J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Jul;26(7):919-926. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.7.919.
CD44 Disruption Attenuates Murine Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kdh2109@eulji.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Medical-Laboratory Science, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1094264
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.7.919
Abstract
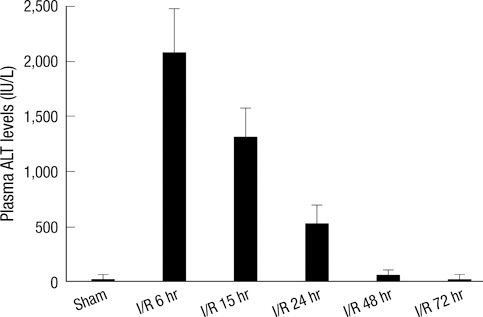
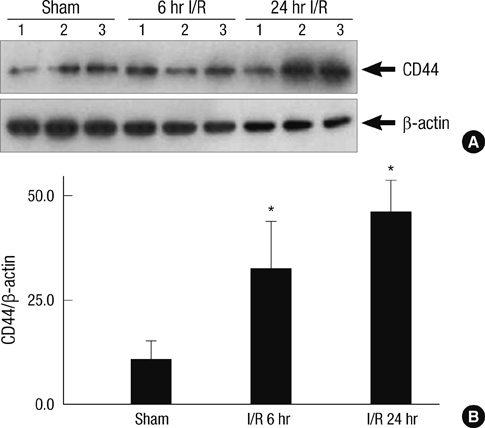
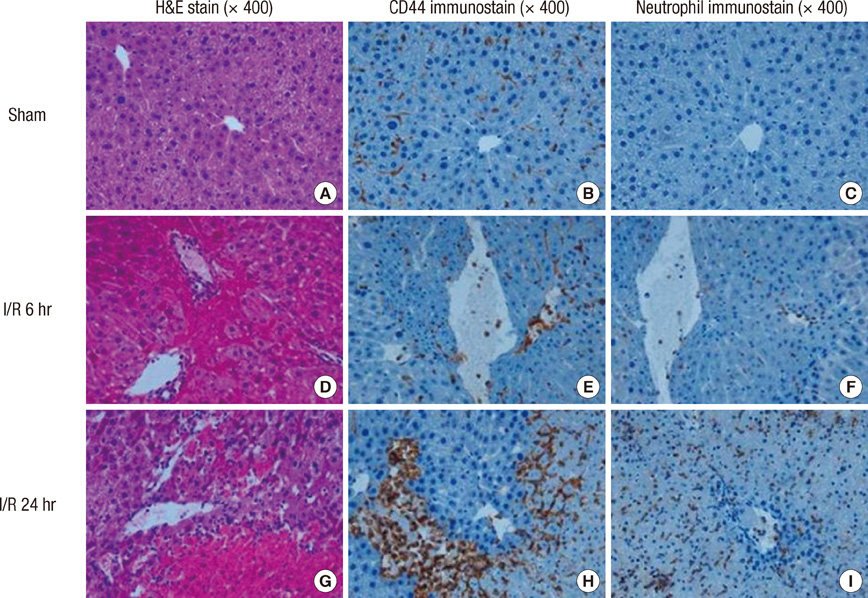
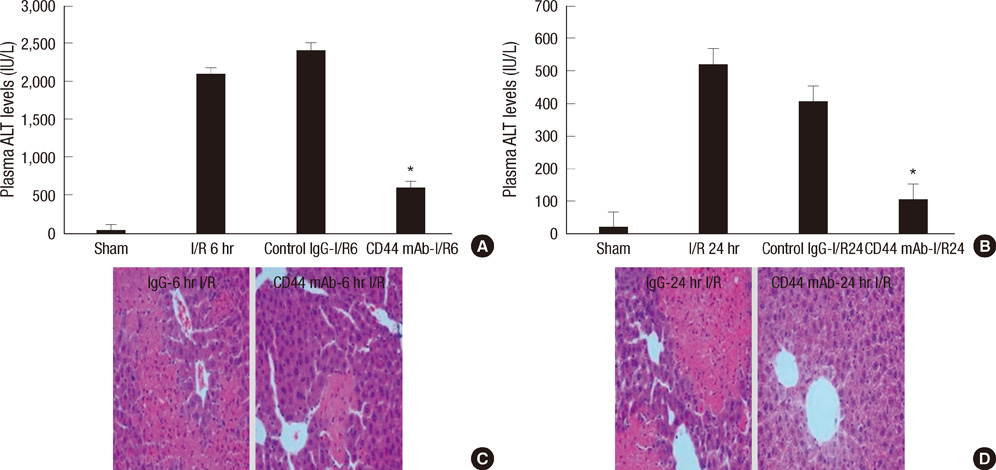
- Neutrophil adhesion and migration are critical in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Despite very strong preclinical data, recent clinical trials failed to show a protective effect of anti-adhesion therapy in reperfusion injury. Therefore, the aim of this study was to assess the role of CD44 in neutrophil infiltration and liver injury from hepatic I/R. In this study, using a partial hepatic ischemic model in vivo, we determined the potential role of CD44 in neutrophil infiltration and liver injury from I/R. Reperfusion caused significant hepatocellular injury as it was determined by plasma ALT levels and liver histopathology. The injury was associated with a marked neutrophil recruitment and CD44 expression into the ischemic livers. Administration of anti-CD44 antibody to mice reduced the infiltration of neutrophil into the ischemic tissue, associated with liver function preservation. These results support crucial roles of CD44 in neutrophil recruitment and infiltration leading to liver damage in hepatic I/R injury. Moreover, they provide the rationale for targeting to CD44 as a potential therapeutic approach in liver I/R injury.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Alanine Transaminase/blood
Animals
Antibodies/immunology/pharmacology
Antigens, CD44/immunology/metabolism/*physiology
Cytokines/metabolism
Disease Models, Animal
Liver/*metabolism/pathology
Male
Mice
Mice, Inbred C57BL
Neutrophils/immunology/physiology
Reperfusion Injury/metabolism/pathology/*prevention & control
Figure
Reference
-
1. Selzner N, Rudiger H, Graf R, Clavien PA. Protective strategies against ischemic injury of the liver. Gastroenterology. 2003. 125:917–936.2. Fondevila C, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW. Hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury: a fresh look. Exp Mol Pathol. 2003. 74:86–93.3. Rhee JE, Jung SE, Shin SD, Suh GJ, Noh DY, Youn YK, Oh SK, Choe KJ. The effects of antioxidants and nitric oxide modulators on hepatic ischemic-reperfusion injury in rats. J Korean Med Sci. 2002. 17:502–506.4. Monson KM, Dowlatshahi S, Crockett ET. CXC-chemokine regulation and neutrophil trafficking in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in P-selectin/ICAM-1 deficient mice. J Inflamm (Lond). 