Korean J Lab Med.
2006 Aug;26(4):282-286. 10.3343/kjlm.2006.28.4.282.
Comparison of 3 Automated Immunoassays for Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bmshin@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 2238836
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2006.28.4.282
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is one of the most important serological markers used to diagnose hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Automated immunoassays have been developed, meeting the current clinical requirement of HBsAg assays over the years. This study was performed to determine the degree of agreements between 3 kinds of HBsAg assay systems.
METHODS
Serum samples from 425 patients were assayed by the HBsAg assay systems of Elecsys (Roche Diagnostics, Germany), ADVIA Centaur (Bayer Diagnostics, USA), and AxSYM (Abbott Laboratories, USA).
RESULTS
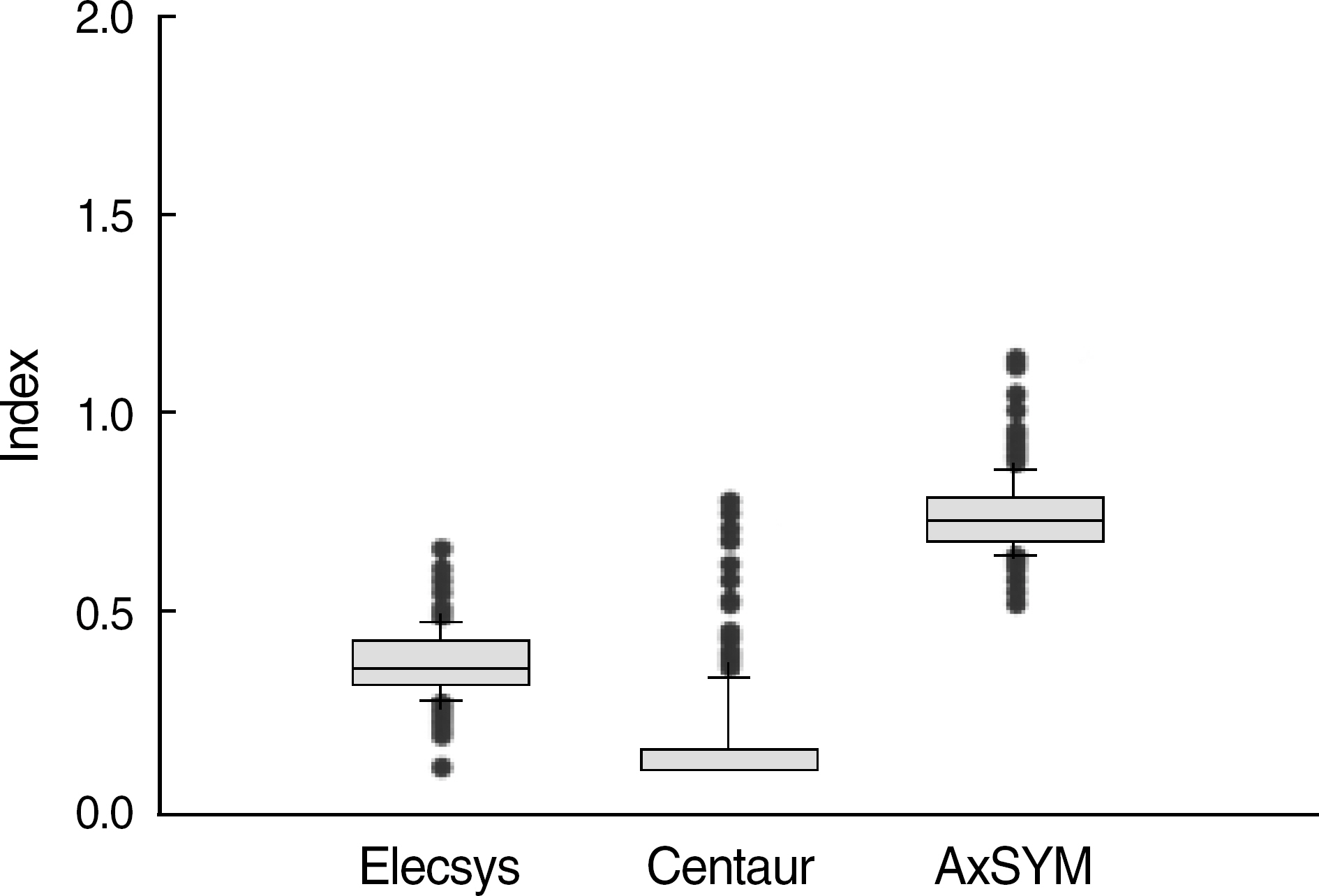
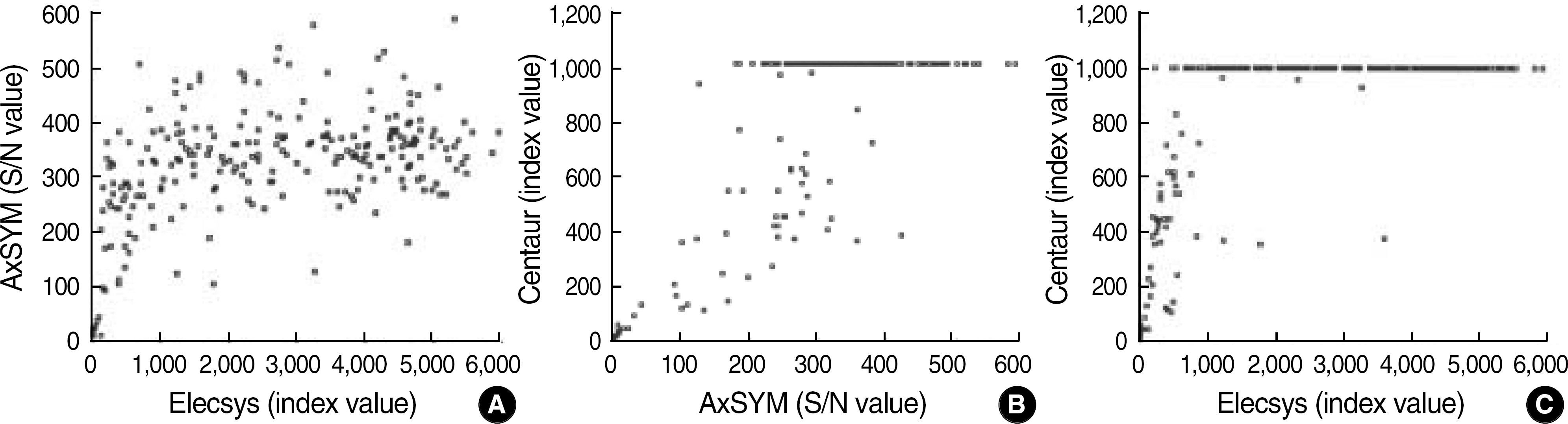
The concordance rates among the 3 assays were 100%. A total of 249 (58.6%) specimens were positive, and their index values showed a weak correlation between the 3 assays; nevertheless, positive specimens with low levels (<10) of index values in one system also presented low values in other systems, and all of them were confirmed by neutralization assays.
