J Bacteriol Virol.
2009 Sep;39(3):173-182. 10.4167/jbv.2009.39.3.173.
Dissemination of Plasmid-mediated qnr, aac(6')-Ib-cr, and qepA Genes Among 16S rRNA Methylase Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. minkim@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1474160
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2009.39.3.173
Abstract
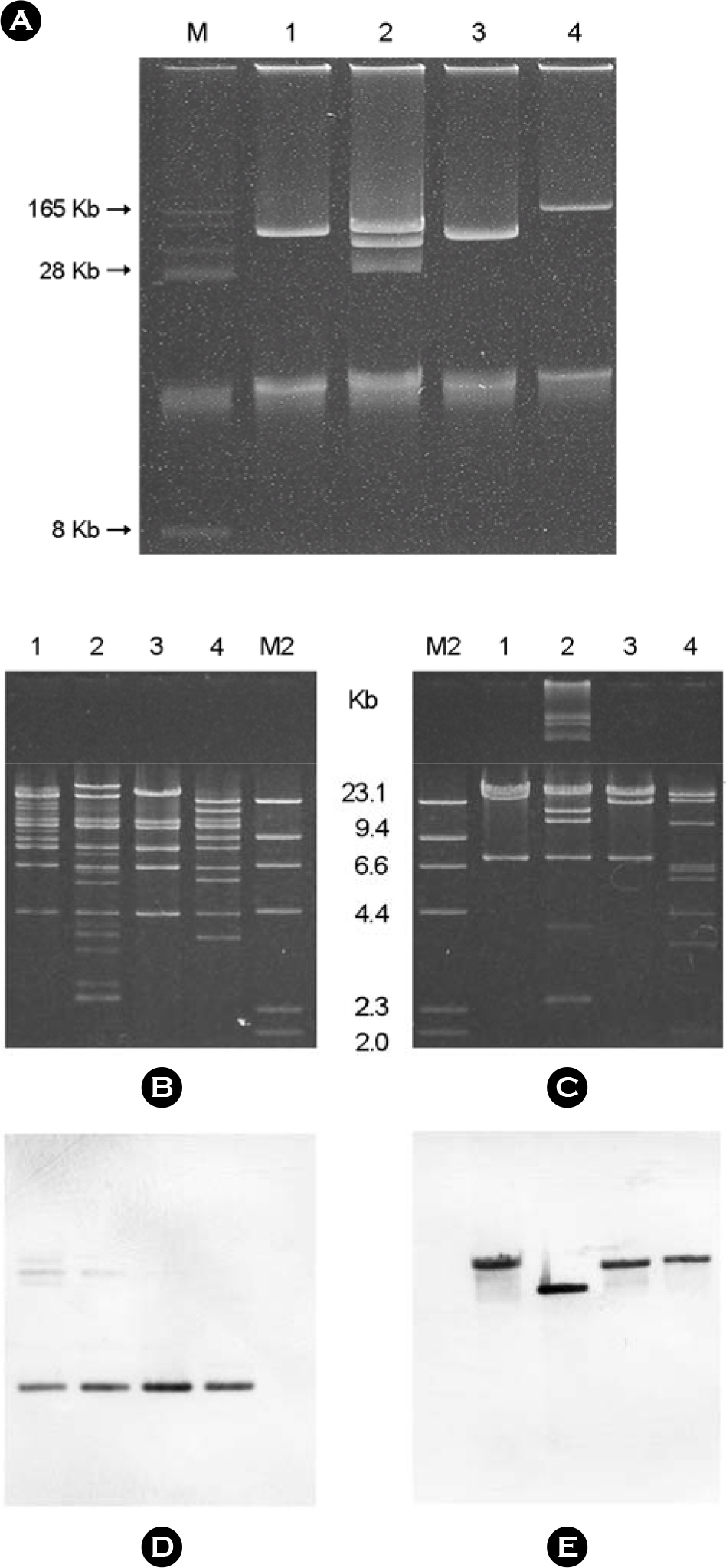
- Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance (PMQR) genes: qnr, aac(6')-Ib-cr, and qepA were investigated among 153 armA and 51 rmtB-positive transconjugants and their 204 clinical isolates of Enterobacteriaceae. Overall, qnrB4 and aac(6')-Ib-cr genes were identified in 52.3% (63 K. pneumoniae, 10 E. coli, 4 E. cloacae, and 3 E. aerogenes) and 24.8% (16 K. pneumoniae, 8 E. coli, 6 S. marcescens, 4 E. cloacae, 3 C. freundii and 1 K. oxytoca) of 153 armA-positive isolates, respectively. Four isolates of K. pneumoniae and two isolates of E. coli positive for armA co-harbored both qnrB4 and aac(6')-Ib-cr. The qepA gene was detected in 11.8% (5 E. coli and 1 K. pneumoniae) of 51 rmtB-positive clinical isolates and their transconjugants. Southern hybridization confirmed the co-localization of qepA and rmtB on a large conjugative plasmid of size between 90 to 170 kb. Inc replicon typing showed that qnrB4/6, aac(6')-Ib-cr, and qepA genes were principally disseminated by IncFIIAs, IncL/M, and IncF plasmids, respectively. This study constitutes the first report of the three known PMQR genes among the 16S rRNA methylase producing Enterobacteriaceae isolates of human origin from Korea.
