Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2013 Apr;17(2):163-167. 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.2.163.
Effect of Cholera Toxin Administered Supraspinally or Spinally on the Blood Glucose Level in Pain and D-Glucose Fed Animal Models
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Natural Medicine, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon 200-702, Korea. hwsuh@hallym.ac.kr
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon 200-702, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Asan Medical Center and University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 138-736, Korea.
- KMID: 1429388
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.2.163
Abstract
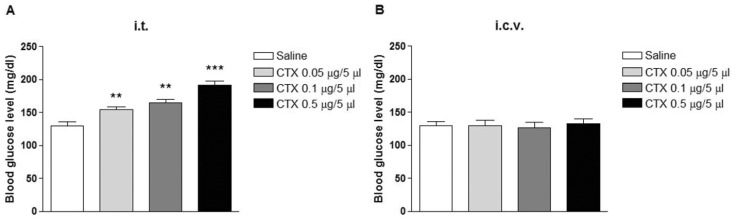
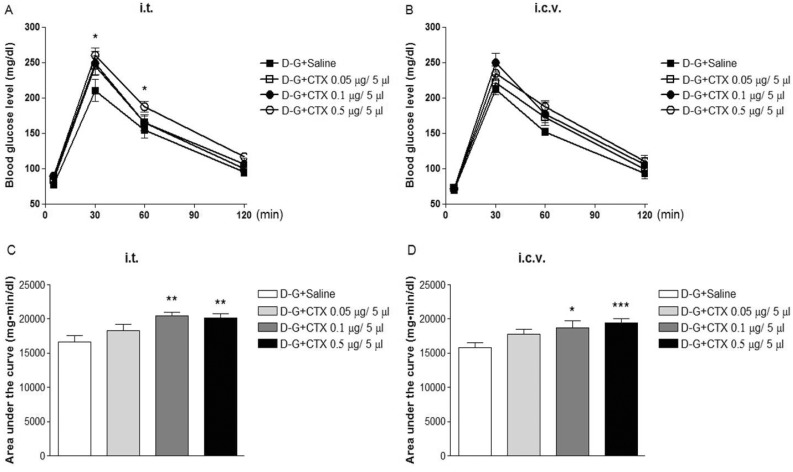
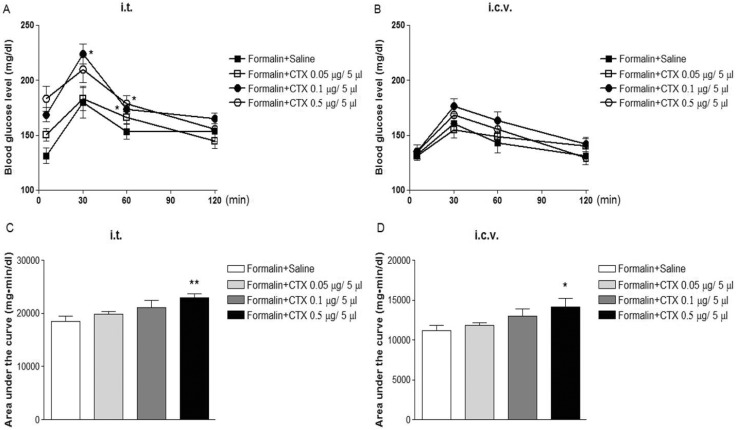
- In the present study, the effect of intrathecal (i.t.) or intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration with cholera toxin (CTX) on the blood glucose level was examined in ICR mice. The i.t. treatment with CTX alone for 24 h dose-dependently increased the blood glucose level. However, i.c.v. treatment with CTX for 24 h did not affect the blood glucose level. When mice were orally fed with D-glucose (2 g/kg), the blood glucose level reached to a maximum level at 30 min and almost returned to the control level at 120 min after D-glucose feeding. I.c.v. pretreatment with CTX increased the blood glucose level in a potentiative manner, whereas i.t. pretreatment with CTX increased the blood glucose level in an additive manner in a D-glucose fed group. In addition, the blood glucose level was increased in formalin-induced pain animal model. I.c.v. pretreatment with CTX enhanced the blood glucose level in a potentiative manner in formalin-induced pain animal model. On the other hand, i.t. pretreatment with CTX increased the blood glucose level in an additive manner in formalin-induced pain animal model. Our results suggest that CTX administered supraspinally or spinally differentially modulates the regulation of the blood glucose level in D-glucose fed model as well as in formalin-induced pain model.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Anti-Depressant Like Effect of Methyl Gallate Isolated from
Acer barbinerve in Mice
Jin-Koo Lee
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;17(5):441-446. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.5.441.
