Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2009 Dec;2(4):175-180. 10.3342/ceo.2009.2.4.175.
Th2 Responses Elicited by Nasal Epithelial Cells Exposed to House Dust Mite Extract
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. hsseung@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1466494
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2009.2.4.175
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
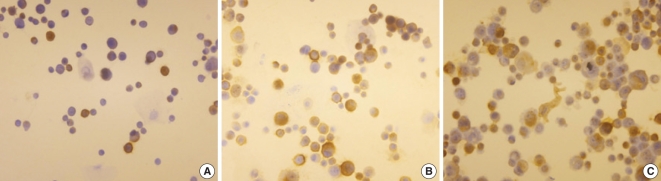
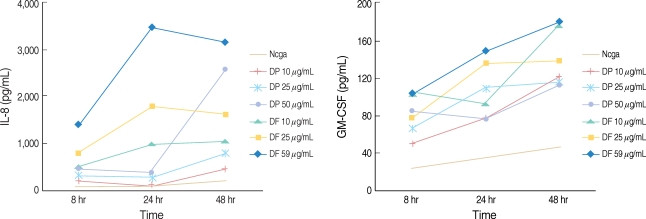
Respiratory epithelial cells are the first site of interaction of allergens with the immune system. The aim of this study was to examine the effect of epithelial cells, which were stimulated with house dust mite (HDM) extracts, on the immune response of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). METHODS: Primary nasal polyp epithelial cells were exposed to dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and dermatophagoides farina for 48 hr, and then the supernatant and cells were collected. After stimulation with HDM extract, the epithelial cells were co-cultured with PBMCs for 72 hr and then the supernatant was collected. We measured the interleukin (IL)-8 and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor to determine the activation of the epithelial cells. The tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, IL-5 and interferon-gamma were measured to evaluate the interaction between the epithelial cells and the PBMCs. The mRNA expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) was assessed using the anti-ICAM-1 antibody. RESULTS: The HDM extracts activated the nasal epithelial cells and enhanced the expression of ICAM-1 mRNA and cell membrane ICAM-1. When the activated epithelial cells were co-cultured with PBMCs, the PBMCs produced lager amounts of TNF-alpha and IL-5. However the cytokine production was not inhibited by pretreatment with ICAM-1 antibody. CONCLUSION: HDM allergens induce allergic inflammation by activating nasal epithelial cells, yet the interaction of the epitheila cells and the PBMCs may not be associated with an ICAM-1 medicated mechanism.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Allergens
Cell Membrane
Colony-Stimulating Factors
Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus
Dust
Epithelial Cells
Immune System
Inflammation
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
Interferon-gamma
Interleukin-5
Interleukins
Nasal Polyps
Pyroglyphidae
RNA, Messenger
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Allergens
Colony-Stimulating Factors
Dust
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
Interferon-gamma
Interleukin-5
Interleukins
RNA, Messenger
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mullol J, Xaubet A, Lopez E, Roca-Ferrer J, Picado C. Comparative study of the effects of different glucocorticoids on eosinophil survival primed by cultured epithelial cell supernatants obtained from nasal mucosa and nasal polyps. Thorax. 1995; 3. 50(3):270–274. PMID: 7660341.2. Roca-Ferrer J, Mullol J, Lopez E, Xaubet A, Pujols L, Fernández JC, et al. Effect of topical anti-inflammatory drugs on epithelial cell induced eosinophil survival and GM-CSF secretion. Eur Respir J. 1997; 7. 10(7):1489–1495. PMID: 9230235.3. Robinson C, Kalsheker NA, Srinivasan N, King CM, Garrod DR, Thompson PJ, et al. On the potential significance of the enzymatic activity of mite allergens to immunogenicity: clues to structure and function revealed by molecular characterization. Clin Exp Allergy. 1997; 1. 27(1):10–21. PMID: 9117873.
Article4. Thomas WR, Smith WA, Hales BJ, Mills KL, O'Brien RM. Characterization and immunobiology of house dust mite allergens. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002; 9. 129(1):1–18. PMID: 12372994.
