J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Apr;22(2):183-191. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.183.
Time Sequence of Airway Remodeling in a Mouse Model of Chronic Asthma: the Relation with Airway Hyperresponsiveness
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. cmcpsh@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1713158
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.183
Abstract
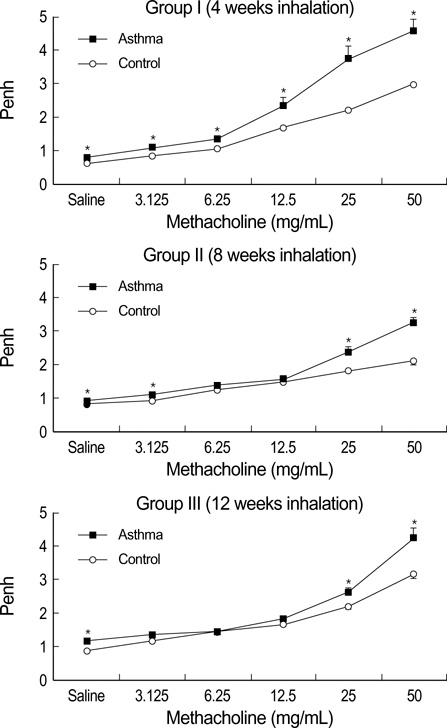
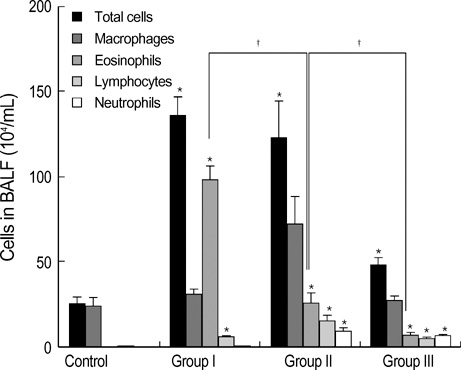
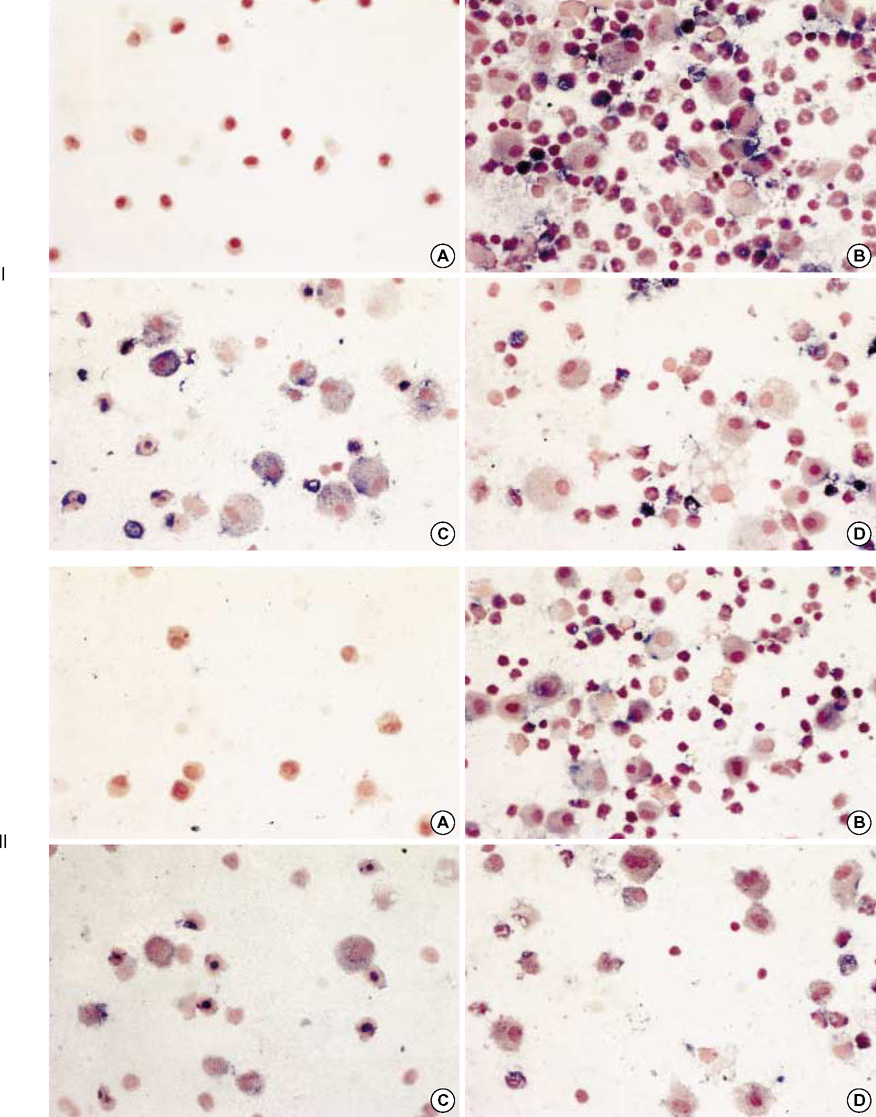
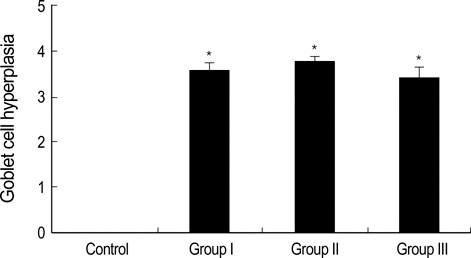
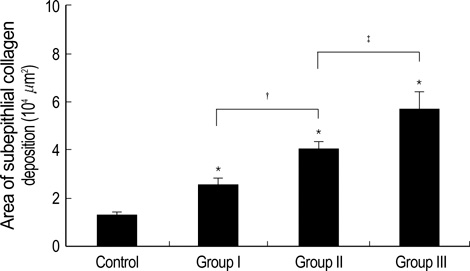
- During the course of establishing an animal model of chronic asthma, we tried to elucidate the time sequence of airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), airway inflammation, airway remodeling, and associated cytokines. Seven-week-old female BALB/c mice were studied as a chronic asthma model using ovalbumin (OVA). After sensitization, mice were exposed twice weekly to aerosolized OVA, and were divided into three groups depending on the duration of 4 weeks, 8 weeks, and 12 weeks. At each time point, airway responsiveness, inflammatory cells, cytokines in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids (BALF), serum OVA-specific IgE, IgG1, IgG2a, and histological examination were carried out. AHR to methacholine, increased levels of OVA-specific IgG1 and IgG2a, and goblet cell hyperplasia were continuously sustained at each time point of weeks. In contrast, we observed a time-dependent decrease in serum OVA-specific IgE, BALF eosinophils, BALF cytokines such as IL-13, transforming growth factor-beta1, and a time-dependent increase in BALF promatrix metalloproteinase-9 and peribronchial fibrosis. In this OVA-induced chronic asthma model, we observed airway remodelings as well as various cytokines and inflammatory cells being involved in different time-dependent manners. However, increased airway fibrosis did not directly correlate with a further increase in airway hyperresponsiveness.