Korean J Radiol.
2014 Aug;15(4):411-422. 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.4.411.
Trastuzumab-Conjugated Liposome-Coated Fluorescent Magnetic Nanoparticles to Target Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam 463-707, Korea. kimsmlms@daum.net
- 2Nanoimaging and Therapy Research Center, Institute of Nanoconvergence, Advanced Institutes of Convergence Technology, Seoul National University, Suwon 443-270, Korea.
- 3NanoBio Materials Chemistry Lab., Department of Applied Bioscience, CHA University, Pocheon 487-010, Korea.
- 4Program in Nano Science and Technology, Department of Transdisciplinary Studies, Seoul National University Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Suwon 443-270, Korea.
- KMID: 1731043
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.4.411
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To synthesize mesoporous silica-core-shell magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) encapsulated by liposomes (Lipo [MNP@m-SiO2]) in order to enhance their stability, allow them to be used in any buffer solution, and to produce trastuzumab-conjugated (Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2]-Her2Ab) nanoparticles to be utilized in vitro for the targeting of breast cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
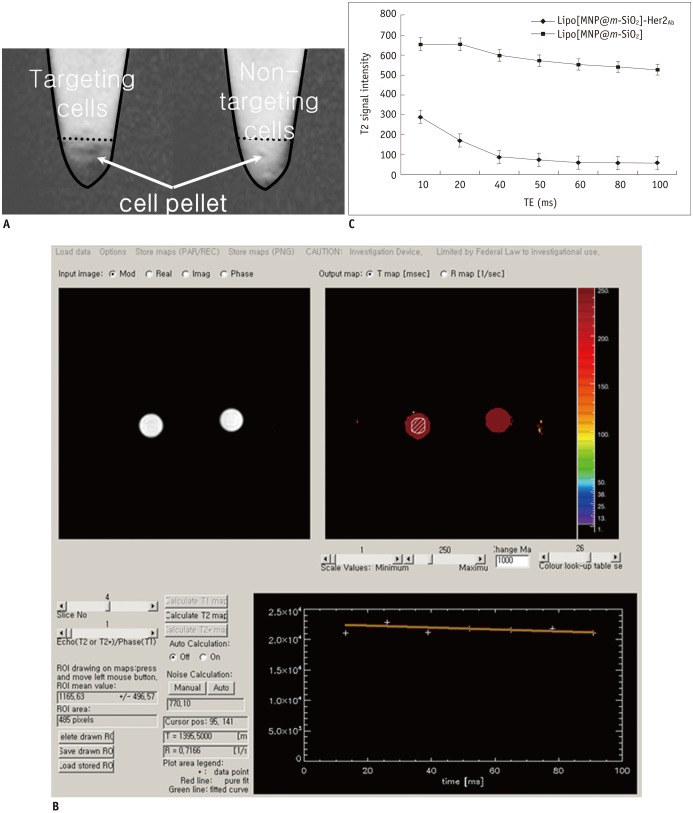
The physiochemical characteristics of Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] were assessed in terms of size, morphological features, and in vitro safety. The multimodal imaging properties of the organic dye incorporated into Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] were assessed with both in vitro fluorescence and MR imaging. The specific targeting ability of trastuzumab (Her2/neu antibody, Herceptin(R))-conjugated Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] for Her2/neu-positive breast cancer cells was also evaluated with fluorescence and MR imaging.