Article5. King C, Brennan S, Thompson PJ, Stewart GA. Dust mite proteolytic allergens induce cytokine release from cultured airway epithelium. J Immunol. 1998; 10. 01. 161(7):3645–3651. PMID: 9759888.6. Herbert CA, King CM, Ring PC, Holgate ST, Stewart GA, Thompson PJ, et al. Augmentation of permeability in the bronchial epithelium by the house dust mite allergen Der p1. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995; 4. 12(4):369–378. PMID: 7695916.
Article7. Mckay DM, Croitoru K, Perdue M. T cell-monocyte interactions regulate epithelial physiology in a coculture model of inflammation. Am J Physiol. 1996; 2. 270(2 Pt 1):C418–C428. PMID: 8779903.
Article8. Agace WW, Higgins JM, Sadasivan B, Brenner MB, Parker CM. T-lymphocyte-epithelial-cell interaction: integrin αE(CD103)β7, LEEP-CAM and chemokines. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000; 10. 12(5):563–568. PMID: 10978890.9. Tovey ER, Chapman MD, Platts-Mills TA. Mite faeces are a major source of house dust allergens. Nature. 1981; 2. 12. 289(5798):592–593. PMID: 7464922.
Article10. De Wit D, Amraoui Z, Vincart B, Michel O, Michils A, Van Overvelt L, et al. Helper T-cell responses elicited by Der p1-pulsed dendritic cells and recombinant IL-12 in atopic and healthy subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 2. 105(2 Pt 1):346–352. PMID: 10669857.11. Pichavant M, Charbonnier AS, Taront S, Brichet A, Wallaert B, Pestel J, et al. Asthmatic bronchial epithelium activated by the proteolytic allergen Der p 1 increases selective dendritic cell recruitment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 4. 115(4):771–778. PMID: 15805997.
Article12. Asokananthan N, Graham PT, Stewart DJ, Bakker AJ, Eidne KA, Thompson PJ, et al. House dust mite allergens induce proinflammatory cytokines from respiratory epithelial cells: The cytokine protease allergen, Der p 1, activated protease-activated receptor (PAR)-2 and inactivates PAR-1. J Immunol. 2002; 10. 15. 169(8):4572–4578. PMID: 12370395.13. Stacey MA, Sun G, Vassalli G, Marini M, Bellini A, Mattoli S. The allergen Der p 1 induces NF-κB activation through interference with IκB α function in asthmatic bronchial epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997; 7. 18. 236(2):522–526. PMID: 9240473.14. Shin SH, Lee YH, Jeon CH. Protease-dependent activatio of nasal polyp epithelial cells by airborne fungi leads to migration of eosinophils and neutrophils. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006; 12. 126(12):1286–1294. PMID: 17101590.15. Rosseau S, Selhorst J, Wiechmann K, Leissner K, Maus U, Mayer K, et al. Monocyte migration through the alveolar epithelial barrier: adhesion molecule mechanisms and impact of chemokines. J Immunol. 2000; 1. 01. 164(1):427–435. PMID: 10605039.
Article16. Perdue MH, McKay DM. Intergrative immunophysiology in the intestinal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1994; 8. 267(2 Pt 1):G151–G165. PMID: 8074215.17. Kimura M, Tsuruta S, Yoshida T. Correlation of house dust mite-specific lymphocyte proliferation with IL-5 production, eosinophilila, and the severity of symptoms in infants with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998; 1. 101(1 Pt 1):84–89. PMID: 9449505.18. Nurse B, Puterman AS, Haus M, Berman D, Weinberg EG, Potter PC. PBMCs from both atopic asthmatic and nonatopic children show a TH2 cytokine response to house dust mite allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 7. 106(1 Pt 1):84–91. PMID: 10887310.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- House Dust Mite Extract Induces PLC/IP3-dependent Ca2+ Signaling and IL-8 Expression in Human Gingival Epithelial Cells
- Correlation of Appearance of Nasal Eosinophils with Levels of Total Eosinophil Counts, Total IgE, and House Dust Mite Specific IgE in Children with Symptoms of Rhinitis
- Distribution of House Dust Mites in the Bedroom of Patients with Allergic Rhinitis in Pusan Area
- The Innate Immune Response in House Dust Mite-Induced Allergic Inflammation
- Expression of TARC in Nasal Epithelial Cells by IL-4/IL-13 and TNF-alpha in Allergic Rhinitis