Reference
-
1. de los Santos-Arteaga M, Sierra-Domínguez SA, Fontanella GH, Delgado-García JM, Carrión AM. Analgesia induced by dietary restriction is mediated by the kappa-opioid system. J Neurosci. 2003; 23:11120–11126. PMID: 14657170.2. Blackburn-Munro G, Blackburn-Munro R. Pain in the brain: are hormones to blame? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 14:20–27. PMID: 12475608.
Article3. Won JS, Suh HW. The comparative analysis of proenkephalin mRNA expression induced by cholera toxin and pertussis toxin in primary cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2001; 88:83–93. PMID: 11295234.
Article4. Bullock BP, Habener JF. Phosphorylation of the cAMP response element binding protein CREB by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A and glycogen synthase kinase-3 alters DNA-binding affinity, conformation, and increases net charge. Biochemistry. 1998; 37:3795–3809. PMID: 9521699.
Article5. Kaupp UB. The cyclic nucleotide-gated channels of vertebrate photoreceptors and olfactory epithelium. Trends Neurosci. 1991; 14:150–157. PMID: 1710853.6. Facci L, Skaper SD, Favaron M, Leon A. A role for gangliosides in astroglial cell differentiation in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1988; 106:821–828. PMID: 2831235.7. Chung KM, Lee KC, Song DK, Huh SO, Choi MR, Kim YH, Suh HW. Differential modulatory roles of cholera toxin and pertussis toxin in the regulation of pain responses induced by excitatory amino acids administered intrathecally in mice. Brain Res. 2000; 867:246–249. PMID: 10837821.
Article8. Suh HW, Song DK, Sim YB, Choi YS, Kim YH. Effect of intrathecal or intracerebroventricular pretreatment with cholera toxin on antinociception induced by opioids administered intracerebroventricularly in mice. Pharmacol Commun. 1995; 6:187–294.9. Sim YB, Park SH, Kang YJ, Jung JS, Ryu OH, Choi MG, Suh HW. Various pain stimulations cause an increase of the blood glucose level. Animal Cells Syst. 2012; 16:385–390.
Article10. Kwon MS, Shim EJ, Seo YJ, Choi SS, Lee JY, Lee HK, Suh HW. Differential modulatory effects of cholera toxin and pertussis toxin on pain behavior induced by TNF-alpha, interleukin-1beta and interferon-gamma injected intrathecally. Arch Pharm Res. 2005; 28:582–586. PMID: 15974446.11. Hylden JL, Wilcox GL. Intrathecal substance P elicits a caudally-directed biting and scratching behavior in mice. Brain Res. 1981; 217:212–215. PMID: 6167328.
Article12. Haley TJ. Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral administration of drugs of unrelated structure to conscious mice. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1957; 110:239–244. PMID: 13435953.13. Hunskaar S, Berge OG, Hole K. Antinociceptive effects of orphenadrine citrate in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985; 111:221–226. PMID: 4018126.
Article14. Sim YB, Park SH, Kang YJ, Jung JS, Ryu OH, Choi MG, Suh HW. Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) increases pain behavior and the blood glucose level: possible involvement of sympathetic nervous system. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012; 102:170–176. PMID: 22548833.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Repaglinide, but Not Nateglinide Administered Supraspinally and Spinally Exerts an Anti-Diabetic Action in D-Glucose Fed and Streptozotocin-Treated Mouse Models
- Effect of Sulfonylureas Administered Centrally on the Blood Glucose Level in Immobilization Stress Model
- Effect of D-glucose feeding on mortality induced by sepsis
- The Modulatory Role of Spinally Located Histamine Receptors in the Regulation of the Blood Glucose Level in D-Glucose-Fed Mice
- Effect of pertussis toxin pretreated centrally on blood glucose level induced by stress