RESULTS
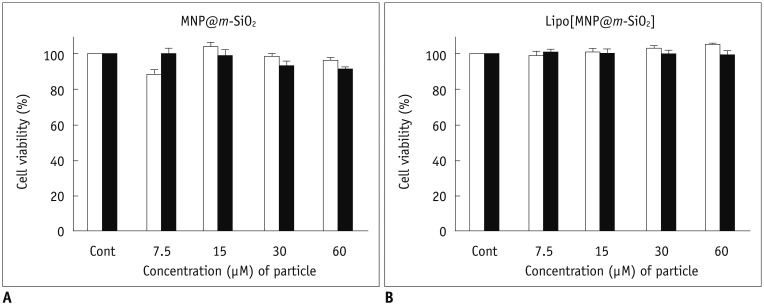
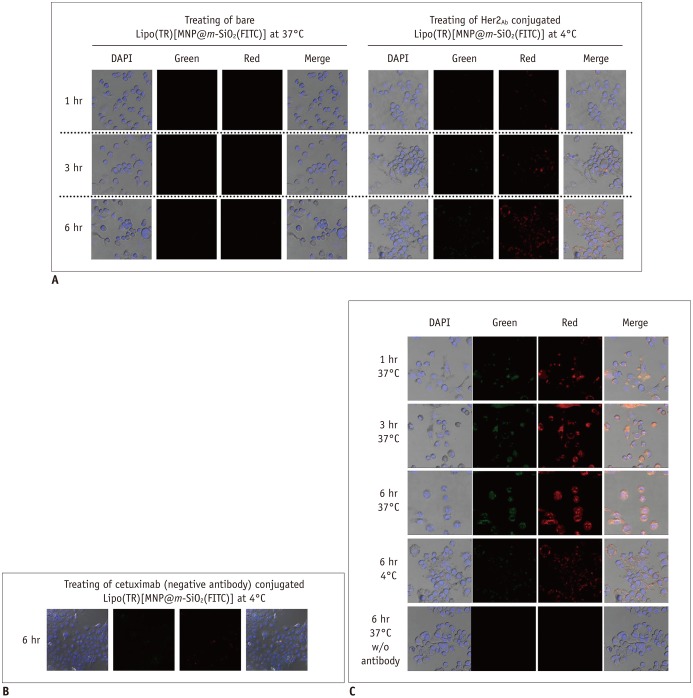
We obtained uniformly-sized and evenly distributed Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] that demonstrated biological stability, while not disrupting cell viability. Her2/neu-positive breast cancer cell targeting by trastuzumab-conjugated Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] was observed by in vitro fluorescence and MR imaging.
CONCLUSION
Trastuzumab-conjugated Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] is a potential treatment tool for targeted drug delivery in Her2/neu-positive breast cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
3T3 Cells
Animals
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Humanized/*administration & dosage
Antineoplastic Agents/*administration & dosage
Breast Neoplasms/chemistry/*drug therapy
Cell Line, Tumor
Drug Delivery Systems/methods
Female
Ferric Compounds/chemistry
Humans
Liposomes