Keyword
- qnr; aac(6')-Ib-cr; qepA; armA; rmtB; Resistance
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Mutations in gyrA and parC Genes and Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance in Non-typhoid Salmonella Isolated from Pediatric Patients with Diarrhea in Seoul
Young-hee Jin, Ji-hun Jung, Su-jin Jeon, Jae-kyoo Lee, Young-hee Oh, Sung-min Choi, Young-zoo Chae
J Bacteriol Virol. 2012;42(3):203-210. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2012.42.3.203.
Reference
-
1). Ruiz J. Mechanisms of resistance to quinolones: target alterations, decreased accumulation and DNA gyrase protection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003. 51:1109–17.
Article2). Martinez-Martinez L., Pascual A., Jacoby GA. Quinolone resistance from a transferable plasmid. Lancet. 1998. 351:797–9.3). Tran JH., Jacoby GA. Mechanism of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002. 99:5638–42.
Article4). Jacoby GA., Walsh KE., Mills DM., Walker VJ., Oh H., Robicsek A., Hooper DC. qnrB, another plasmid-mediated gene for quinolone resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. 50:1178–82.5). Hata M., Suzuki M., Matsumoto M., Takahashi M., Sato K., Ibe S., Sakae K. Cloning of a novel gene for quinolone resistance from a transferable plasmid in Shigella flexneri 2b. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. 49:801–3.6). Nordmann P., Poirel L. Emergence of plasmid-mediated resistance to quinolones in Enterobacteriaceae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005. 56:463–9.7). Wang M., Guo Q., Xu X., Wang X., Ye X., Wu S., Hooper DC., Wang M. New plasmid-mediated quinolone resistant gene, qnrC, found in a clinical isolate of Proteus mirabilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. 53:1892–7.8). Jacoby G., Cattoir V., Hooper D., Martínez-Martínez L., Nordmann P., Pascual A., Poirel L., Wang M. qnr Gene nomenclature. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. 52:2297–9.9). Robicsek A., Strahilevitz J., Jacoby GA., Macielag M., Abbanat D., Park CH., Bush K., Hooper DC. Fluoroquinolone-modifying enzyme: a new adaptation of a common aminoglycoside acetyltransferase. Nat Med. 2006. 12:83–8.
Article10). Ambrozic Avgustin J., Keber R., Zerjavic K., Orazem T., Grabnar M. Emergence of the quinolone resistance-mediating gene aac(6′)-Ib-cr in extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella isolates collected in Slovenia between 2000 and 2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. 51:4171–3.11). Park CH., Robicsek A., Jacoby GA., Sahm D., Hooper DC. Prevalence in the United States of aac(6′)-Ib-cr encoding a ciprofloxacin-modifying enzyme. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. 50:3953–5.12). Wang M., Tran JH., Jacoby GA., Zhang Y., Wang F., Hooper DC. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli from Shanghai, China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. 47:2242–8.13). Yamane K., Wachino J., Suzuki S., Kimura K., Shibata N., Kato H., Shibayama K., Konda T., Arakawa Y. New plasmid-mediated fluoroquinolone efflux pump, QepA, found in an Escherichia coli clinical isolate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. 51:3354–60.14). Perichon B., Courvalin P., Galimand M. Transferable resistance to aminoglycosides by methylation of G1405 in 16S rRNA and to hydrophilic fluoroquinolones by QepA-mediated efflux in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. 51:2464–9.15). Cattoir V., Poirel L., Nordmann P. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance pump QepA2 in an Escherichia coli isolate from France. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. 52:3801–4.16). Doi Y., Yokoyama K., Yamane K., Wachino J., Shibata N., Yagi T., Shibayama K., Kato H., Arakawa Y. Plasmid-mediated 16S rRNA methylase in Serratia marcescens conferring high-level resistance to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. 48:491–6.17). Galimand M., Courvalin P., Lambert T. Plasmid-mediated high-level resistance to aminoglycosides in Entero-bacteriaceae due to 16S rRNA methylation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. 47:2565–71.18). Wachino J., Yamane K., Shibayama K., Kurokawa H., Shibata N., Suzuki S., Doi Y., Kimura K., Ike Y., Arakawa Y. Novel plasmid-mediated 16S rRNA methylase, RmtC, found in a Proteus mirabilis isolate demonstrating extraordinary high-level resistance against various aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. 