CONCLUSIONS
The 3 automated HBsAg assay systems presented a high level of concordance.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Performance Evaluation of 3 Kinds of HBsAg Qualitative Assays and 2 Kinds of Quantitative Assays
Jae-Sun Park, Jung-In Choi, Ji-Hun Lim, Joseph Jung, Seon-Ho Lee, Neung Hwa Park, Jung Woo Shin, Yang Won Nah, Chang Woo Nam, Young Joo Cha, Sung-Ryul Kim
Lab Med Online. 2013;3(3):160-168. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2013.3.3.160.Comparison Study with Enzyme Immunoassay and Chemiluminescence Immunoassay for Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Detection
Hee Jin Huh, Seok-Lae Chae, Young Joo Cha
Korean J Lab Med. 2007;27(5):355-359. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2007.27.5.355.
Reference
-
References
1. Song SM, Oh WI, Kim DW. Evaluation of serologic marker tests for hepatitis B viral infection using the automated immunoassay system ARCHITECT i2000. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2002; 22:42–6.2. Gitlin N. Hepatitis B: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Clin Chem. 1997; 43:1500–6.
Article3. Stevens CE, Taylor PE, Tong MJ, Toy PT, Vyas GN, Nair PV, et al. Yeast-recombinant hepatitis B vaccine. Efficacy with hepatitis B immune globulin in prevention of perinatal hepatitis B virus transmission. JAMA. 1987; 257:2612–6.
Article4. Moerman B, Moons V, Sommer H, Schmitt Y, Stetter M. Evaluation of sensitivity for wild type and mutant forms of hepatitis B surface antigen by four commercial HBsAg assays. Clin Lab. 2004; 50:159–62.5. Taylor P, Pickard G, Gammie A, Atkins M. Comparison of the ADVIA Centaur and Abbott AxSYM immunoassay systems for a routine diagnostic virology laboratory. J Clin Virol. 2004; 30:S11–5.
Article6. Chen D, Kaplan L, Liu Q. Evaluation of two chemiluminescent immunoassays of ADVIA Centaur for hepatitis B serology markers. Clin Chim Acta. 2005; 355:41–5.
Article7. Weber B, Dengler T, Berger A, Doerr HW, Rabenau H. Evaluation of two new automated assays for hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) detection: IMMULITE HBsAg and IMMULITE 2000 HBsAg. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:135–43.
Article8. Bonino F, Hoyer B, Nelson J, Engle R, Verme G, Gerin J. Hepatitis B virus DNA in the sera of HBsAg carriers: a marker of active hepatitis B virus replication in the liver. Hepatology. 1981; 1:386–91.
Article9. van Helden J, Denoyel GA. Experience with the IVDD performance evaluations of the ADVIA Centaur infectious disease assays. J Clin Virol. 2004; 30:S16–8.
Article10. Song BC, Kim SH, Kim H, Ying YH, Kim HJ, Kim YJ, et al. Prevalence of naturally occurring surface antigen variants of hepatitis B virus in Korean patients infected chronically. J Med Virol. 2005; 76:194–202.
Article11. Park JW, Yoon JH, Hwang YJ, Lee HS, Kim CY. Mutations at the gene encoding the ‘a’ determinant of HBsAg in chronic hepatitis B patients with concurrent HBsAg and anti-HBs positivity. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1997; 29:182–91.12. Cha YJ. Detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen mutants. Korean J Lab Med. 2005; 25:442–7.13. Kuhns MC, Kleinman SH, McNamara AL, Rawal B, Glynn S, Busch MP. Lack of correlation between HBsAg and HBV DNA levels in blood donors who test positive for HBsAg and anti-HBc: implications for future HBV screening policy. Transfusion. 2004; 44:1332–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen in pediatric in patients
- The Eligibility Study of Anesthesia and Surgery for HBs Antigen Positive Patients
- Establishment of a Korean Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Low Titer Performance Panel for Performance Validation of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Immunoassays
- Growing attention to an old marker, hepatitis B surface antigen, in the natural history of chronic hepatitis B
- The prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen among Korean by literature review