Ann Lab Med.
2013 Sep;33(5):379-382. 10.3343/alm.2013.33.5.379.
16S Ribosomal RNA Identification of Prevotella nigrescens from a Case of Cellulitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. leehejo@khmc.or.kr
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Biomedical Science, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781348
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2013.33.5.379
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Acupuncture Therapy
Ampicillin/pharmacology/therapeutic use
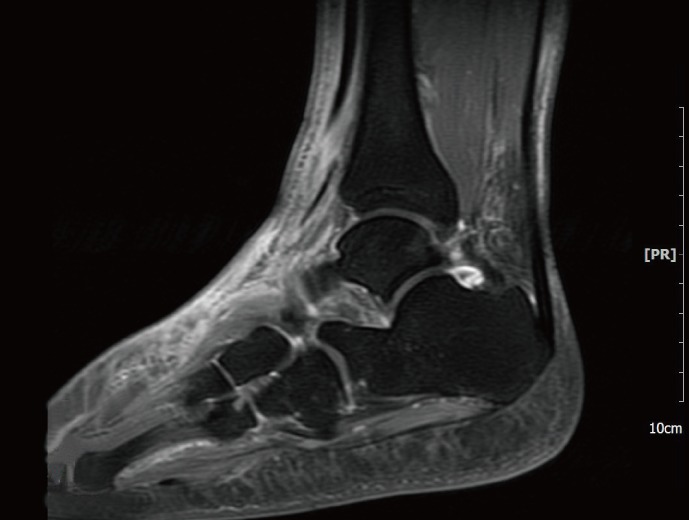
Ankle/ultrasonography
Anti-Bacterial Agents/pharmacology/therapeutic use
Cellulitis/complications/diagnosis/drug therapy/*microbiology
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/complications
Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections/complications/diagnosis/drug therapy/*microbiology
Humans
Hypertension/complications
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Middle Aged
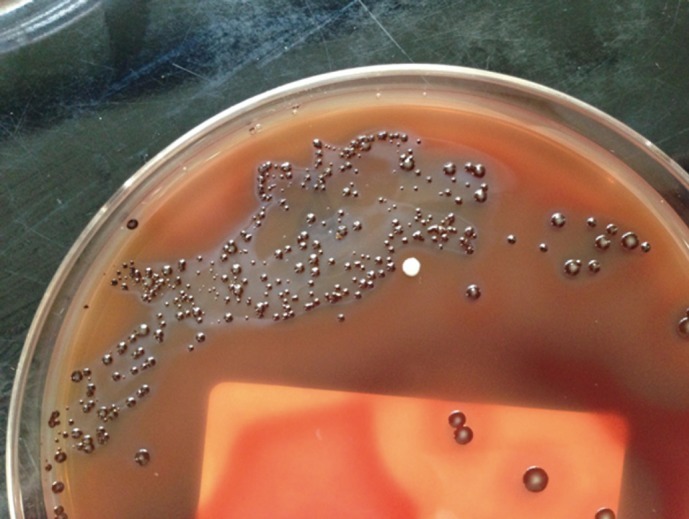
Prevotella nigrescens/drug effects/*genetics/isolation & purification
RNA, Ribosomal, 16S/*analysis
Sulbactam/pharmacology/therapeutic use
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Ampicillin
Anti-Bacterial Agents
RNA, Ribosomal, 16S
Sulbactam
Figure
Reference
-
1. Finegold SM, Strong CA, McTeague M, Marina M. The importance of black-pigmented gram-negative anaerobes in human infections. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1993; 6:77–82. PMID: 8518764.
Article2. Jousimies-Somer H, Savolainen S, Mäkitie A, Ylikoski J. Bacteriologic findings in peritonsillar abscesses in young adults. Clin Infect Dis. 1993; 16(Suppl 4):S292–S298. PMID: 8324134.
Article3. Mättö J, Asikainen S, Väisänen ML, Rautio M, Saarela M, Summanen P, et al. Role of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, and Prevotella nigrescens in extraoral and some odontogenic infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1997; 25(Suppl 2):S194–S198. PMID: 9310676.4. Frandsen EV, Poulsen K, Kilian M. Confirmation of the species Prevotella intermedia and Prevotella nigrescens. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1995; 45:429–435. PMID: 8590668.5. Gharbia SE, Haapasalo M, Shah HN, Kotiranta A, Lounatmaa K, Pearce MA, et al. Characterization of Prevotella intermedia and Prevotella nigrescens isolates from periodontic and endodontic infections. J Periodontol. 1994; 65:56–61. PMID: 7907659.6. Mättö J, Saarela M, von Troil-Lindén B, Alaluusua S, Jousimies-Somer H, Asikainen S. Similarity of salivary and subgingival Prevotella intermedia and Prevotella nigrescens isolates by arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1996; 11:395–401. PMID: 9467372.7. Shah HN, Gharbia SE. Biochemical and chemical studies on strains designated Prevotella intermedia and proposal of a new pigmented species, Prevotella nigrescens sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992; 42:542–546. PMID: 1390107.8. Brook I. Microbiology of polymicrobial abscesses and implications for therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002; 50:805–810. PMID: 12460997.
Article9. Kim SS, Ha GI. Mediastinitis caused by Prevotella intermedia/nigrescens occurred after acupuncture: a case report. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000; 33:440–444.10. Lee Y, Park Y, Kim MS, Yong D, Jeong SH, Lee K, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns for recent clinical isolates of anaerobic bacteria in South Korea. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010; 54:3993–3997. PMID: 20585132.
Article11. Stubbs S, Park SF, Bishop PA, Lewis MA. Direct detection of Prevotella intermedia and P. nigrescens in suppurative oral infection by amplification of 16S rRNA gene. J Med Microbiol. 1999; 48:1017–1022. PMID: 10535646.12. Könönen E, Wade WG, Citron DM. Bacteroides, Porphyromonas, Prevotella, Fusobacterium, and other anaerobic gram-negative rods. Versalovic J. Manual of clinical microbiology. 10th ed. Washington: ASM Press;2011. p. 858–880.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Frequency of Detecting Prevotella intermedia and Prevotella nigrescens in Korean Adult Periodontitis Patients
- Interleukin-8 production and interleukin-8 mRNA expression induced by lipopolysaccharides from Prevotella intermedia and Prevotella nigrescens in monocyte-derived macrophages
- Identification of putative pathogens in acute endodontic infections by PCR based on 16S rDNA
- Laboratory Identification of Leptotrichia Species Isolated From Bacteremia Patients at a Single Institution
- Acute Cellulitis Caused by Neisseria skkuensis