Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2013 Dec;17(6):493-497. 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.6.493.
Repaglinide, but Not Nateglinide Administered Supraspinally and Spinally Exerts an Anti-Diabetic Action in D-Glucose Fed and Streptozotocin-Treated Mouse Models
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Natural Medicine, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon 200-702, Korea. hwsuh@hallym.ac.kr
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon 200-702, Korea.
- KMID: 2285475
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.6.493
Abstract
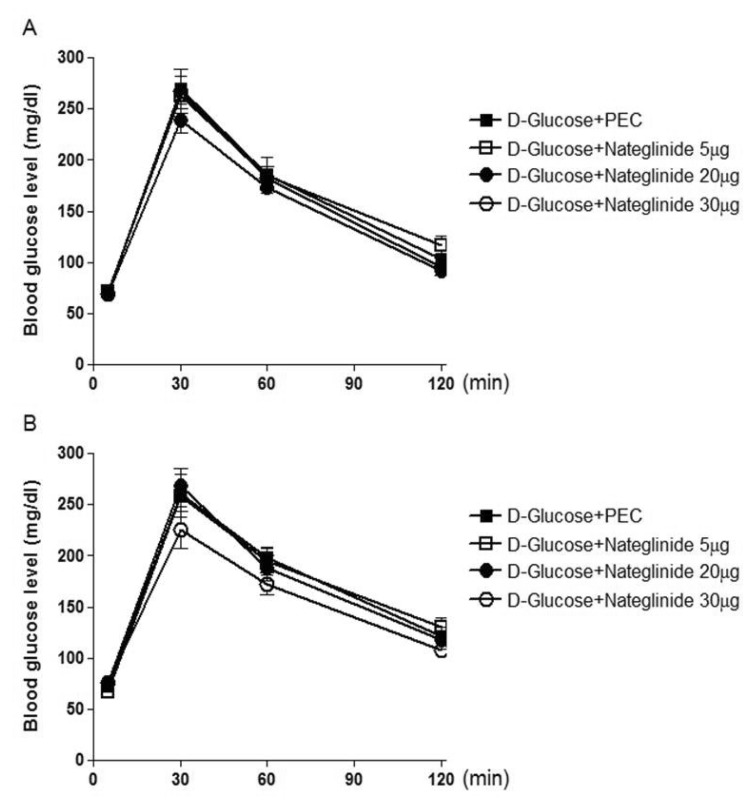
- We have recently demonstrated that some anti-diabetic drugs such as biguanide and thizolidinediones administered centrally modulate the blood glucose level, suggesting that orally administered anti-diabetic drugs may modulate the blood glucose level by acting on central nervous system. The present study was designed to explore the possible action of another class of anti-diabetic drugs, glinidies, administered centrally on the blood glucose level in ICR mice. Mice were administered intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.) or intrathecally (i.t.) with 5 to 30 microg of repaglinide or nateglinide in D-glucose-fed and streptozotocin (STZ)-treated models. We found that i.c.v. or i.t. injection with repaglinide dose-dependently attenuated the blood glucose level in D-glucose-fed model, whereas i.c.v. or i.t. injection with nateglinide showed no modulatory action on the blood glucose level in D-glucose-fed model. Furthermore, the effect of repaglinide administered i.c.v. or i.t. on the blood glucose level in STZ-treated model was studied. We found that repaglinide administered i.c.v. slightly enhanced the blood glucose level in STZ-treated model. On the other hand, i.t. injection with repaglinide attenuated the blood glucose level in STZ-treated model. The plasma insulin level was enhanced by repaglinide in D-glucose-fed model, but repaglinide did not affect the plasma insulin level in STZ-treated model. In addition, nateglinide did not alter the plasma insulin level in both D-glucose-fed and STZ-treated models. These results suggest that the anti-diabetic action of repaglinide appears to be, at least, mediated via the brain and the spinal cord as revealed in both D-glucose fed and STZ-treated models.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of Sulfonylureas Administered Centrally on the Blood Glucose Level in Immobilization Stress Model
Naveen Sharma, Yun-Beom Sim, Soo-Hyun Park, Su-Min Lim, Sung-Su Kim, Jun-Sub Jung, Jae-Seung Hong, Hong-Won Suh
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015;19(3):197-202. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.3.197.
Reference
-
1. Cheng AY, Fantus IG. Oral antihyperglycemic therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. CMAJ. 2005; 172:213–226. PMID: 15655244.
Article2. Farret A, Lugo-Garcia L, Galtier F, Gross R, Petit P. Pharmacological interventions that directly stimulate or modulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cell: implications for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2005; 19:647–656. PMID: 16313276.
Article3. Horton ES, Clinkingbeard C, Gatlin M, Foley J, Mallows S, Shen S. Nateglinide alone and in combination with metformin improves glycemic control by reducing mealtime glucose levels in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23:1660–1665. PMID: 11092289.
