Lab Anim Res.
2011 Dec;27(4):343-346. 10.5625/lar.2011.27.4.343.
Shigella flexneri infection in a newly acquired rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Xenotransplantation Research Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. chgpark@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1444968
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2011.27.4.343
Abstract
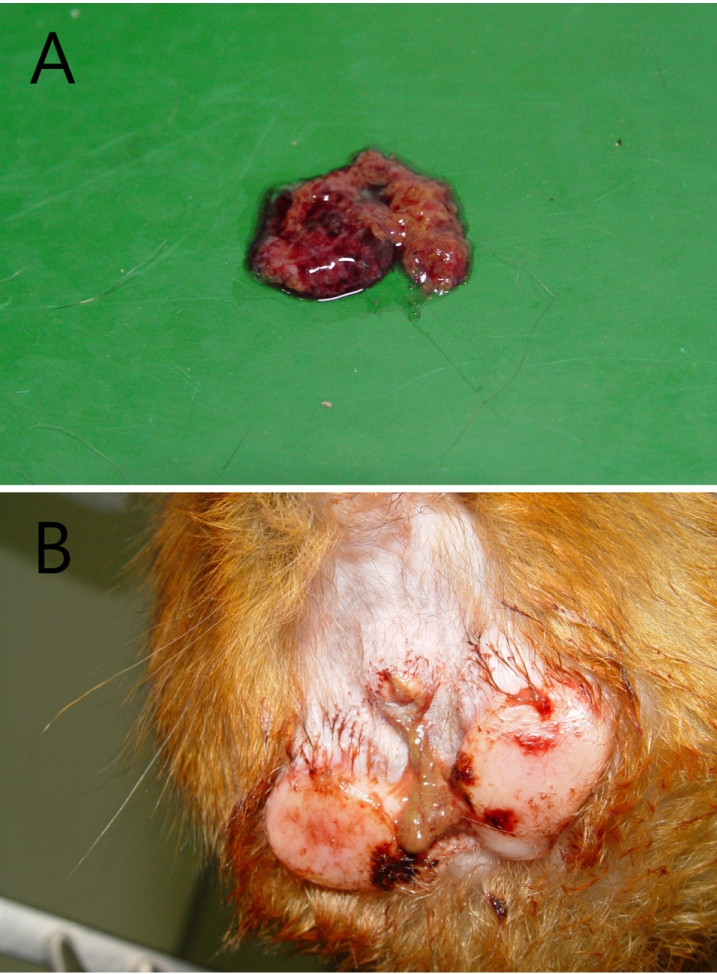
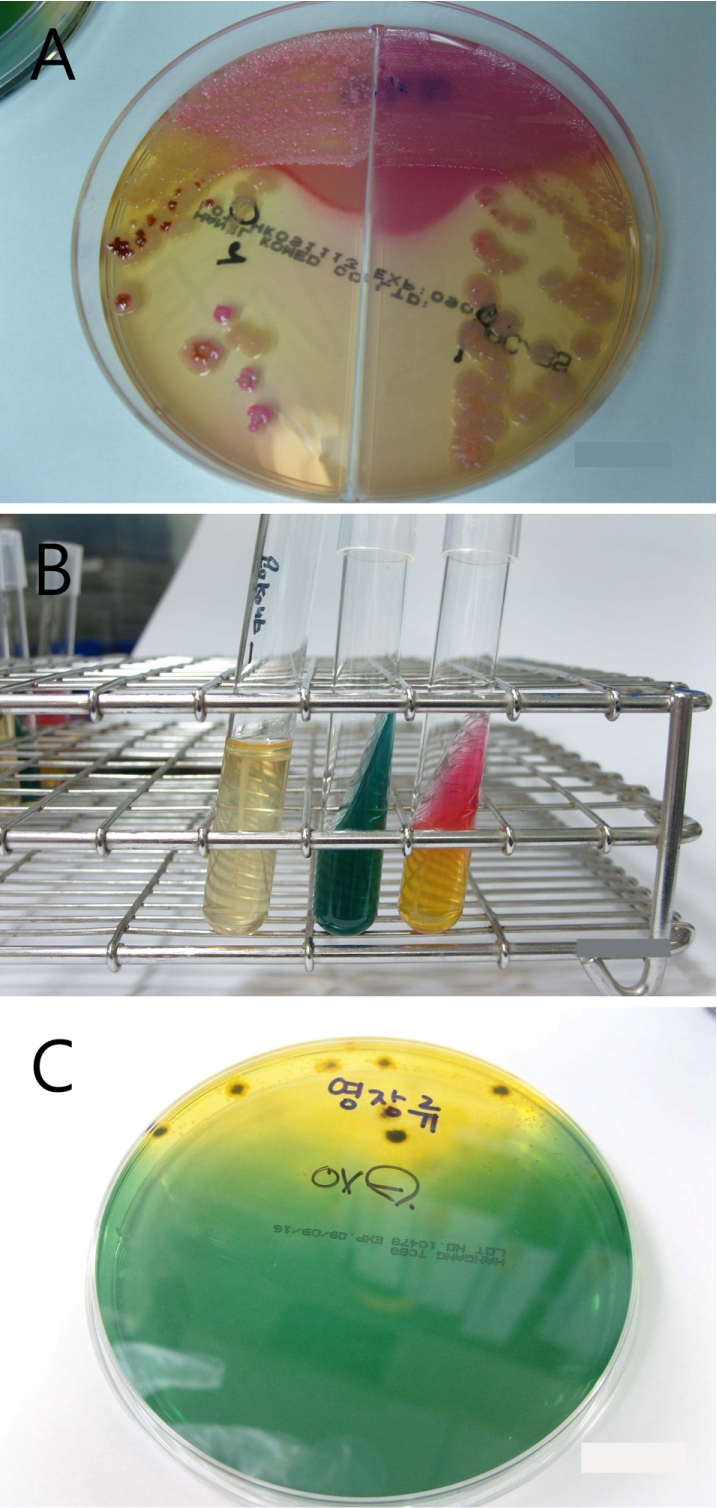
- A 3.4 year-old rhesus macaque weighing 4.5 kg, was suffering from anorexia, acute mucous and bloody diarrhea. On physical examination, the monkey showed a loss of activity, hunched posture, abdominal pain, dehydration, mild gingivitis and unclean anus with discharge. Whole blood was collected for the examination of electrolytes, hematology and serum chemistry; fresh stool was also collected for bacterial culture. Blood profiles showed leukocytosis (14.5 K/microL) and neutrophilia (11.0 K/microL) on complete blood cell count and imbalanced electrolytes associated with diarrhea. As a result of bacterial culture, Shigella flexneri was identified through Mac/SS, IMVIC test, TCBS and VITEK II. Based on these results, this monkey was diagnosed as having acute enteritis caused by Shigella flexneri. Treatment was performed with enrofloxacin prior to the isolation of Shigella flexneri to prevent the transmission of disease. Fortunately, mucus and bloody diarrhea did not persist and general conditions fully recovered. Our results show that the use of enrofloxacin is effective in controlling Shigella flexneri infection in newly acquired rhesus monkeys.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Banish LD, Sims R, Sack D, Montali RJ, Phillips L Jr, Bush M. Prevalence of shigellosis and other enteric pathogens in a zoologic collection of primates. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1993; 203(1):126–132. PMID: 8407446.2. Kelly-Hope LA, Alonso WJ, Thiem VD, Anh DD, Canh do G, Lee H, Smith DL, Miller MA. Geographical distribution and risk factors associated with enteric diseases in Vietnam. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007; 76(4):706–712. PMID: 17426175.
Article3. Pucak GJ, Orcutt RP, Judge RJ, Rendon F. Elimination of the Shigella carrier state in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) by trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. J Med Primatol. 1977; 6(2):127–132. PMID: 875006.4. Talukder KA, Mondol AS, Islam MA, Islam Z, Dutta DK, Khajanchi BK, Azmi IJ, Hossain MA, Rahman M, Cheasty T, Cravioto A, Nair GB, Sack DA. A novel serovar of Shigella dysenteriae from patients with diarrhoea in Bangladesh. J Med Microbiol. 2007; 56:654–658. PMID: 17446289.5. Good RC, May BD, Kawatomari T. Enteric pathogens in monkeys. J Bacteriol. 1969; 97(3):1048–1055. PMID: 4180466.
Article6. Vickers JH. Infectious diseases of primates related to capture and transportation. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1973; 38(2):511–513. PMID: 4347673.
Article7. Beecham HJ 3rd, Lebron CI, Echeverria P. Short report: impact of traveler's diarrhea on United States troops deployed to Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997; 57(6):699–701. PMID: 9430530.
Article8. Thornton SA, Sherman SS, Farkas T, Zhong W, Torres P, Jiang X. Gastroenteritis in US Marines during Operation Iraqi Freedom. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 40(4):519–525. PMID: 15712073.
Article9. Riddle MS, Sanders JW, Putnam SD, Tribble DR. Incidence, etiology, and impact of diarrhea among long-term travelers (US military and similar populations): a systematic review. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006; 74(5):891–900. PMID: 16687698.
Article10. Collins TA, Barnoy S, Baqar S, Ranallo RT, Nemelka KW, Venkatesan MM. Safety and colonization of two novel VirG(IcsA)-based live Shigella sonnei vaccine strains in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Comp Med. 2008; 58(1):88–94. PMID: 19793462.11. Kennedy FM, Astbury J, Needham JR, Cheasty T. Shigellosis due to occupational contact with non-human primates. Epidemiol Infect. 1993; 110(2):247–251. PMID: 8472767.
Article12. Bernacky BJ, Gibson SV, Kelling ME, Abee CR. Fox JG, editor. Nonhuman Primates. Laboratory Animal Medicine. 2002. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Academic Press;p. 730–732.
Article13. Armitage GC, Newbrun E, Hoover CI, Anderson JH. Periodontal disease associated with Shigella flexneri in rhesus monkeys. J Periodontal Res. 1982; 17(2):131–144. PMID: 6124590.14. Armitage GC, Banks TA, Newbrun E, Greenspan JS, Hoover CI, Anderson JH. Immunologic observations in macaques with Shigella-associated periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 1983; 18(2):139–148. PMID: 6135769.15. Fortman JD, Hewett TA, Bennett BT. Laboratory Nonhuman Primate. 2002. 1st ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press;p. 100–101.16. Levine MM, Kotloff KL, Barry EM, Pasetti MF, Sztein MB. Clinical trials of Shigella vaccines: two steps forward and one step back on a long, hard road. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007; 5(7):540–553. PMID: 17558427.17. Oaks EV, Turbyfill KR. Development and evaluation of a Shigella flexneri 2a and S. sonnei bivalent invasin complex (Invaplex) vaccine. Vaccine. 2006; 24(13):2290–2301. PMID: 16364513.18. Passwell JH, Ashkenazi S, Harlev E, Miron D, Ramon R, Farzam N, Lerner-Geva L, Levi Y, Chu C, Shiloach J, Robbins JB, Schneerson R. Safety and immunogenicity of Shigella sonnei-CRM9 and Shigella flexneri type 2a-rEPAsucc conjugate vaccines in one- to four-year-old children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003; 22(8):701–706. PMID: 12913770.19. Ranallo RT, Thakkar S, Chen Q, Venkatesan MM. Immunogenicity and characterization of WRSF2G11: a second generation live attenuated Shigella flexneri 2a vaccine strain. Vaccine. 2007; 25(12):2269–2278. PMID: 17229494.20. Venkatesan MM, Ranallo RT. Live-attenuated Shigella vaccines. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2006; 5(5):669–686. PMID: 17181440.21. Kaartinen L, Salonen M, Alli L, Pyörälä S. Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin after single intravenous, intramuscular and subcutaneous injections in lactating cows. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1995; 18(5):357–362. PMID: 8587154.
Article22. Aramayona JJ, Mora J, Fraile LJ, García MA, Abadía AR, Bregante MA. Penetration of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin into breast milk, and pharmacokinetics of the drugs in lactating rabbits and neonatal offspring. Am J Vet Res. 1996; 57(4):547–553. PMID: 8712523.23. Klein H, Hasselschwert D, Handt L, Kastello M. A pharmacokinetic study of enrofloxacin and its active metabolite ciprofloxacin after oral and intramuscular dosing of enrofloxacin in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). J Med Primatol. 2008; 37(4):177–183. PMID: 18384536.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Heavy metal concentrations in hair of newly imported China-origin rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta)
- Infection of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Producing Shigella flexneri in Children Attending a Childcare Center in Korea
- Degenerative joint disease in the temporomandibular joint with fibrous ankylosis in a rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta)
- Shigella flexneri bacteremia: A case report
- Reference values of hematological and biochemical parameters in young-adult cynomolgus monkey (Macaca fascicularis) and rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) anesthetized with ketamine hydrochloride