Ann Lab Med.
2024 Mar;44(2):174-178. 10.3343/alm.2023.0250.
A Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Simultaneously Determining Meropenem and Linezolid in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Biochemistry, Institute of Pediatrics, Jagiellonian University Medical College, Krakow, