J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Apr;21(2):253-258. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.253.
Prognostic Significance of Multidrug Resistance Gene 1 (MDR1), Multidrug Resistance-related Protein (MRP) and Lung Resistance Protein (LRP) mRNA Expression in Acute Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. cjpark@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Dogguk University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781831
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.253
Abstract
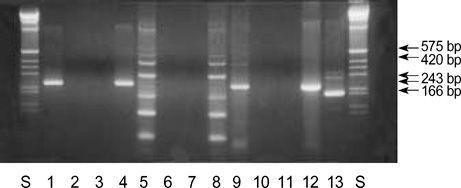
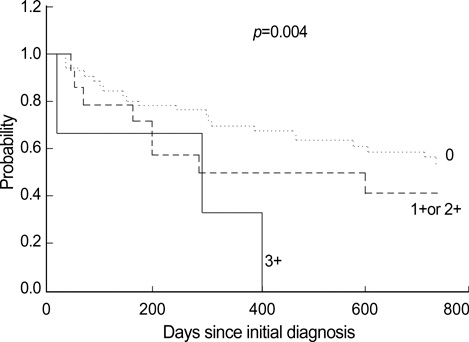
- The prognostic significance of multidrug resistance (MDR) gene expression is controversial. We investigated whether multidrug resistance gene 1 (MDR1), multidrug resistance-related protein (MRP) and lung resistance protein (LRP) mRNA expression are associated with outcomes in acute leukemia patients. At diagnosis we examined MDR1, MRP and LRP mRNA expression in bone marrow samples from 71 acute leukemia patients (39 myeloid, 32 lymphoblastic) using nested RT-PCR. The expression of each of these genes was then expressed as a ratio in relation to beta-actin gene expression, and the three genes were categorized as being either 0, 1+, 2+ or 3+. MDR1, MRP and LRP mRNA expression was detected in 23.9%, 83.1% and 45.1 %, respectively. LRP mRNA expression was significantly associated with resistance to induction chemotherapy in acute leukemia patients, and in the AML proportion (p=0.02 and p=0.03, respectively). MRP and high MDR1 mRNA expression was associated with poorer 2-yr survival (p=0.049 and p=0.04, respectively). Patients expressing both MRP and LRP mRNA had poorer outcomes and had worse 2-yr survival. The present data suggest that MDR expression affects complete remission and survival rates in acute leukemia patients. Thus, determination of MDR gene expression at diagnosis appears likely to provide useful prognostic information for acute leukemia patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Vault Ribonucleoprotein Particles/*genetics
Survival Rate
RNA, Neoplasm/genetics
RNA, Messenger/genetics
Prognosis
Neoplasm Proteins/*genetics
Multidrug Resistance-Associated Proteins/*genetics
Middle Aged
Male
Leukemia, Myelocytic, Acute/drug therapy/genetics/mortality
Leukemia, Lymphocytic, Acute/drug therapy/genetics/mortality
Leukemia/drug therapy/*genetics/mortality
Infant
Humans
*Genes, MDR
Gene Expression
Female
Child, Preschool
Child
Base Sequence
Aged
Adult
Adolescent
Figure
Reference
-
1. Riordan JR, Ling V. Genetic and biochemical characterization of multidrug resistance. Pharmacol Ther. 1985. 28:51–75.
Article2. McKenna SL, Padua RA. Multidrug resistance in leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1997. 96:659–674.
Article3. Shen DW, Cardarelli C, Hwang J, Cornwell M, Richert N, Ishii S, Pastan I, Gottesman MM. Multiple drug-resistant human KB carcinoma cells independently selected for high-level resistance to colchicine, adriamycin, or vinblastine show changes in expression of specific proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986. 261:7762–7770.
Article4. Lee NY, Bae HG, Kwon EH, Heo WB, Shin SH, Suh JS. Relation among the tests and comparison of positivity of tests for multi-drug resistance in newly diagnosed acute leukemia. Korean J Lab Med. 2003. 23:143–150.5. Chauncey TR. Drug resistance mechanisms in acute leukemia. Curr Opin Oncol. 2001. 13:21–26.
Article6. Kruh GD, Chan A, Myers K, Gaughan K, Miki T, Aaronson SA. Expression complementary DNA library transfer establishes mrp as a multidrug resistance gene. Cancer Res. 1994. 54:1649–1652.7. Scheper RJ, Broxterman HJ, Scheffer GL, Kaaijk P, Dalton WS, van Heijningen TH, van Kalken CK, Slovak ML, de Vries EG, van der Valk P. Overexpression of a M (r) 110,000 vesicular protein in non-P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Cancer Res. 1993. 53:1475–1479.8. Szabo D, Keyzer H, Kaiser HE, Molnar J. Reversal of multidrug resistance of tumor cells. Anticancer Res. 2000. 20:4261–4274.9. Kakihara T, Tanaka A, Watanabe A, Yamamoto K, Kanto K, Kataoka S, Ogawa A, Asami K, Uchiyama M. Expression of multidrug resistance-related genes does not contribute to risk factors in newly diagnosed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Int. 1999. 41:641–647.
