Korean J Lab Med.
2011 Oct;31(4):279-281. 10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.4.279.
Aminoglycoside Susceptibility Profiles of Enterobacter cloacae Isolates Harboring the aac(6')-Ib Gene
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, St. Vincent's Hospital, Suwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. yjpk@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1781692
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.4.279
Abstract
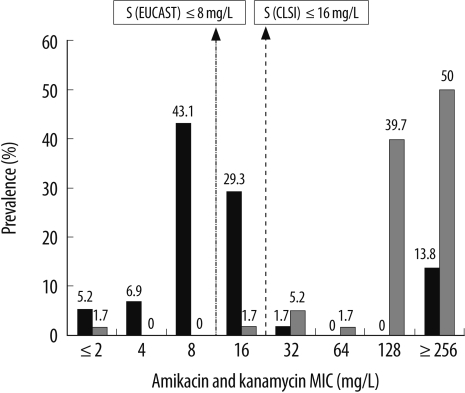
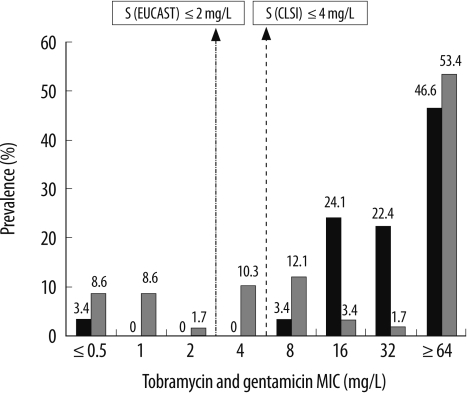
- The aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferases of type Ib (aac(6')-Ib) gene confers resistance to amikacin, tobramycin, kanamycin, and netilmicin but not gentamicin. However, some isolates harboring this gene show reduced susceptibility to amikacin. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) recommends a revision of the phenotypic description for isolates harboring the aac(6')-Ib gene. In this study, we determined the aminoglycoside susceptibility profiles of 58 AAC(6')-Ib-producing Enterobacter cloacae isolates. On the basis of the CLSI and EUCAST breakpoints, a large proportion (84.5% and 55.2%, respectively) of these 58 isolates were found to be susceptible to amikacin. However, among the isolates that were shown to be anikacin-susceptible according to the CLSI and EUCAST breakpoints, only 30.6% and 18.8% isolates, respectively, could be considered to have intermediate resistance on the basis of the EUCAST expert rules. Further studies should be conducted to determine the aminoglycoside susceptibility profiles of aac(6')-Ib-harboring isolates from various geographic regions and to monitor the therapeutic efficacy of amikacin in infections caused by these isolates.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acetyltransferases/*genetics
Amikacin/pharmacology
Aminoglycosides/*pharmacology
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*pharmacology
Drug Resistance, Bacterial/genetics
Enterobacter cloacae/*genetics/isolation & purification
Enterobacteriaceae Infections/diagnosis/microbiology
Humans
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Figure
Reference
-
1. Neonakis I, Gikas A, Scoulica E, Manios A, Georgiladakis A, Tselentis Y. Evolution of aminoglycoside resistance phenotypes of four gram-negative bacteria: an 8-year survey in a university hospital in Greece. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2003; 22:526–531. PMID: 14602373.
Article2. Kim JY, Park YJ, Kwon HJ, Han K, Kang MW, Woo GJ. Occurrence and mechanisms of amikacin resistance and its association with β-lactamases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a Korean nationwide study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008; 62:479–483. PMID: 18606785.3. Sabtcheva S, Kaku M, Saga T, Ishii Y, Kantardjjev T. High prevalence of the aac(6')-Ib-cr gene and its dissemination among Enterobacteriaceae isolates by CTX-M-15 plasmids in Bulgaria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53:335–336. PMID: 19001110.4. Kim SY, Park YJ, Yu JK, Kim YS, Han K. Prevalence and characteristics of aac(6')-Ib-cr in AmpC-producing Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter freundii, and Serratia marcescens: a multicenter study from Korea. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009; 63:314–318. PMID: 19216942.5. Casin I, Bordon F, Bertin P, Coutrot A, Podglajen I, Brasseur R, et al. Aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase variants of the Ib type with altered substrate profile in clinical isolates of Enterobacter cloacae and Citrobacter freundii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998; 42:209–215. PMID: 9527761.6. Rather PN, Munayyer H, Mann PA, Hare RS, Miller GH, Shaw KJ. Genetic analysis of bacterial acetyltransferases: identification of amino acids determining the specificities of the aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase Ib and IIa proteins. J Bacteriol. 1992; 174:3196–3203. PMID: 1577689.7. Shmara A, Weinsetel N, Dery KJ, Chavideh R, Tolmasky ME. Systematic analysis of a conserved region of the aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase type Ib. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001; 45:3287–3292. PMID: 11709299.8. Park CH, Robicsek A, Jacoby GA, Sahm D, Hooper DC. Prevalence in the United States of aac(6')-Ib-cr encoding a ciprofloxacin-modifying enzyme. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006; 50:3953–3955. PMID: 16954321.9. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). M100-S19. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Nineteenth informational supplement. 2009. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.10. Tenover FC, Arbeit RD, Goering RV, Mickelsen PA, Murray BE, Persing DH, et al. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol. 1995; 33:2233–2239. PMID: 7494007.
Article11. Caulin E, Coutrot A, Carbon C, Collatz E. Resistance to amikacin and isepamicin in rabbits with experimental endocarditis of an aac(6')-Ib-bearing strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae susceptible in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996; 40:2848–2853. PMID: 9124853.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dissemination of Plasmid-mediated qnr, aac(6')-Ib-cr, and qepA Genes Among 16S rRNA Methylase Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Korea
- Prevalence and Characterization of Plasmid-Medicated Quinolone Resistance Genes among Clinical Isolates of Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporin Resistant Enterobacter cloacae
- Emergence of CTX-M-9 Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacter cloacae Isolates
- Detection of mcr-1 Plasmids in Enterobacteriaceae Isolates From Human Specimens: Comparison With Those in Escherichia coli Isolates From Livestock in Korea
- Characteristics of aac(6')-Ib-cr Gene in Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Chungnam Area