50:178–84.19). Doi Y., de Oliveira Garcia D., Adams J., Paterson DL. Coproduction of novel 16S rRNA methylase RmtD and metallo-beta-lactamase SPM-1 in a panresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate from Brazil. Anti-microb Agents Chemother. 2007. 51:852–6.20). Kang HY., Kim KY., Kim J., Lee JC., Lee YC., Cho DT., Seol SY. Distribution of conjugative-plasmid-mediated 16S rRNA methylase genes among amikacin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates collected in 1995 to 1998 and 2001 to 2006 at a university hospital in South Korea and identification of conjugative plasmids mediating dissemination of 16S rRNA methylase. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. 46:700–6.21). Robicsek A., Strahilevitz J., Sahm DF., Jacoby GA., Hooper DC. qnr prevalence in ceftazidime-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates from the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. 50:2872–4.22). Tamang MD., Seol SY., Oh JY., Kang HY., Lee JC., Lee YC., Cho DT., Kim J. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants qnrA, qnrB, and qnrS among clinical isolates of Enterobacteriaceae in a Korean hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. 52:4159–62.23). Shi WF., Jiang JP., Mi ZH. Relationship between antimicrobial resistance and aminoglycoside-modifying enzyme gene expressions in Acinetobacter baumannii. Chin Med J. 2005. 118:141–5.24). Carattoli A., Bertini A., Villa L., Falbo V., Hopkins KL., Threlfall EJ. Identification of plasmids by PCR-based replicon typing. J Microbiol Methods. 2005. 63:219–28.
Article25). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 16th Informational Supplement. M100-S16. Wayne PA: CLSI. 2006.26). Sambrook J., Russell DW. Preparation of plasmid DNA by alkaline lysis with SDS: minipreparation. In Molecular Cloning: A laboratory manual. 3rd ed.New York: Cold spring Harbour Laboratory Press;2001. p. 1–32.27). Ma J., Zeng Z., Chen Z., Xu X., Wang X., Deng Y., Lü D., Huang L., Zhang Y., Liu J., Wang M. High prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants qnr, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, and qepA among ceftiofur-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates from companion and food-producing animals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. 53:519–24.28). Yamane K., Wachino J., Suzuki S., Arakawa Y. Plasmid-mediated qepA gene among Escherichia coli clinical isolates from Japan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. 52:1564–6.29). Liu JH., Deng YT., Zeng ZL., Gao JH., Chen L., Arakawa Y., Chen ZL. Coprevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants QepA, Qnr, and AAC(6′)-Ib-cr among 16S rRNA methylase RmtB-producing Escherichia coli isolates from pigs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. 52:2992–3.30). Kim HB., Park CH., Kim CJ., Kim EC., Jacoby GA., Hooper DC. Prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants over a 9-year period. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. 53:639–45.
Article31). Park YJ., Yu JK., Kim SI., Lee K., Arakawa Y. Accumulation of plasmid-mediated fluoroquinolone resistance genes, qepA and qnrS1, in Enterobacter aerogenes co-producing RmtB and class A β-lactamase LAP-1. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2009. 39:55–9.32). Cavaco LM., Hasman H., Xia S., Aarestrup FM. QnrD, a novel gene conferring transferable quinolone resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky and Bovismorbificans of human origin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. 53:603–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Characteristics of aac(6')-Ib-cr Gene in Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Chungnam Area
- Prevalence and Characterization of Plasmid-Medicated Quinolone Resistance Genes among Clinical Isolates of Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporin Resistant Enterobacter cloacae
- Molecular and Phenotypic Characteristics of 16S rRNA Methylase-producing Gram-negative Bacilli
- Coproduction of qnrB and armA from Extended-Spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Erratum: Emergence of NDM-1–producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa Sequence Type 773 Clone: Shift of Carbapenemase Molecular Epidemiology and Spread of 16S rRNA Methylase Genes in Korea