ, Yoo ES, Kang HK, Suk K, Eun SY. Neuroprotective effect of methyl lucidone against microglia-mediated neurotoxicity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012; 690:4–12. PMID: 22683871.
Article22. Park GH, Jeon SJ, Ko HM, Ryu JR, Lee JM, Kim HY, Han SH, Kang YS, Park SH, Shin CY, Ko KH. Activation of microglial cells via protease-activated receptor 2 mediates neuronal cell death in cultured rat primary neuron. Nitric Oxide. 2010; 22:18–29. PMID: 19887113.
Article23. Wang S, Wang H, Guo H, Kang L, Gao X, Hu L. Neuroprotection of Scutellarin is mediated by inhibition of microglial inflammatory activation. Neuroscience. 2011; 185:150–160. PMID: 21524691.
Article24. Dohi K, Ohtaki H, Nakamachi T, Yofu S, Satoh K, Miyamoto K, Song D, Tsunawaki S, Shioda S, Aruga T. Gp91phox (NOX2) in classically activated microglia exacerbates traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2010; 7:41. PMID: 20659322.
Article25. Zhao S, Zhang L, Lian G, Wang X, Zhang H, Yao X, Yang J, Wu C. Sildenafil attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory responses through down-regulation of intracellular ROS-related MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways in N9 microglia. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011; 11:468–474. PMID: 21220057.
Article26. Tsai HH, Lee WR, Wang PH, Cheng KT, Chen YC, Shen SC. Propionibacterium acnes-induced iNOS and COX-2 protein expression via ROS-dependent NF-κB and AP-1 activation in macrophages. J Dermatol Sci. 2013; 69:122–131. PMID: 23178030.
Article27. Zhang H, Wang ZW, Wu HB, Li Z, Li LC, Hu XP, Ren ZL, Li BJ, Hu ZP. Transforming growth factor-β1 induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in rat vascular smooth muscle cells via ROS-dependent ERK-NF-κB pathways. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013; 375:11–21. PMID: 23275087.
Article28. Ko HM, Koppula S, Kim BW, Kim IS, Hwang BY, Suk K, Park EJ, Choi DK. Inflexin attenuates proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappaB activation in LPS-treated microglia. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010; 633:98–106. PMID: 20159010.29. Lin HY, Tang CH, Chen YH, Wei IH, Chen JH, Lai CH, Lu DY. Peptidoglycan enhances proinflammatory cytokine expression through the TLR2 receptor, MyD88, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT and NF-kappaB pathways in BV-2 microglia. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010; 10:883–891. PMID: 20451669.
Article30. Karunakaran S, Ravindranath V. Activation of p38 MAPK in the substantia nigra leads to nuclear translocation of NFkappaB in MPTP-treated mice: implication in Parkinson\'s disease. J Neurochem. 2009; 109:1791–1799. PMID: 19457134.31. Manea A, Tanase LI, Raicu M, Simionescu M. Transcriptional regulation of NADPH oxidase isoforms, Nox1 and Nox4, by nuclear factor-kappaB in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010; 396:901–907. PMID: 20457132.32. Ago T, Kuroda J, Kamouchi M, Sadoshima J, Kitazono T. Pathophysiological roles of NADPH oxidase/nox family proteins in the vascular system. -Review and perspective-. Circ J. 2011; 75:1791–1800. PMID: 21673456.33. Beckman JS, Koppenol WH. Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: the good, the bad, and ugly. Am J Physiol. 1996; 271:C1424–C1437. PMID: 8944624.
Article34. Gibbons HM, Dragunow M. Microglia induce neural cell death via a proximity-dependent mechanism involving nitric oxide. Brain Res. 2006; 1084:1–15. PMID: 16564033.
Article35. Rhee SG, Chang TS, Bae YS, Lee SR, Kang SW. Cellular regulation by hydrogen peroxide. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003; 14(8 Suppl 3):S211–S215. PMID: 12874433.
Article36. Hattori K, Naguro I, Runchel C, Ichijo H. The roles of ASK family proteins in stress responses and diseases. Cell Commun Signal. 2009; 7:9. PMID: 19389260.
Article37. Huo Y, Rangarajan P, Ling EA, Dheen ST. Dexamethasone inhibits the Nox-dependent ROS production via suppression of MKP-1-dependent MAPK pathways in activated microglia. BMC Neurosci. 2011; 12:49. PMID: 21615929.
Article38. Yang CS, Shin DM, Lee HM, Son JW, Lee SJ, Akira S, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, El-Benna J, Ichijo H, Jo EK. ASK1-p38 MAPK-p47phox activation is essential for inflammatory responses during tuberculosis via TLR2-ROS signalling. Cell Microbiol. 2008; 10:741–754. PMID: 18028450.
Article39. Yang CS, Lee HM, Lee JY, Kim JA, Lee SJ, Shin DM, Lee YH, Lee DS, El-Benna J, Jo EK. Reactive oxygen species and p47phox activation are essential for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced pro-inflammatory response in murine microglia. J Neuroinflammation. 2007; 4:27. PMID: 18036262.
Article40. Tanga FY, Nutile-McMenemy N, DeLeo JA. The CNS role of Toll-like receptor 4 in innate neuroimmunity and painful neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:5856–5861. PMID: 15809417.
Article41. Cao CX, Yang QW, Lv FL, Cui J, Fu HB, Wang JZ. Reduced cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in Toll-like receptor 4 deficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007; 353:509–514. PMID: 17188246.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- NADPH oxidase mediated oxidative stress in hepatic fibrogenesis
- NADPH Oxidase Mediates β-Amyloid Peptide-Induced Neuronal Death in Mouse Cortical Cultures
- Function of NADPH Oxidases in Diabetic Nephropathy and Development of Nox Inhibitors
- Resveratrol inhibits foam cell formation via NADPH oxidase 1-mediated reactive oxygen species and monocyte chemotactic protein-1
- Neuroprotection Signaling of Nuclear Akt in Neuronal Cells