Magnetite Nanoparticles/administration & dosage/*chemistry
Mice
Molecular Targeted Therapy/methods
Nanoconjugates/administration & dosage/*chemistry
Nanoparticles/chemistry
*Receptor, erbB-2/immunology
Silicon Dioxide/administration & dosage/*chemical synthesis/chemistry
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Humanized
Antineoplastic Agents
Ferric Compounds
Liposomes
Magnetite Nanoparticles
Nanoconjugates
Silicon Dioxide
Receptor, erbB-2
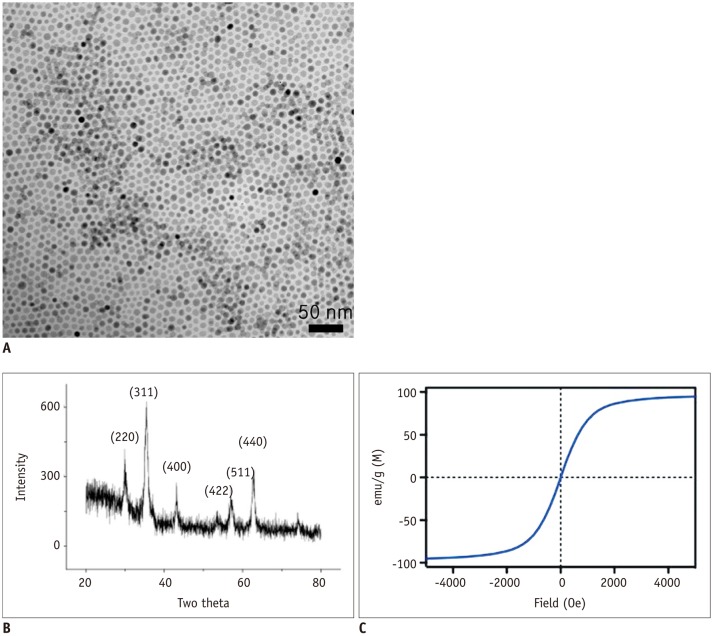
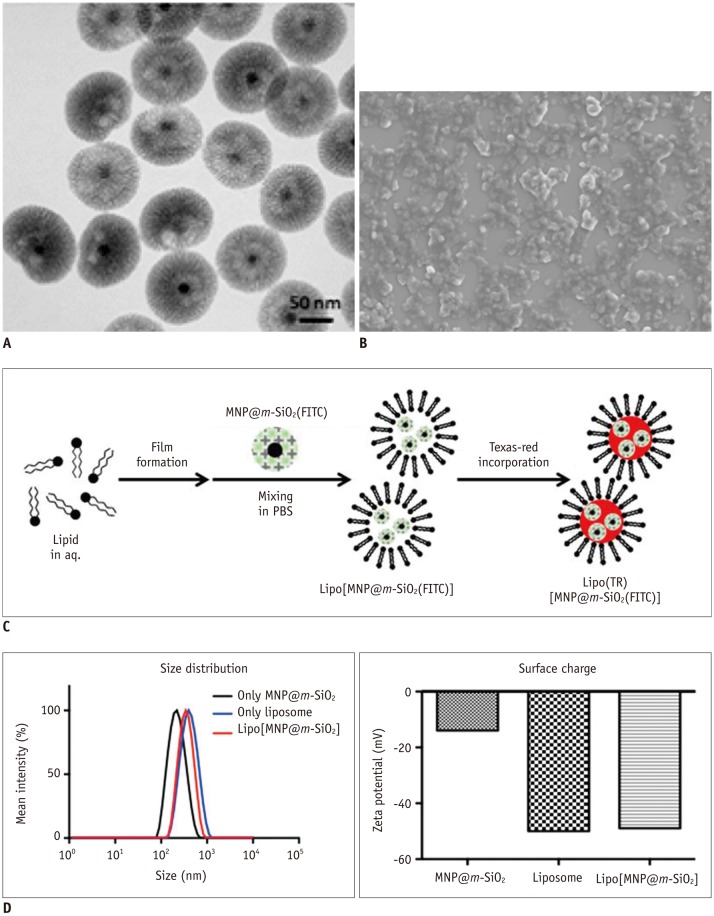
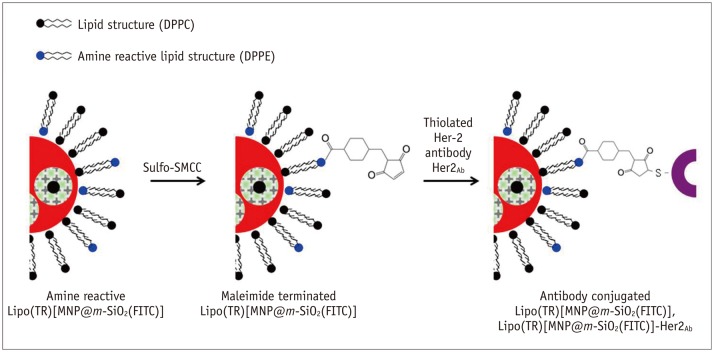
Figure
Reference
-
1. Atri M. New technologies and directed agents for applications of cancer imaging. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:3299–3308. PMID: 16829654.
Article2. Funovics MA, Kapeller B, Hoeller C, Su HS, Kunstfeld R, Puig S, et al. MR imaging of the her2/neu and 9.2.27 tumor antigens using immunospecific contrast agents. Magn Reson Imaging. 2004; 22:843–850. PMID: 15234453.