Article4. Perfetti R, Barnett PS, Mathur R, Egan JM. Novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1998; 14:207–225. PMID: 9816470.
Article5. Sunaga Y, Gonoi T, Shibasaki T, Ichikawa K, Kusama H, Yano H, Seino S. The effects of mitiglinide (KAD-1229), a new anti-diabetic drug, on ATP-sensitive K+ channels and insulin secretion: comparison with the sulfonylureas and nateglinide. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001; 431:119–125. PMID: 11716850.6. Bokvist K, Hoy M, Buschard K, Holst JJ, Thomsen MK, Gromada J. Selectivity of prandial glucose regulators: nateglinide, but not repaglinide, accelerates exocytosis in rat pancreatic A-cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999; 386:105–111. PMID: 10611470.
Article7. Bryan J, Crane A, Vila-Carriles WH, Babenko AP, Aguilar-Bryan L. Insulin secretagogues, sulfonylurea receptors and K(ATP) channels. Curr Pharm Des. 2005; 11:2699–2716. PMID: 16101450.
Article8. Gribble FM, Reimann F. Differential selectivity of insulin secretagogues: mechanisms, clinical implications, and drug interactions. J Diabetes Complications. 2003; 17(2 Suppl):11–15. PMID: 12623163.9. Henquin JC. Pathways in beta-cell stimulus-secretion coupling as targets for therapeutic insulin secretagogues. Diabetes. 2004; 53(Suppl 3):S48–S58. PMID: 15561921.
Article10. Islam MS. The ryanodine receptor calcium channel of betacells: molecular regulation and physiological significance. Diabetes. 2002; 51:1299–1309. PMID: 11978625.11. Benzo CA. Minireview. The hypothalamus and blood glucose regulation. Life Sci. 1983; 32:2509–2515. PMID: 6304437.12. Ohnuma H, Yamatani K, Igarashi M, Sugiyama K, Manaka H, Tominaga M, Sasaki H. Intracerebroventricular injection of methylatropine suppresses insulin response to oral glucose load in rats. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1996; 57:43–48. PMID: 8867084.
Article13. Petit F, Jarrous A, Dickinson RD, Molina PE, Abumrad NN, Lang CH. Contribution of central and peripheral adrenergic stimulation to IL-1 alpha-mediated glucoregulation. Am J Physiol. 1994; 267:E49–E56. PMID: 8048512.
Article14. Sala F, Menna G, Bricolo A, Young W. Role of glycemia in acute spinal cord injury. Data from a rat experimental model and clinical experience. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999; 890:133–154. PMID: 10668421.
Article15. Ritter S, Bugarith K, Dinh TT. Immunotoxic destruction of distinct catecholamine subgroups produces selective impairment of glucoregulatory responses and neuronal activation. J Comp Neurol. 2001; 432:197–216. PMID: 11241386.
Article16. Sim YB, Park SH, Kang YJ, Jung JS, Ryu OH, Choi MG, Suh HW. Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) increases pain behavior and the blood glucose level: possible involvement of sympathetic nervous system. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012; 102:170–176. PMID: 22548833.
Article17. Sim YB, Park SH, Kang YJ, Jung JS, Ryu OH, Choi MG, Suh HW. Various pain stimulations cause an increase of the blood glucose level. Animal Cells Syst. 2012; 16:385–390.
Article18. Sim YB, Park SH, Kang YJ, Kim SS, Kim CH, Kim SJ, Jung JS, Ryu OH, Choi MG, Suh HW. Central anti-diabetic action of biguanide and thizolidinediones in D-glucose fed and streptozotocin-treated mouse models. Neurosci Lett. 2012; 528:73–77. PMID: 22960361.
Article19. Hylden JL, Wilcox GL. Intrathecal substance P elicits a caudally-directed biting and scratching behavior in mice. Brain Res. 1981; 217:212–215. PMID: 6167328.
Article20. Haley TJ. Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral administration of drugs of unrelated structure to conscious mice. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1957; 110:239–244. PMID: 13435953.21. Zhang Y, Zhou J, Corll C, Porter JR, Martin RJ, Roane DS. Evidence for hypothalamic K+(ATP) channels in the modulation of glucose homeostasis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004; 492:71–79. PMID: 15145709.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Cholera Toxin Administered Supraspinally or Spinally on the Blood Glucose Level in Pain and D-Glucose Fed Animal Models
- Sorghum extract exerts an anti-diabetic effect by improving insulin sensitivity via PPAR-gamma in mice fed a high-fat diet
- Effects of Legume Supplementation on the Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Lipid Peroxidation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Effect of Capsaicin on Glucose Metabolism in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Effects of Fluvastatin on the Pharmacokinetics of Repaglinide: Possible Role of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein Inhibition by Fluvastatin