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brown PJ, Greville HW, Finucane KE. Asthma and irreversible airflow obstruction. Thorax. 1984. 39:131–136.
Article2. Broide DH, Lotz M, Cuomo AJ, Coburn DA, Federman EC, Wasserman SI. Cytokines in symptomatic asthma airways. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992. 89:958–967.
Article3. Jeffery PK, Wardlaw AJ, Nelson FC, Collins JV, Kay AB. Bronchial biopsies in asthma. An ultrastructural, quantitative study and correlation with hyperreactivity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989. 140:1745–1753.
Article4. Bousquet J, Chanez P, Lacoste JY, White R, Vic P, Godard P, Michel FB. Asthma: a disease remodeling the airways. Allergy. 1992. 47:3–11.
Article5. Redington AE, Howarth PH. Airway wall remodelling in asthma. Thorax. 1997. 52:310–312.
Article6. Akkoc T, Tolunay S, Barlau I, Basaran M. Airway remodeling and serum total immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels in a murine model of asthma. J Asthma. 2001. 38:585–591.7. Hoshino M, Nakamura Y, Sim JJ. Expression of growth factors and remodelling of the airway wall in bronchial asthma. Thorax. 1998. 53:21–27.
Article8. Aikawa T, Shimura S, Sasaki H, Ebina M, Takashima T. Marked goblet cell hyperplasia with mucus accumulation in the airways of patients who died of severe acute asthma attack. Chest. 1992. 101:916–921.
Article9. Cui ZH, Skoogh BE, Pullerits T, Lotvall J. Bronchial hyperresponsiveness and airway wall remodelling induced by exposure to allergen for 9 weeks. Allergy. 1999. 54:1074–1082.
Article10. Kumar RK, Foster PS. Murine model of chronic human asthma. Immunol Cell Biol. 2001. 79:141–144.