Article10. List AF, Spier CS, Grogan TM, Johnson C, Roe DJ, Greer JP, Wolff SN, Broxterman HJ, Scheffer GL, Scheper RJ, Dalton WS. Overexpression of the major vault transporter protein lung-resistance protein predicts treatment outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1996. 87:2464–2469.
Article11. Dhooge C, De Moerloose B, Laureys G, Kint J, Ferster A, De Bacquer D, Philippe J, Benoit Y. P-glycoprotein is an independent prognostic factor predicting relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: results of a 6-year prospective study. Br J Haematol. 1999. 105:676–683.
Article12. Gurbuxani S, Zhou D, Simonin G, Raina V, Arya LS, Sazawal S, Marie JP, Bhargava M. Expression of genes implicated in multidrug resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia in India. Ann Hematol. 1998. 76:195–200.
Article13. Xu D, Arestrom I, Virtala R, Pisa P, Peterson C, Gruber A. High levels of lung resistance related protein mRNA in leukaemic cells from patients with acute myelogenous leukaemia are associated with inferior response to chemotherapy and prior treatment with mitoxantrone. Br J Haematol. 1999. 106:627–633.
Article14. Laurencot CM, Scheffer GL, Scheper RJ, Shoemaker RH. Increased LRP mRNA expression is associated with the MDR phenotype in intrinsically resistant human cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1997. 72:1021–1026.15. Sauerbrey A, Voigt A, Wittig S, Hafer R, Zintl F. Messenger RNA analysis of the multidrug resistance related protein (MRP1) and the lung resistance protein (LRP) in de novo and relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002. 43:875–879.
Article16. Guerci A, Merlin JL, Missoum N, Feldmann L, Marchal S, Witz F, Rose C, Guerci O. Predictive value for treatment outcome in acute myeloid leukemia of cellular daunorubicin accumulation and P-glycoprotein expression simultaneously determined by flow cytometry. Blood. 1995. 85:2147–2153.
Article17. Mahadevan D, List AF. Targeting the multidrug resistance-1 transporter in AML: molecular regulation and therapeutic strategies. Blood. 2004. 104:1940–1951.
Article18. Schaich M, Soucek S, Thiede C, Ehninger G, Illmer T. MDR1 and MRP1 gene expression are independent predictors for treatment outcome in adult acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2005. 128:324–332.
Article19. Borg AG, Burgess R, Green LM, Scheper RJ, Yin JA. Overexpression of lung-resistance protein and increased P-glycoprotein function in acute myeloid leukaemia cells predict a poor response to chemotherapy and reduced patient survival. Br J Haematol. 1998. 103:1083–1091.
Article20. den Boer ML, Pieters R, Kazemier KM, Rottier MM, Zwaan CM, Kaspers GJ, Janka-Schaub G, Henze G, Creutzig U, Scheper RJ, Veerman AJ. Relationship between major vault protein/lung resistance protein, multidrug resistance-associated protein, P-glycoprotein expression, and drug resistance in childhood leukemia. Blood. 1998. 91:2092–2098.
Article21. Legrand O, Simonin G, Beauchamp-Nicoud A, Zittoun R, Marie JP. Simultaneous activity of MRP1 and Pgp is correlated with in vitro resistance to daunorubicin and with in vivo resistance in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1999. 94:1046–1056.
Article22. Valera ET, Scrideli CA, Queiroz RG, Mori BM, Tone LG. Multiple drug resistance protein (MDR-1), multidrug resistance-related protein (MRP) and lung resistance protein (LRP) gene expression in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sao Paulo Med J. 2004. 122:166–171.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) and multidrug resistance (MDR1) gene expression in osteosarcoma and their prognostic significance
- Expression of Multidrug Resistance Genes, mdr1, mrp, Topo IIalpha and Topo IIbeta in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Expression of Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein(MRP), c-myc and c-fos in L1210 Cells
- Expression analysis of genes related to multidrug resistance (MDR) in ovarian cancer cell line A2780 and cisplatinum resistant cell line A2780cp
- Prognostic Significance of the Expression of MRP and p53 in Colorectal Carcinoma