J Vet Sci.
2006 Jun;7(2):111-117. 10.4142/jvs.2006.7.2.111.
Development of immunoassays for the detection of kanamycin in veterinary fields
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute for Zoonotic Disease, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea.
- 2Department of Biochemistry, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea. vetlee@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1059194
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2006.7.2.111
Abstract
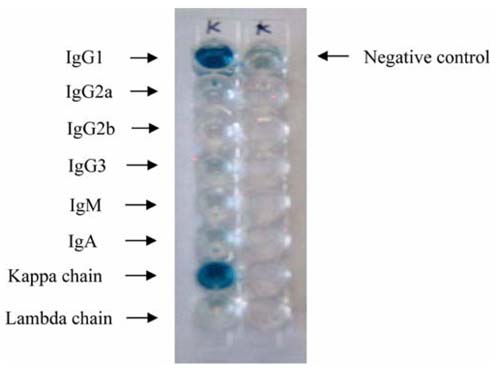
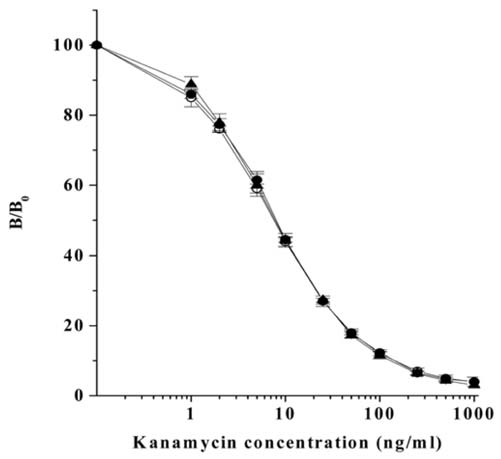
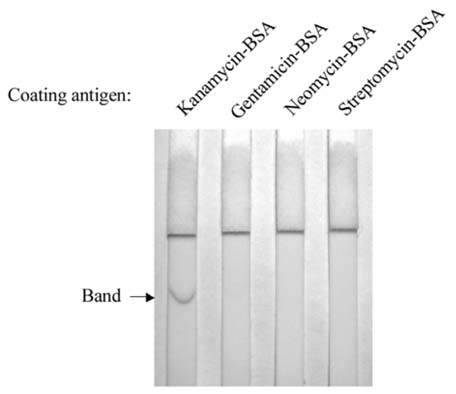
- Monoclonal antibody against kanamycin was prepared, and competitive direct ELISA and immunochromatographic assay were developed using the antibody to detect kanamycin in animal plasma and milk. The monoclonal antibody produced was identified to be IgG1, which has a kappa light chain. No cross-reactivity of the antibody was detected with other aminoglycosides, indicating that the monoclonal antibody was highly specific for kanamycin. Based on competitive direct ELISA, the detection limits of kanamycin were determined to be 1.1 ng/ml in PBS, 1.4 ng/ml in plasma, and 1.0 ng/ml in milk. The concentration of intramuscularly injected kanamycin was successfully monitored in rabbit plasma with competitive direct ELISA. Based on the colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic assay, the detection limits of kanamycin were estimated to be about 6-8 ng/ml in PBS, plasma, and milk. The immunochromatographic assay would be suitable for rapid and simple screening of kanamycin residues in veterinary medicine. Screened positives can be confirmed using a more sensitive laboratory method such as competitive direct ELISA. Therefore, the assays developed in this study could be used to complement each other as well as other laboratory findings. Moreover, instead of slaughtering the animals to obtain test samples, these methods could be applied to determine kanamycin concentration in the plasma of live animals.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cleveland CB, Francke DE, Heller WM, Kepler JA, Provost GP, Reilly MJ. AHFS Drug Information. 1990. Bethesda: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists Press;51–67.2. DeCastro AF, Place JD, Lam CT, Patel C. Determination of kanamycin concentration in serum by substrate-labeled fluorescent immunoassay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986. 29:961–964.