Article11. Kumar RK, Foster PS. Modeling allergic asthma in mice; pitfalls and opportunities. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002. 27:267–272.12. Blyth DI, Wharton TF, Pedrick MS, Savage TJ, Sanjar S. Airway subepithelial fibrosis in a murine model of atopic asthma; Suppression by dexamethasone or anti-interleukin-5 antibody. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2000. 23:241–246.13. Leong KP, Huston DP. Understanding the pathogenesis of allergic asthma using mouse models. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001. 87:96–110.
Article14. Temelkovski J, Hogan SP, Shepherd DB, Foster PS, Kumar PK. An improved murine model of asthma: selective airway inflammation, epithelial lesions and increased methacholine responsiveness following chronic exposure to aerosolised allergen. Thorax. 1998. 53:849–856.
Article15. Trifilieff A, El-Hashim A, Bertrand C. Time course of inflammatory and remodeling events in a murine model of asthma: effect of steroid treatment. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000. 279:L1120–L1128.16. Padrid P, Snook S, Finucane T, Shiue P, Cozzi P, Solway J, Leff AR. Persistent airway hyperresponsiveness and histologic alterations after chronic antigen challenge in cats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 151:184–193.
Article17. Sakai K, Yokoyama A, Kohno N, Hamada H, Hiwada K. Prolonged antigen exposure ameliorates airway inflammation but not remodeling in a mouse model of bronchial asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001. 126:126–134.
Article18. Kamath AV, Pavord ID, Ruparelia PR, Chilvers ER. Is the neutrophil the key effector cell in severe asthma? Thorax. 2005. 60:529–530.
Article19. Louis R, Djukanovic R. Is the neutrophil a worthy target in severe asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Clin Exp Allergy. 2006. 36:563–567.
Article20. Tanaka H, Masuda T, Tokuoka S, Komai M, Nagao K, Takahashi Y, Nagai H. The effect of allergen-induced airway inflammation on airway remodeling in a murine model of allergic asthma. Inflamm Res. 2001. 50:616–624.
Article21. Morcillo EJ, Cortijo J. Mucus and MUC in asthma. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2006. 12:1–6.
Article22. Wills-Karp M, Chiaramonte M. Interleukin-13 in asthma. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2003. 9:21–27.
Article23. Takayama G, Arima K, Kanaji T, Toda S, Tanaka H, Shoji S, McKenzie AN, Nagai H, Hotokebuchi T, Izuhara K. Periostin: a novel component of subepithelial fibrosis of bronchial asthma downstream of IL-4 and IL-13 signals. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. 118:98–104.
Article24. Palmans E, Kips JC, Pauwels RA. Prolonged allergen exposure induces structural airway changes in sensitized rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 161:627–635.
Article25. Lee YM, Kim YK, Park JK, Suh J, Kim KU, Kim DJ, Uh ST, Kim YH, Park CS. Alteration of airway hyperresponsiveness and expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in bronchial tissue by nebulized IFN-γ in murine model of asthma. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 23:788–799.26. Cataldo DD, Gueders M, Munaut C, Rocks N, Bartsch P, Foidart JM, Noel A, Louis R. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases mRNA transcripts in the bronchial secretions of asthmatics. Lab Invest. 2004. 84:418–424.
Article27. Matsumoto H, Niimi A, Takemura M, Ueda T, Minakuchi M, Tabuena R, Chin K, Mio T, Ito Y, Muro S, Hirai T, Morita S, Fukuhara S, Mishima M. Relationship of airway wall thickening to an imbalance between matrix metalloproteinase-9 and its inhibitor in asthma. Thorax. 2005. 60:277–281.
Article28. Lee JH, Lee JH, Song DY, Baek SH, Kang IJ. Changes of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor matrix metalloproteinase-1 in sputum from moderate to severe acute asthma after corticosteroid therapy. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis (Korea). 2005. 15:389–398.29. Tang LF, Du LZ, Chen ZM, Zou CC. Levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and its inhibitor in bronchoalveolar lavage cells of asthmatic children. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2006. 25:1–7.
Article30. Cho JY, Miller M, McElwain K, McElwain S, Shim JY, Raz E, Broide DH. Remodeling associated expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 but not tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 in airway epithelium: modulation by immunostimulatory DNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. 117:618–625.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides in Chronic Inflammation and Remodeling of Airway in a Murine Model of Bronchial Asthma
- Bronchial Structural Changes in Childhood Asthma
- Evolution of Asthma Concept and Effect of Current Asthma Management Guidelines
- Airway remodelling in asthma: role for mechanical forces
- Expression of Muscarinic Receptors and the Effect of Tiotropium Bromide in Aged Mouse Model of Chronic Asthma