Ann Lab Med.
2012 Sep;32(5):324-330. 10.3343/alm.2012.32.5.324.
AbaR7, a Genomic Resistance Island Found in Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates in Daejeon, Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Far East University, Eumseong, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. shkoo@cnu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Jeonju Kijeon College, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 1387346
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2012.32.5.324
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Acinetobacter baumannii resistance islands (AbaRs) have been recently recognized as mobile genetic elements that harbor multiple resistance determinants and are associated with multidrug resistance (MDR). In the present study, we aimed to determine the AbaRs conferring multiple antimicrobial resistance and their clonal relatedness to MDR A. baumannii clinical isolates obtained from a university hospital in Daejeon, Korea.
METHODS
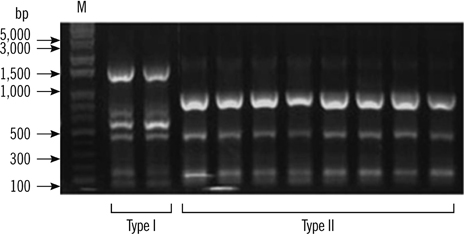
This study included 29 MDR A. baumannii strains isolated in Daejeon, Korea. The minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined by Etest. A. baumannii isolates were characterized using the 2 multiplex PCR assays and multilocus sequence typing (MLST) scheme. To detect and characterize AbaRs, PCR and PCR mapping experiments were performed.
RESULTS
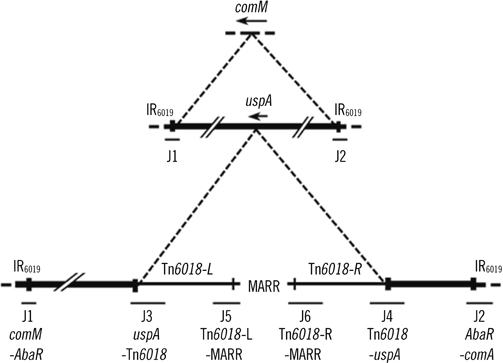
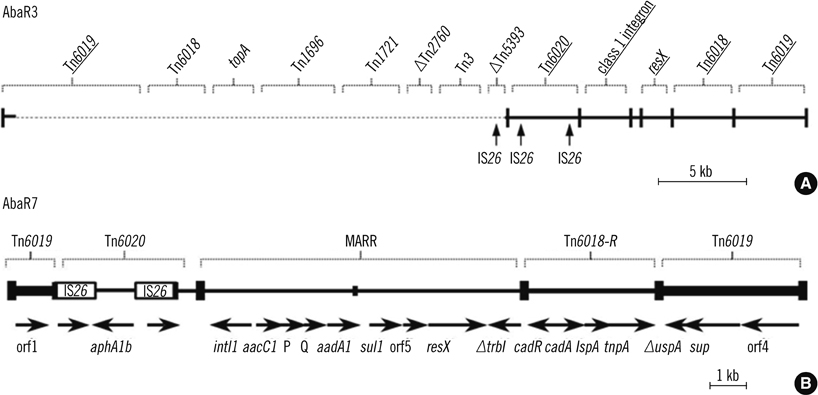
Twenty-seven of the 29 isolates belonged to the European (EU) clone II lineage and contained 5 sequence types (STs) (75, 92, 137, 138, and 357). In this study, ST357 was confirmed for the first time in Korea. Only 2 of the 29 isolates belonged to the EU clone I lineage, and were confirmed as ST109. These 2 isolates harbored the 22-kb AbaR7 aacC1-orfP-orfQ-aadA1 gene cassette array. In contrast, AbaR was not found in EU clone II isolates.
CONCLUSIONS
This is the first study that attempted to determine the AbaRs in MDR A. baumannii isolates in Korea. We found 2 EU clone I isolates (ST109) that harbored AbaR7.
MeSH Terms
-
Acinetobacter baumannii/drug effects/*isolation & purification/metabolism
Anti-Bacterial Agents/pharmacology
Bacterial Proteins/*genetics/metabolism
Drug Resistance, Multiple, Bacterial/drug effects
Humans
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction
Republic of Korea
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Figure
Reference
-
1. Peleg AY, Seifert H, Paterson DL. Acinetobacter baumannii: emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2008. 21:538–582.2. Krizova L, Dijkshoorn L, Nemec A. Diversity and evolution of AbaR genomic resistance islands in Acinetobacter baumannii strains of European clone I. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. 55:3201–3206.3. Petersen A, Guardabassi L, Dalsgaard A, Olsen JE. Class I integrons containing a dhfrI trimethoprim resistance gene cassette in aquatic Acinetobacter spp. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000. 182:73–76.4. Post V, White PA, Hall RM. Evolution of AbaR-type genomic resistance islands in multiply antibiotic-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010. 65:1162–1170.5. Sung JY, Kwon KC, Cho HH, Koo SH. Antimicrobial resistance determinants in imipenem-nonsusceptible Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumannii complex isolated in Daejeon, Korea. Korean J Lab Med. 2011. 31:265–270.6. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Twentieth informational supplement, M100-S20. 2010. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.7. Ko KS, Suh JY, Kwon KT, Jung SI, Park KH, Kang CI, et al. High rates of resistance to colistin and polymyxin B in subgroups of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from Korea. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007. 60:1163–1167.8. Lee K, Yong D, Jeong SH, Chong Y. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter spp.: increasingly problematic nosocomial pathogens. Yonsei Med J. 2011. 52:879–891.9. Turton JF, Gabriel SN, Valderrey C, Kaufmann ME, Pitt TL. Use of sequence-based typing and multiplex PCR to identify clonal lineages of outbreak strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007. 13:807–815.10. Bou G, Cervero G, Dominguez MA, Quereda C, Martinez-Beltran J. PCR-based DNA fingerprinting (REP-PCR, AP-PCR) and pulsed field gel electrophoresis characterization of a nosocomial outbreak caused by imipenem- and meropenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2000. 6:635–643.11. Bartual SG, Seifert H, Hippler C, Luzon MA, Wisplinghoff H, Rodríguez-Valera F. Development of a multilocus sequence typing scheme for characterization of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:4382–4390.12. Higgins PG, Dammhayn C, Hackel M, Seifert H. Global spread of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010. 65:233–238.13. Hamidian M, Hall RM. AbaR4 replaces AbaR3 in a carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolate belonging to global clone 1 from an Australian hospital. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011. 66:2484–2491.14. Turton JF, Kaufmann ME, Glover J, Coelho JM, Warner M, Pike R, et al. Detection and typing of integrons in epidemic strains of Acinetobacter baumannii found in the United Kingdom. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:3074–3082.15. Adams MD, Goglin K, Molyneaux N, Hujer KM, Lavender H, Jamison JJ, et al. Comparative genome sequence analysis of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Bacteriol. 2008. 190:8053–8064.16. Shaikh F, Spence RP, Levi K, Ou HY, Deng Z, Towner KJ, et al. ATPase genes of diverse multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates frequently harbor integrated DNA. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009. 63:260–264.17. Mugnier PD, Poirel L, Naas T, Nordmann P. Worldwide dissemination of the blaOXA-23 carbapenemase gene of Acinetobacter baumannii. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010. 16:35–40.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dissemination of an AbaR-type Resistance Island in Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Global Clone 2 in Daejeon of Korea
- Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- The Genetic Characteristics of Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Coproducing 16S rRNA Methylase armA and Carbapenemase OXA-23
- Clinical Features of Acinetobacter Baumannii Keratitis
- Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter spp.: Increasingly Problematic Nosocomial Pathogens