Article3. Dixon DE, Warner RL, Ram BP, Hart LP, Pestka JJ. Hybridoma cell line production of specific monoclonal antibody to the mycotoxins zearalenone and a-zearalenol. J Agric Food Chem. 1987. 35:122–126.
Article4. European Agency for the Evaluation of Medical Products (EMEA). 2003. London: Regulation No. EMEA/MRL/886/03-FINAL.5. Finitzo-Hieber T, McCracken GH Jr, Roeser RJ, Allen DA, Chrane DF, Morrow J. Ototoxicity in neonates treated with gentamicin and kanamycin: results of a four-year controlled follow-up study. Pediatrics. 1979. 63:443–450.
Article6. Fourmy D, Yoshizawa S, Puglisi JD. Paromomycin binding induces a local conformational change in the A-site of 16S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1998. 277:333–345.
Article7. Haasnoot W, Stouten P, Cazemier G, Lommen A, Nouws JFM, Keukens HJ. Immunochemical detection of aminoglycosides in milk and kidney. Analyst. 1999. 124:301–305.
Article8. Harlow ED, Lane D. Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual. 1988. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory;196–214.9. Isoherranen N, Soback S. Chromatographic methods for analysis of aminoglycoside antibiotics. J AOAC Int. 1999. 82:1017–1045.
Article10. Kitagawa T, Fujiwara K, Tomonoh S, Takahashi K, Koida M. Enzyme immunoassays of kanamycin group antibiotics with high sensitivities using anti-kanamycin as a common antiserum: reasoning and selection of a heterologous enzyme label. J Biochem. 1983. 94:1165–1172.
Article11. Kubo H, Kobayashi Y, Nishikawa T. Rapid method for determination of kanamycin and dibekacin in serum by use of high-pressure liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985. 28:521–523.
Article12. Lewis JE, Nelson JC, Elder HA. Radioimmunoassay of an antibiotic: gentamicin. Nat New Biol. 1972. 239:214–216.
Article13. Maitra SK, Yoshikawa TT, Guze LB, Schotz MC. Determination of aminoglycoside antibiotics in biological fluids: a review. Clin Chem. 1979. 25:1361–1367.
Article14. Putalun W, Morinaga O, Tanaka H, Shoyama Y. Development of a one-step immunochromatographic strip test for the detection of sennosides A and B. Phytochem Anal. 2004. 15:112–116.
Article15. Ren YG, Martinez J, Kirsebom LA, Virtanen A. Inhibition of Klenow DNA polymerase and poly(A)-specific ribonuclease by aminoglycosides. RNA. 2002. 8:1393–1400.
Article16. Martindale W, Reynolds JEF. The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 1993. 30th ed. London: Pharmaceutical Press;109–113.17. Riviere JE, Spoo JW. Adams HR, editor. Aminoglycoside antibiotics. Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2001. 8th ed. Ames: Iowa State University Press;841–867.18. Shyu RH, Shyu HF, Liu HW, Tang SS. Colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic assay for detection of ricin. Toxicon. 2002. 40:255–258.
Article19. Watanabe H, Satake A, Matsumoto M, Kido Y, Tsuji A, Ito K, Maeda M. Monoclonal-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunochromatographic rapid assay for monensin. Analyst. 1998. 123:2573–2578.
Article20. Watanabe H, Satake A, Kido Y, Tsuji A. Production of monoclonal antibody and development of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for kanamycin in biological matrices. Analyst. 1999. 124:1611–1615.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of allergic contact dermatitis caused by kanamycin
- Kanamycin as a Ca++ Antagonist
- Comparison of the Effect of Cefadroxil and Kanamycin Sulfate in the Treatment of Male Gonorrhoea
- The standardization of the Korean-English veterinary medical terminology
- Prevention and Dissociation of the Platelet Aggregation in a Patient with EDTA-dependent Pseudothrombocytopenia by Supplementation of Kanamycin: A Case Report