Ann Clin Microbiol.
2013 Jun;16(2):75-80. 10.5145/ACM.2013.16.2.75.
Dissemination of an AbaR-type Resistance Island in Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Global Clone 2 in Daejeon of Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Far East University, Eumseong, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. azaza72@naver.com
- 3Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Jeonju Kijeon College, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 1431768
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2013.16.2.75
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Acinetobacter baumannii resistance islands (AbaRs) are transposons that have the role of important vehicles for the acquisition of antimicrobial resistance genes, and are associated with multidrug resistance (MDR). In this study, we aimed to determine the AbaRs in MDR A. baumannii global clone 2 (GC2) clinical isolates obtained from a university hospital in Daejeon, Korea.
METHODS
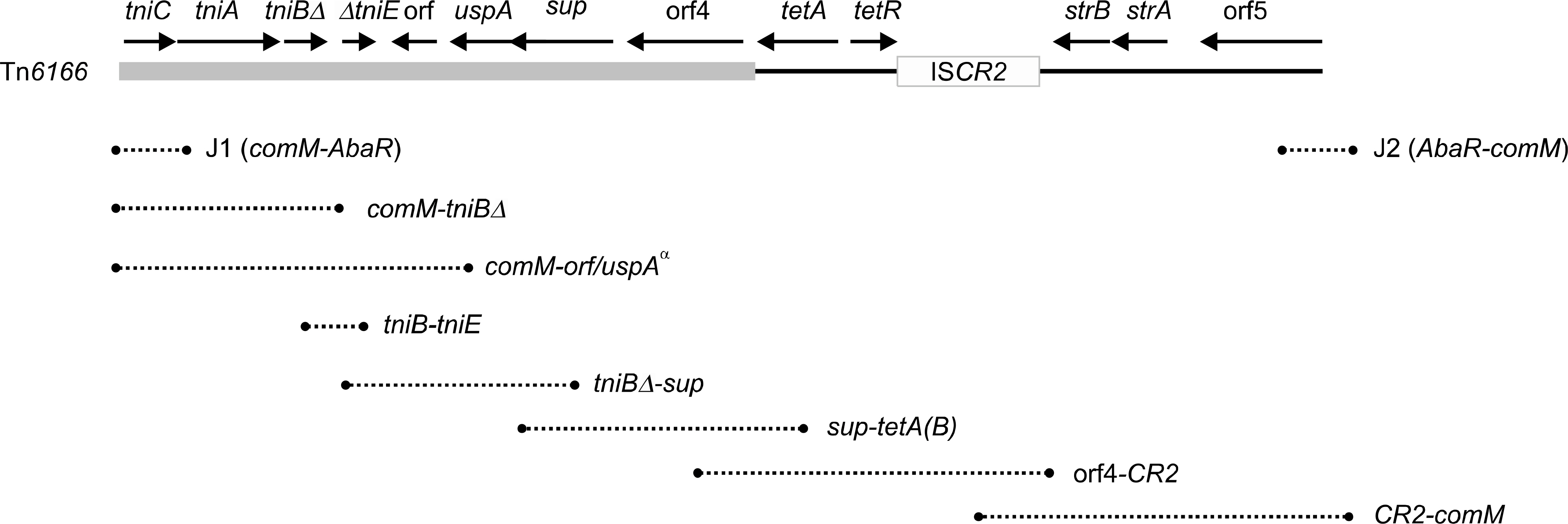
This study included 17 MDR A. baumannii strains isolated in Daejeon, Korea. The minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined by Etest. A. baumannii isolates were characterized using 2 multiplex PCR assays and a multilocus sequence typing (MLST) scheme. To detect and characterize AbaRs, PCR and PCR mapping experiments were performed.