2007. 4:11.5. Jaeschke H. Preservation injury: mechanisms, prevention and consequences. J Hepatol. 1996. 25:774–780.6. Colletti LM, Kunkel SL, Walz A, Burdick MD, Kunkel RG, Wilke CA, Strieter RM. The role of cytokine networks in the local liver injury following hepatic ischemia/reperfusion in the rat. Hepatology. 1996. 23:506–514.7. Jaeschke H, Farhood A. Neutrophil and Kupffer cell-induced oxidant stress and ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1991. 260:G355–G362.8. McDonald B, McAvoy EF, Lam F, Gill V, de la Motte C, Savani RC, Kubes P. Interaction of CD44 and hyaluronan is the dominant mechanism for neutrophil sequestration in inflamed liver sinusoids. J Exp Med. 2008. 205:915–927.9. Liu L, Kubes P. Molecular mechanisms of leukocyte recruitment: organ-specific mechanisms of action. Thromb Haemost. 2003. 89:213–220.10. Jaeschke H. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and preconditioning. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003. 284:G15–G26.11. Jaeschke H, Smith CW. Cell adhesion and migration. III. Leukocyte adhesion and transmigration in the liver vasculature. Am J Physiol. 1997. 273:G1169–G1173.12. Wong J, Johnston B, Lee SS, Bullard DC, Smith CW, Beaudet AL, Kubes P. A minimal role for selectins in the recruitment of leukocytes into the inflamed liver microvasculature. J Clin Invest. 1997. 99:2782–2790.13. Harlan JM, Winn RK. Leukocyte-endothelial interactions: clinical trials of anti-adhesion therapy. Crit Care Med. 2002. 30:5 Suppl. S214–S219.14. Lee WY, Kubes P. Leukocyte adhesion in the liver: distinct adhesion paradigm from other organs. J Hepatol. 2008. 48:504–512.15. Tsung A, Sahai R, Tanaka H, Nakao A, Fink MP, Lotze MT, Yang H, Li J, Tracey KJ, Geller DA, Billiar TR. The nuclear factor HMGB1 mediates hepatic injury after murine liver ischemia-reperfusion. J Exp Med. 2005. 201:1135–1143.16. Weiss L, Slavin S, Reich S, Cohen P, Shuster S, Stern R, Kaganovsky E, Okon E, Rubinstein AM, Naor D. Induction of resistance to diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice by targeting CD44 with a specific monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:285–290.17. Budd RC, Cerottini JC, Horvath C, Bron C, Pedrazzini T, Howe RC, MacDonald HR. Distinction of virgin and memory T lymphocytes. Stable acquisition of the Pgp-1 glycoprotein concomitant with antigenic stimulation. J Immunol. 1987. 138:3120–3129.18. Foster LC, Arkonac BM, Sibinga NE, Shi C, Perrella MA, Haber E. Regulation of CD44 gene expression by the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1998. 273:20341–20346.19. Mikecz K, Brennan FR, Kim JH, Glant TT. Anti-CD44 treatment abrogates tissue edema and leukocyte infiltration in murine arthritis. Nat Med. 1995. 