Ann Lab Med.
2017 May;37(3):272-276. 10.3343/alm.2017.37.3.272.
Laboratory Identification of Leptotrichia Species Isolated From Bacteremia Patients at a Single Institution
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pmhhj77@gmail.com micro.lee@samsung.com
- 2SD Genomics Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2369754
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2017.37.3.272
Abstract
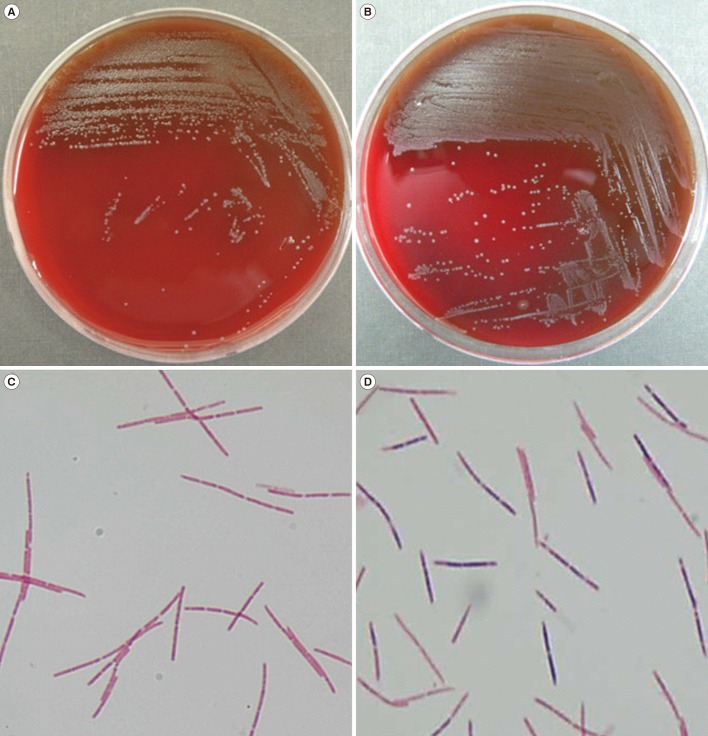
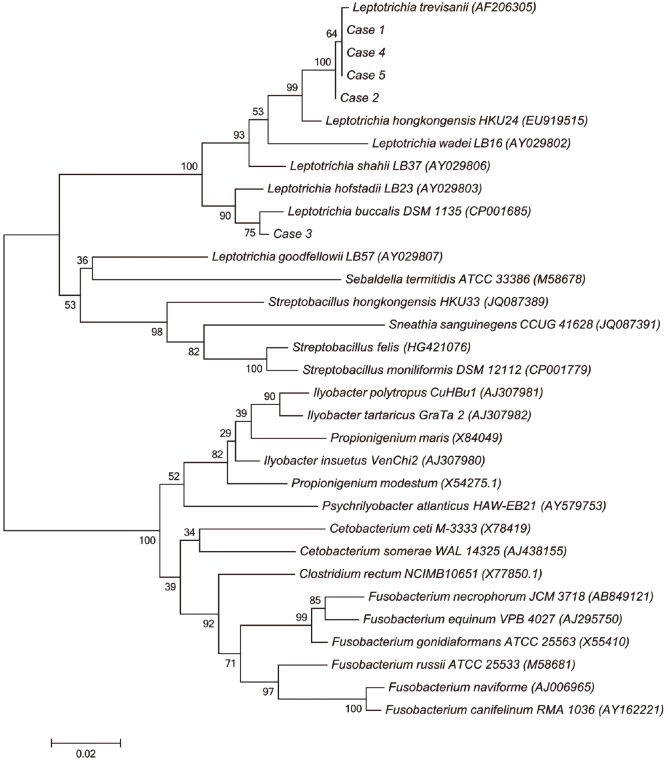
- We describe the laboratory identification of Leptotrichia species from clinical isolates collected over a six-year period. Five isolates from blood cultures were identified as Leptotrichia species. Gram stain showed large, fusiform, gram-negative or -variable bacilli. Identification based on biochemical testing was unsuccessful; however, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry proved to be a useful tool for identifying Leptotrichia species to the genus level. Species level identification was successfully achieved by using 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Eribe ER, Olsen I. Leptotrichia species in human infections. Anaerobe. 2008; 14:131–137. PMID: 18539056.2. Ulstrup AK, Hartzen SH. Leptotrichia buccalis: a rare cause of bacteraemia in non-neutropenic patients. Scand J Infect Dis. 2006; 38:712–716. PMID: 16857623.3. Colombo AP, Haffajee AD, Dewhirst FE, Paster BJ, Smith CM, Cugini MA, et al. Clinical and microbiological features of refractory periodontitis subjects. J Clin Periodontol. 1998; 25:169–180. PMID: 9495617.4. Caram LB, Linefsky JP, Read KM, Murdoch DR, Lalani T, Woods CW, et al. Leptotrichia endocarditis: report of two cases from the International Collaboration on Endocarditis (ICE) database and review of previous cases. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008; 27:139–143. PMID: 17960435.5. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Interpretive criteria for identification of bacteria and fungi by DNA target sequencing: Approved Guideline. CLSI document MM18-A. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2008.6. Park KS, Ki CS, Kang CI, Kim YJ, Chung DR, Peck KR, et al. Evaluation of the GenBank, EzTaxon, and BIBI services for molecular identification of clinical blood culture isolates that were unidentifiable or misidentified by conventional methods. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:1792–1795. PMID: 22403421.7. Woo PC, Wong SS, Teng JL, Leung KW, Ngan AH, Zhao DQ, et al. Leptotrichia hongkongensis sp. nov., a novel Leptotrichia species with the oral cavity as its natural reservoir. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010; 11:391–401. PMID: 20506569.8. Couturier MR, Slechta ES, Goulston C, Fisher MA, Hanson KE. Leptotrichia bacteremia in patients receiving high-dose chemotherapy. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:1228–1232. PMID: 22205794.9. Beveridge TJ. Mechanism of gram variability in select bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990; 172:1609–1620. PMID: 1689718.10. Blairon L, De Gheldre Y, Delaere B, Sonet A, Bosly A, Glupczynski Y. A 62-month retrospective epidemiological survey of anaerobic bacteraemia in a university hospital. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006; 12:527–532. PMID: 16700700.11. Kumagai J, Takiguchi Y, Shono K, Suruga Y, Akiba Y, Yamamoto K, et al. Acute myelogenous leukemia with Leptotrichia trevisanii bacteremia. Intern Med. 2013; 52:2573–2576. PMID: 24240799.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bacteremia Caused by Eggerthella lenta in an Elderly Patient with an Intra-abdominal Abscess
- Catheter-related Bacteremia due to Microbacterium oxydans Identified by 16S rRNA Sequencing Analysis and Biochemical Characteristics
- Speicies Identification and Antimicrobial Resistance of Coagulase-negative Staphylococcal Bacteremia
- Identification of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi Isolated from Blood Culture
- A Case of Bacteremia Due to Microbacterium oleivorans Identified by 16S rRNA Sequencing Analysis