RESULTS
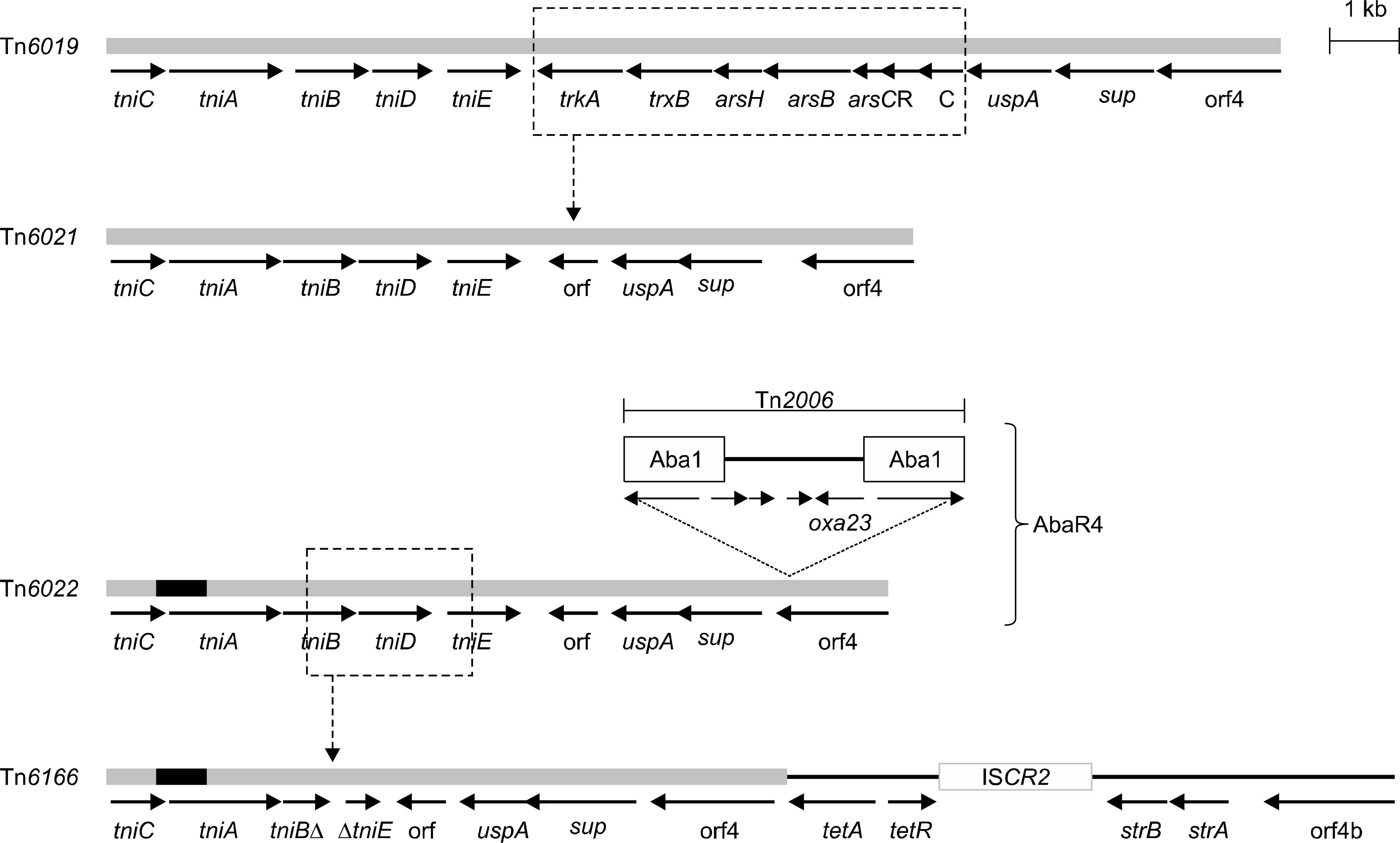
All 17 MDR A. baumannii isolates tested in this study belonged to GC2 and contained 5 sequence types (STs): 75, 92, 137, 138, and 357. Tn6166 that contains antimicrobial resistance genes and is also known as AbaR4a was found in all 17 GC2 strains. This is the first report of Tn6166 in MDR A. baumannii GC2 isolates in Korea. In contrast, AbaR4 was not found in the GC2 isolates.
