Korean J Lab Med.
2006 Dec;26(6):431-435. 10.3343/kjlm.2006.26.6.431.
Comparison of Three Assay Systems for Qualitative and Quantitative Results of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bmshin@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 1889822
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2006.26.6.431
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: With a technical improvement of the assay system, automated immunoassay analyzers for hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs) are widely used. However, some discrepancies
between assays are still being reported. We compared the qualitative and quantitative results of three kinds of anti-HBs assays.
METHODS
Serum samples were collected from 517 patients and anti-HBs were determined using AxSYM AUSAB, Bayer ADVIA Centaur, and Roche Elecsys assay systems.
RESULTS
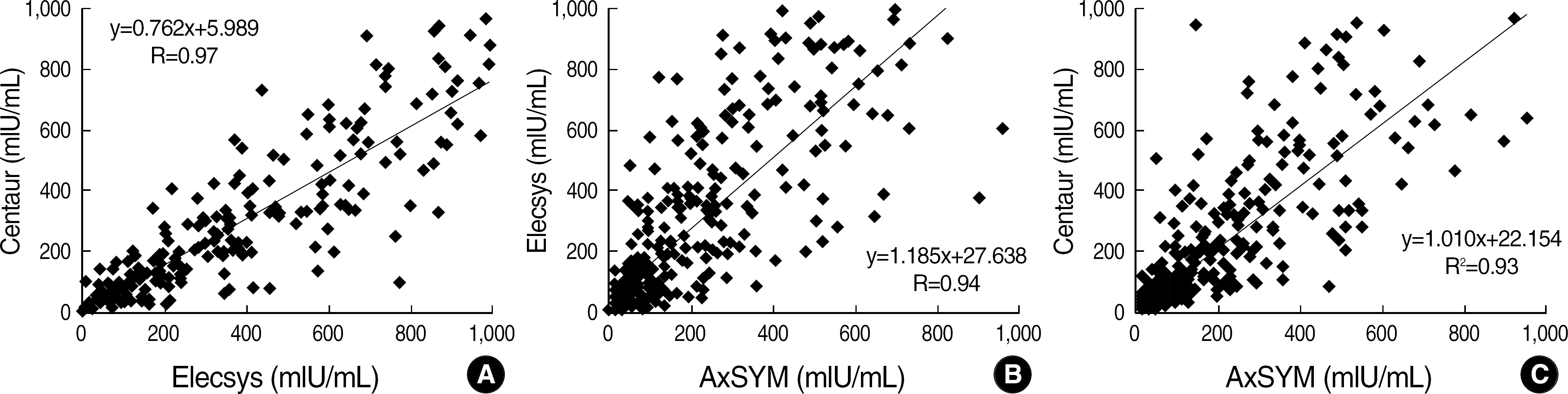
The concordance rates between the three assays were 95.1% (543/571). The concordance rates were 97.7% between Centaur and Elecsys, 96.3% between AxSYM and Centaur, and 95.6% between AxSYM and Elecsys. Their correlation coefficients for quantitative results were 0.97, 0.94, and 0.93 in the same order. Twenty-eight specimens showed discrepant results, and all of them had antibody values below 31.5 mIU/mL.
CONCLUSIONS
Three immunoassays for anti-HBs presented a high concordance and correlation; however, the results should be interpreted with caution, because there were still significant differences between assay methods, especially for a low-level of anti-HBs.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cha YJ, Kwon SY, Kum DG, Kim SW, Kim TY, Kim JR, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in immunoserology in Korea (2003). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2004; 26:47–69.2. Davidson M, Krugman S. Recombinant yeast hepatitis B vaccine compared with plasma-derived vaccine: immunogenicity and effect of a booster dose. J Infect. 1986; 13:S31–8.
Article3. Player VA, White D. Comparison of an ELISA system for the quantification of hepatitis B antibody with an automated and a semiautomated system. J Virol Methods. 1993; 45:67–72.
Article4. Whang DH, Shin BM. Comparison of four-assay system for the quantification of hepatitis B surface antibody. Korean J Lab Med. 2002; 22:424–30.5. Heijtink RA, Schneeberger PM, Postma B, Crombach W. Anti-HBs levels after hepatitis B immunisation depend on test reagents: routinely determined 10 and 100 IU/l seroprotection levels unreliable. Vaccine. 2002; 20:2899–905.
Article6. McCartney RA, Harbour J, Roome AP, Caul EO. Comparison of enhanced chemiluminescence and microparticle enzyme immunoassay for the measurement of hepatitis B surface antibody. Vaccine. 1993; 11:941–5.
Article7. Whang DH, Um TH. Comparison of immunochromatography assays and quantitative immunoassays for detecting HBsAg and anti-HBs. Korean J Lab Med. 2005; 25:186–91.8. Oh JH, Kim TY, Yoon HJ, Min HS, Lee HR, Choi TY. Evaluation of Genedia HBsAg Rapid Genedia Anti-HBs Rapid for the screening of HBsAg and Anti-HBs. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1999; 19:114–7.9. Taylor P, Pickard G, Gammie A, Atkins M. Comparison of the AD-VIA Centaur and Abbott AxSYM immunoassay systems for a routine diagnostic virology laboratory. J Clin Virol. 2004; 30:S11–5.
Article10. Ostrow DH, Edwards B, Kimes D, Macioszek J, Irace H, Nelson L, et al. Quantitation of hepatitis B surface antibody by an automated microparticle enzyme immunoassay. J Virol Methods. 1991; 32:265–76.
Article11. Doche C, Thome M, Dimet I, Bienvenu J. Evaluation of the fully automated Cobas Core enzyme immunoassay for the quantitation of antibodies against hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1996; 34:365–8.12. Chen Y, Wu W, Li LJ, Lou B, Zhang J, Fan J. Comparison of the results for three automated immunoassay systems in determining serum HBV markers. Clin Chim Acta. 2006; 372:129–33.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Four-Assay Systems for the Quantification of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
- Comparison of 3 Automated Immunoassays for Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
- Performance Evaluation of 3 Kinds of HBsAg Qualitative Assays and 2 Kinds of Quantitative Assays
- Prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen(HBsAg), anti-hepatitis C virus(HCV) antibody-treponemal antibody and anti-HIV-1 antibody in donor's bloods
- Comparison of COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan HCV Qualitative Test v2.0 with COBAS AMPLICOR Hepatitis C Virus Test v2.0 for the Qualitative Detection of Hepatitis C Virus RNA in Korean Clinical Samples