1:558–563.20. Brocke S, Piercy C, Steinman L, Weissman IL, Veromaa T. Antibodies to CD44 and integrin alpha4, but not L-selectin prevent central nervous system inflammation and experimental encephalomyelitis by blocking secondary leukocyte recruitment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. 96:6896–6901.21. Moon C, Jeong CW, Kim H, Ahn M, Kim S, Shin T. Expression of CD44 adhesion molecule in rat testis with ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Vet Med Sci. 2006. 68:761–764.22. Jaeschke H. Mechanisms of liver injury. II. Mechanisms of neutrophil-induced liver cell injury during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion and other acute inflammatory conditions. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006. 290:G1083–G1088.23. Cerqueira NF, Hussni CA, Yoshida WB. Pathophysiology of mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion: a review. Acta Cir Bras. 2005. 20:336–343.24. Heinzelmann M, Mercer-Jones MA, Passmore JC. Neutrophils and renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999. 34:384–399.25. Rouschop KM, Roelofs JJ, Claessen N, da Costa Martins P, Zwaginga JJ, Pals ST, Weening JJ, Florquin S. Protection against renal ischemia reperfusion injury by CD44 disruption. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005. 16:2034–2043.26. Wang Q, Teder P, Judd NP, Noble PW, Doerschuk CM. CD44 deficiency leads to enhanced neutrophil migration and lung injury in Escherichia coli pneumonia in mice. Am J Pathol. 2002. 161:2219–2228.27. Khan AI, Kerfoot SM, Heit B, Liu L, Andonegui G, Ruffell B, Johnson P, Kubes P. Role of CD44 and hyaluronan in neutrophil recruitment. J Immunol. 2004. 173:7594–7601.28. Kuboki S, Shin T, Huber N, Eismann T, Galloway E, Schuster R, Blanchard J, Edwards MJ, Lentsch AB. Hepatocyte signaling through CXC chemokine receptor-2 is detrimental to liver recovery after ischemia/reperfusion in mice. Hepatology. 2008. 48:1213–1223.29. de Vries B, Köhl J, Leclercq WK, Wolfs TG, van Bijnen AA, Heeringa P, Buurman WA. Complement factor C5a mediates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury independent from neutrophils. J Immunol. 2003. 170:3883–3889.30. Kato A, Gabay C, Okaya T, Lentsch AB. Specific role of interleukin-1 in hepatic neutrophil recruitment after ischemia/reperfusion. Am J Pathol. 2002. 161:1797–1803.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury with respect to oxidative stress and inflammatory response: a narrative review
- An Experimental Study in Mice for Inducing the Optimal Hepatic Ischemia Followed by Reperfusion
- SP600125, a selective JNK inhibitor, aggravates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury
- Experiment of Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury of the Cirrhotic Liver in the Murine Mouse Model
- The Effects of Glutathione and Prostaglandin E1 on Recovery of Hepatic Function during Hepatic Ischemia and Reperfusion in Rabbits