CONCLUSION
Tn6166 has been disseminated among MDR A. baumannii GC2 isolates in Korea. Further investigation is needed to recover the various types of AbaRs in MDR A. baumannii GC2 isolates in Korea are responsible for the multiple antimicrobial resistance mechanisms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Hamouda A., Evans BA., Towner KJ., Amyes SG. Characterization of epidemiologically unrelated Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from four continents by use of multilocus sequence typing, pulsed- field gel electrophoresis, and sequence-based typing of bla OXA-51-like genes. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:2476–83.2.Petersen A., Guardabassi L., Dalsgaard A., Olsen JE. Class I integrons containing a dhfrI trimethoprim resistance gene cassette in aquatic Acinetobacter spp. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000. 182:73–6.3.Post V., White PA., Hall RM. Evolution of AbaR-type genomic resistance islands in multiply antibiotic-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010. 65:1162–70.4.Nigro SJ., Hall RM. Antibiotic resistance islands in A320 (RUH134), the reference strain for Acinetobacter baumannii global clone 2. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012. 67:335–8.5.Hamidian M., Hall RM. AbaR4 replaces AbaR3 in a carba-penem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolate belonging to global clone 1 from an Australian hospital. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011. 66:2484–91.6.Kim DH., Choi JY., Jung SI., Thamlikitkul V., Song JH., Ko KS. AbaR4-type resistance island including the bla OXA-23 gene in Acinetobacter nosocomialis isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. 56:4548–9.7.Lee HY., Chang RC., Su LH., Liu SY., Wu SR., Chuang CH, et al. Wide spread of Tn2006 in an AbaR4-type resistance island among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in Taiwan. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012. 40:163–7.8.Sung JY., Kwon KC., Cho HH., Koo SH. Antimicrobial resistance determinants in imipenem-nonsusceptible Acinetobacter calcoaceticus- baumannii complex isolated in Daejeon, Korea. Korean J Lab Med. 2011. 31:265–70.9.Lee K., Yong D., Jeong SH., Chong Y. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter spp.: increasingly problematic nosocomial pathogens. Yonsei Med J. 2011. 52:879–91.10.Turton JF., Gabriel SN., Valderrey C., Kaufmann ME., Pitt TL. Use of sequence-based typing and multiplex PCR to identify clonal lineages of outbreak strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007. 13:807–15.11.Bartual SG., Seifert H., Hippler C., Luzon MA., Wisplinghoff H., Rodríguez-Valera F. Development of a multilocus sequence typing scheme for characterization of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:4382–90.12.Bonnin RA., Poirel L., Nordmann P. AbaR-type transposon structures in Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012. 67:234–6.13.Seputiene V., Povilonis J., Suziedeliene E. Novel variants of AbaR resistance islands with a common backbone in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates of European clone II. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. 56:1969–73.14.Adams MD., Goglin K., Molyneaux N., Hujer KM., Lavender H., Jamison JJ, et al. Comparative genome sequence analysis of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Bacteriol. 2008. 190:8053–64.15.Shaikh F., Spence RP., Levi K., Ou HY., Deng Z., Towner KJ, et al. ATPase genes of diverse multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates frequently harbour integrated DNA. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009. 63:260–4.16.Turton JF., Baddal B., Perry C. Use of the accessory genome for characterization and typing of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 2011. 49:1260–6.17.Lee HY., Chang RC., Su LH., Liu SY., Wu SR., Chuang CH, et al. Wide spread of Tn2006 in an AbaR4-type resistance island among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in Taiwan. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012. 40:163–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- AbaR7, a Genomic Resistance Island Found in Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates in Daejeon, Korea
- Clinical Features of Acinetobacter Baumannii Keratitis
- Sentinel Surveillance and Molecular Epidemiology of Multidrug Resistance Bacteria
- Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter spp.: Increasingly Problematic Nosocomial Pathogens