Ann Lab Med.
2013 Mar;33(2):121-124. 10.3343/alm.2013.33.2.121.
Comparison of 3 Automated Immunoassays for Detection of Anti-Hepatitis A Virus Immunoglobulin M in a Tertiary Care Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. eysong1@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 1781311
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2013.33.2.121
Abstract
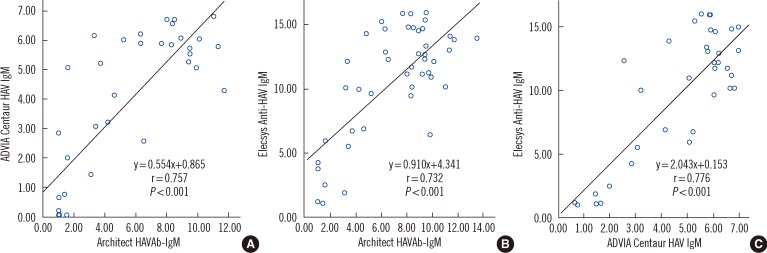
- Three automated immunoassay kits for anti-Hepatitis A Virus (HAV) IgM-Architect, (Abbott Laboratories, USA), Elecsys (Roche Diagnostics, Germany), and ADVIA Centaur (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc., USA)-were compared. We included 178 consecutive samples, for which an anti-HAV IgM test was requested at Seoul National University Hospital from September 2009 to January 2010. Reviewing of medical records, reverse transcription (RT)-PCR for HAV RNA, or total anti-HAV assay were performed on 16 (9.0%) samples with discrepant results. The percent agreements (kappas) of the Architect and ADVIA Centaur, Architect and Elecsys, and ADVIA Centaur and Elecsys kits were 96.6% (0.91), 96.6% (0.92), and 97.8% (0.94), respectively. Eight out of 16 discrepant samples showed gray-zone values in Architect but were nonreactive in the others. Slightly earlier seroconversion was suspected in Elecsys. The 3 assays showed comparable performances with excellent agreements in a tertiary care hospital setting.
MeSH Terms
-
Hepatitis A virus/genetics/*immunology
Hepatitis B/*diagnosis
Hospitals, University
Humans
Immunoassay/*methods
Immunoglobulin M/*analysis
RNA, Viral/analysis
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Retrospective Studies
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
Tertiary Healthcare
Immunoglobulin M
RNA, Viral
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dufour DR, Talastas M, Fernandez MD, Hwang JH, Kim JW, Kim NY, et al. Chemiluminescence assay improves specificity of hepatitis C antibody detection. Clin Chem. 2003; 49:940–944. PMID: 12765991.
Article2. Hess G, Faatz E, Melchior W, Bayer H. Analysis of immunoassays to detect antibodies to hepatitis A virus (anti-HAV) and anti-HAV immunoglobulin M. J Virol Methods. 1995; 51:221–228. PMID: 7738142.
Article3. Wiedmann M, Boehm S, Schumacher W, Swysen C, Zauke M. Evaluation of three commercial assays for the detection of hepatitis a virus. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2003; 22:129–130. PMID: 12627291.
Article4. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Assessment of laboratory tests when proficiency testing is not available; Approved guideline. CLSI document, GP29-A. 2008. 2nd ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.5. Mylonakis E, Paliou M, Lally M, Flanigan TP, Rich JD. Laboratory testing for infection with the human immunodeficiency virus: established and novel approaches. Am J Med. 2000; 109:568–576. PMID: 11063959.
Article6. Cavalier E, Carlisi A, Chapelle JP, Delanaye P. False positive PTH results: an easy strategy to test and detect analytical interferences in routine practice. Clin Chim Acta. 2008; 387:150–152. PMID: 17904113.
Article7. Kellar KL, Kalwar RR, Dubois KA, Crouse D, Chafin WD, Kane BE. Multiplexed fluorescent bead-based immunoassays for quantitation of human cytokines in serum and culture supernatants. Cytometry. 2001; 45:27–36. PMID: 11598944.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Two Automated Immunoassays for the Detection of Anti-Hepatitis A Virus Total Immunoglobulin and IgM
- Comparison of 3 Automated Immunoassays for Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
- Comparison of Three Assay Systems for Qualitative and Quantitative Results of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
- The Comparison between Serologic Tests and Magicplex HepaTrio Real-time PCR in the Diagnosis of Viral Hepatitis
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination