J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Aug;25(8):1152-1159. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.8.1152.
Identification of Novel Methylation Markers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma using a Methylation Array
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Epigenetics, Cancer Research Institute and Brain Korea 2nd Stage, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. ghkang@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Korea University Medical School, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1714035
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.8.1152
Abstract
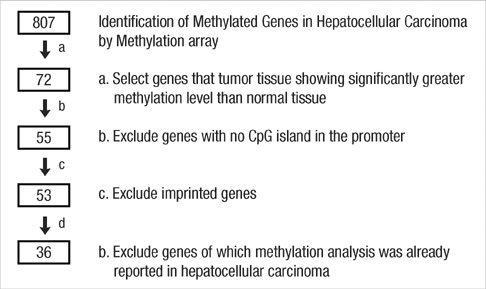
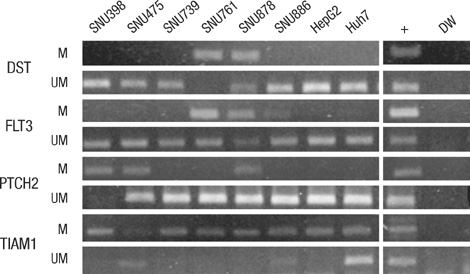
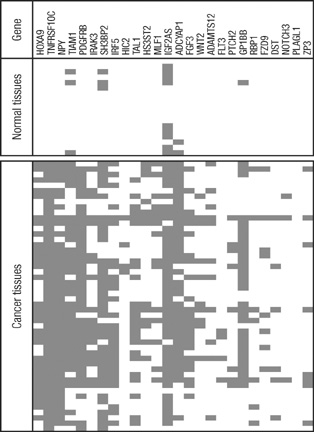
- Promoter CpG island hypermethylation has become recognized as an important mechanism for inactivating tumor suppressor genes or tumor-related genes in human cancers of various tissues. Gene inactivation in association with promoter CpG island hypermethylation has been reported to be four times more frequent than genetic changes in human colorectal cancers. Hepatocellular carcinoma is also one of the human cancer types in which aberrant promoter CpG island hypermethylation is frequently found. However, the number of genes identified to date as hypermethylated for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is fewer than that for colorectal cancer or gastric cancer, which can be attributed to fewer attempts to perform genome-wide methylation profiling for HCC. In the present study, we used bead-array technology and coupled methylation-specific PCR to identify new genes showing cancer-specific methylation in HCC. Twenty-four new genes have been identified as hypermethylated at their promoter CpG island loci in a cancer-specific manner. Of these, TNFRSF10C, HOXA9, NPY, and IRF5 were frequently hypermethylated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue samples and their methylation was found to be closely associated with inactivation of gene expression. Further study will be required to elucidate the clinicopathological implications of these newly found DNA methylation markers in hepatocellular carcinoma.
MeSH Terms
-
Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic/therapeutic use
Azacitidine/analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular/drug therapy/*genetics
Cell Line, Tumor
CpG Islands
*DNA Methylation
GPI-Linked Proteins/genetics
Gene Expression Profiling
Homeodomain Proteins/genetics
Humans
Interferon Regulatory Factors/genetics
Liver Neoplasms/drug therapy/*genetics
Neuropeptide Y/genetics
Oligonucleotide Array Sequence Analysis
Promoter Regions, Genetic
Tumor Necrosis Factor Decoy Receptors/genetics
Figure
Reference
-
1. Saxonov S, Berg P, Brutlag DL. A genome-wide analysis of CpG dinucleotides in the human genome distinguishes two distinct classes of promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006. 103:1412–1417.
Article2. Weber M, Hellmann I, Stadler MB, Ramos L, Paabo S, Rebhan M, Schübeler D. Distribution, silencing potential and evolutionary impact of promoter DNA methylation in the human genome. Nat Genet. 2007. 39:457–466.
Article3. Li E, Beard C, Jaenisch R. Role for DNA methylation in genomic imprinting. Nature. 1993. 366:362–365.
Article4. Panning B, Jaenisch R. RNA and the epigenetic regulation of X chromosome inactivation. Cell. 1998. 93:305–308.
Article5. Esteller M. Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer: the DNA hypermethylome. Hum Mol Genet. 2007. 16 Spec No 1:R50–R59.
Article6. Baylin SB, Chen WY. Aberrant gene silencing in tumor progression: implications for control of cancer. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005. 70:427–433.
Article7. Teodoridis JM, Strathdee G, Brown R. Epigenetic silencing mediated by CpG island methylation: potential as a therapeutic target and as a biomarker. Drug Resist Updat. 2004. 7:267–278.
Article8. Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Gorden A, Farina M, Lee JS, Conner EA, Schroeder I, Factor VM, Thorgeirsson SS. Mechanistic and prognostic significance of aberrant methylation in the molecular pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 2007. 117:2713–2722.
Article9. Tischoff I, Tannapfe A. DNA methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. 14:1741–1748.
Article10. Lou C, Yang B, Gao YT, Wang YJ, Nie FH, Yuan Q, Zhang CL, Du Z. Aberrant methylation of multiple genes and its clinical implication in hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2008. 30:831–836.11. Schuebel KE, Chen W, Cope L, Glockner SC, Suzuki H, Yi JM, Chan TA, Van Neste L, Van Criekinge W, van den Bosch S, van Engeland M, Ting AH, Jair K, Yu W, Toyota M, Imai K, Ahuja N, Herman JG, Baylin SB. Comparing the DNA hypermethylome with gene mutations in human colorectal cancer. PLoS Genet. 2007. 3:1709–1723.
Article12. Bibikova M, Lin Z, Zhou L, Chudin E, Garcia EW, Wu B, Doucet D, Thomas NJ, Wang Y, Vollmer E, Goldmann T, Seifart C, Jiang W, Barker DL, Chee MS, Floros J, Fan JB. High-throughput DNA methylation profiling using universal bead arrays. Genome Res. 2006. 16:383–393.
Article13. Cho NY, Kim BH, Choi M, Yoo EJ, Moon KC, Cho YM, Kim D, Kang GH. Hypermethylation of CpG island loci and hypomethylation of LINE-1 and Alu repeats in prostate adenocarcinoma and their relationship to clinicopathological features. J Pathol. 2007. 211:269–277.
Article14. Christman JK. 5-Azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine as inhibitors of DNA methylation: mechanistic studies and their implications for cancer therapy. Oncogene. 2002. 21:5483–5495.
Article15. Jones PA. Altering gene expression with 5-azacytidine. Cell. 1985. 40:485–486.
Article16. Yan C, Boyd DD. Histone H3 acetylation and H3 K4 methylation define distinct chromatin regions permissive for transgene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. 26:6357–6371.
Article17. Lund AH, van Lohuizen M. Polycomb complexes and silencing mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004. 16:239–246.
Article18. Shivapurkar N, Toyooka S, Toyooka KO, Reddy J, Miyajima K, Suzuki M, Shigematsu H, Takahashi T, Parikh G, Pass HI, Chaudhary PM, Gazdar AF. Aberrant methylation of trail decoy receptor genes is frequent in multiple tumor types. Int J Cancer. 2004. 109:786–792.
Article19. Gehring WJ, Affolter M, Burglin T. Homeodomain proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994. 63:487–526.
Article20. Rauch T, Wang Z, Zhang X, Zhong X, Wu X, Lau SK, Kernstine KH, Riggs AD, Pfeifer GP. Homeobox gene methylation in lung cancer studied by genome-wide analysis with a microarray-based methylated CpG island recovery assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007. 104:5527–5532.
Article21. Wu Q, Lothe RA, Ahlquist T, Silins I, Trope CG, Micci F, Nesland JM, Suo Z, Lind GE. DNA methylation profiling of ovarian carcinomas and their in vitro models identifies HOXA9, HOXB5, SCGB3A1, and CRABP1 as novel targets. Mol Cancer. 2007. 6:45.
Article22. Hallden G, Hadi M, Hong HT, Aponte GW. Y receptor-mediated induction of CD63 transcripts, a tetraspanin determined to be necessary for differentiation of the intestinal epithelial cell line, hBRIE 380i cells. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:27914–27924.23. Minth CD, Andrews PC, Dixon JE. Characterization, sequence, and expression of the cloned human neuropeptide Y gene. J Biol Chem. 1986. 261:11974–11979.
Article24. Liu AJ, Furusato B, Ravindranath L, Chen YM, Srikantan V, McLeod DG, Petrovics G, Srivastava S. Quantitative analysis of a panel of gene expression in prostate cancer--with emphasis on NPY expression analysis. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2007. 8:853–859.
Article25. Abe M, Watanabe N, McDonell N, Takato T, Ohira M, Nakagawara A, Ushijima T. Identification of genes targeted by CpG island methylator phenotype in neuroblastomas, and their possible integrative involvement in poor prognosis. Oncology. 2008. 74:50–60.
Article26. Pitha PM, Au WC, Lowther W, Juang YT, Schafer SL, Burysek L, Hiscott J, Moore PA. Role of the interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) in virus-mediated signaling and regulation of cell growth. Biochimie. 1998. 80:651–658.
Article27. Yanai H, Chen HM, Inuzuka T, Kondo S, Mak TW, Takaoka A, Honda K, Taniguchi T. Role of IFN regulatory factor 5 transcription factor in antiviral immunity and tumor suppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007. 104:3402–3407.
Article28. Guenther MG, Levine SS, Boyer LA, Jaenisch R, Young RA. A chromatin landmark and transcription initiation at most promoters in human cells. Cell. 2007. 130:77–88.
Article29. Bernstein BE, Meissner A, Lander ES. The mammalian epigenome. Cell. 2007. 128:669–681.
Article30. Ohm JE, McGarvey KM, Yu X, Cheng L, Schuebel KE, Cope L, Mohammad HP, Chen W, Daniel VC, Yu W, Berman DM, Jenuwein T, Pruitt K, Sharkis SJ, Watkins DN, Herman JG, Baylin SB. A stem cell-like chromatin pattern may predispose tumor suppressor genes to DNA hypermethylation and heritable silencing. Nat Genet. 2007. 39:237–242.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pharmacological Unmasking Microarray Approach-Based Discovery of Novel DNA Methylation Markers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- DNA Methylation in Development
- Detection of Aberrant p16INK4A Methylation in Sera of Patients with Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- RUNX3 Methylation Status in Colonic Carcinoma and Adenoma
- Study of CpG Methylation of the p16 and MGMT Promoter in Hepatocellular Carcinoma