Article3. Rogers WJ, Basu P. Factors regulating macrophage endocytosis of nanoparticles: implications for targeted magnetic resonance plaque imaging. Atherosclerosis. 2005; 178:67–73. PMID: 15585202.
Article4. Gupta AK, Gupta M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2005; 26:3995–4021. PMID: 15626447.
Article5. Schellenberger E, Schnorr J, Reutelingsperger C, Ungethüm L, Meyer W, Taupitz M, et al. Linking proteins with anionic nanoparticles via protamine: ultrasmall protein-coupled probes for magnetic resonance imaging of apoptosis. Small. 2008; 4:225–230. PMID: 18203233.
Article6. Li Z, Tan B, Allix M, Cooper AI, Rosseinsky MJ. Direct coprecipitation route to monodisperse dual-functionalized magnetic iron oxide nanocrystals without size selection. Small. 2008; 4:231–239. PMID: 18213671.
Article7. Kim J, Kim HS, Lee N, Kim T, Kim H, Yu T, et al. Multifunctional uniform nanoparticles composed of a magnetite nanocrystal core and a mesoporous silica shell for magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging and for drug delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008; 47:8438–8441. PMID: 18726979.
Article8. Slowing II, Vivero-Escoto JL, Wu CW, Lin VS. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008; 60:1278–1288. PMID: 18514969.
Article9. Cao H, Gan J, Wang S, Xuan S, Wu Q, Li C, et al. Novel silica-coated iron-carbon composite particles and their targeting effect as a drug carrier. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008; 86:671–677. PMID: 18022840.
Article10. Kim T, Momin E, Choi J, Yuan K, Zaidi H, Kim J, et al. Mesoporous silica-coated hollow manganese oxide nanoparticles as positive T1 contrast agents for labeling and MRI tracking of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2011; 133:2955–2961. PMID: 21314118.
Article11. Yoon TJ, Kim JS, Kim BG, Yu KN, Cho MH, Lee JK. Multifunctional nanoparticles possessing a "magnetic motor effect" for drug or gene delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2005; 44:1068–1071. PMID: 15635729.
Article12. Sun C, Lee JS, Zhang M. Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008; 60:1252–1265. PMID: 18558452.
Article13. Olayioye MA. Update on HER-2 as a target for cancer therapy: intracellular signaling pathways of ErbB2/HER-2 and family members. Breast Cancer Res. 2001; 3:385–389. PMID: 11737890.
Article14. Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, Holt JA, Wong SG, Keith DE, et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989; 244:707–712. PMID: 2470152.15. Chen TJ, Cheng TH, Chen CY, Hsu SC, Cheng TL, Liu GC, et al. Targeted Herceptin-dextran iron oxide nanoparticles for noninvasive imaging of HER2/neu receptors using MRI. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2009; 14:253–260. PMID: 18975017.
Article16. Hilger I, Leistner Y, Berndt A, Fritsche C, Haas KM, Kosmehl H, et al. Near-infrared fluorescence imaging of HER-2 protein over-expression in tumour cells. Eur Radiol. 2004; 14:1124–1129. PMID: 15118831.
Article17. Tran TA, Ekblad T, Orlova A, Sandström M, Feldwisch J, Wennborg A, et al. Effects of lysine-containing mercaptoacetyl-based chelators on the biodistribution of 99mTc-labeled anti-HER2 Affibody molecules. Bioconjug Chem. 2008; 19:2568–2576. PMID: 19035668.
Article18. Lee H, Yoon TJ, Figueiredo JL, Swirski FK, Weissleder R. Rapid detection and profiling of cancer cells in fine-needle aspirates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:12459–12464. PMID: 19620715.
Article19. Stanisic DI, Martin LB, Liu XQ, Jackson D, Cooper J, Good MF. Analysis of immunological nonresponsiveness to the 19-kilodalton fragment of merozoite surface Protein 1 of Plasmodium yoelii: rescue by chemical conjugation to diphtheria toxoid (DT) and enhancement of immunogenicity by prior DT vaccination. Infect Immun. 2003; 71:5700–5713. PMID: 14500491.20. Kim JS, Yoon TJ, Yu KN, Noh MS, Woo M, Kim BG, et al. Cellular uptake of magnetic nanoparticle is mediated through energy-dependent endocytosis in A549 cells. J Vet Sci. 2006; 7:321–326. PMID: 17106221.
Article21. Jain TK, Richey J, Strand M, Leslie-Pelecky DL, Flask CA, Labhasetwar V. Magnetic nanoparticles with dual functional properties: drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials. 2008; 29:4012–4021. PMID: 18649936.
Article22. Cheng HL, Stikov N, Ghugre NR, Wright GA. Practical medical applications of quantitative MR relaxometry. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 36:805–824. PMID: 22987758.23. Lee JE, Lee N, Kim T, Kim J, Hyeon T. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanocomposite nanoparticles for theranostic applications. Acc Chem Res. 2011; 44:893–902. PMID: 21848274.
Article24. Casciaro S, Conversano F, Ragusa A, Malvindi MA, Franchini R, Greco A, et al. Optimal enhancement configuration of silica nanoparticles for ultrasound imaging and automatic detection at conventional diagnostic frequencies. Invest Radiol. 2010; 45:715–724. PMID: 20562708.
Article25. Napierska D, Thomassen LC, Rabolli V, Lison D, Gonzalez L, Kirsch-Volders M, et al. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of monodisperse silica nanoparticles in human endothelial cells. Small. 2009; 5:846–853. PMID: 19288475.
Article26. Fu C, Liu T, Li L, Liu H, Chen D, Tang F. The absorption, distribution, excretion and toxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in mice following different exposure routes. Biomaterials. 2013; 34:2565–2575. PMID: 23332175.
Article27. Sung CK, Hong KA, Lin S, Lee Y, Cha J, Lee JK, et al. Dualmodal nanoprobes for imaging of mesenchymal stem cell transplant by MRI and fluorescence imaging. Korean J Radiol. 2009; 10:613–622. PMID: 19885318.
Article28. Bumb A, Regino CA, Egen JG, Bernardo M, Dobson PJ, Germain RN, et al. Trafficking of a dual-modality magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging superparamagnetic iron oxide-based nanoprobe to lymph nodes. Mol Imaging Biol. 2011; 13:1163–1172. PMID: 21080233.
Article29. Lu CW, Hung Y, Hsiao JK, Yao M, Chung TH, Lin YS, et al. Bifunctional magnetic silica nanoparticles for highly efficient human stem cell labeling. Nano Lett. 2007; 7:149–154. PMID: 17212455.
Article30. Veiseh O, Sun C, Gunn J, Kohler N, Gabikian P, Lee D, et al. Optical and MRI multifunctional nanoprobe for targeting gliomas. Nano Lett. 2005; 5:1003–1008. PMID: 15943433.
Article31. Maeda H, Wu J, Sawa T, Matsumura Y, Hori K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: a review. J Control Release. 2000; 65:271–284. PMID: 10699287.
Article32. Noguchi Y, Wu J, Duncan R, Strohalm J, Ulbrich K, Akaike T, et al. Early phase tumor accumulation of macromolecules: a great difference in clearance rate between tumor and normal tissues. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1998; 89:307–314. PMID: 9600125.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Trastuzumab Exposure during Pregnancy with Invasive Breast Cancer
- Psoriasis Induced by Trastuzumab (Herceptin(R))
- The Study of EGFR Expression on Malignant Skin Tumor and Molecular Labelling Using Gold Nanoparticles
- Intrathecal Trastuzumab Treatment in Patients with Breast Cancer and Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
- Targeting Colon Cancer Cells with Fluorescent Magnetic Nanoparticles Conjugated to Anti-epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Antibodies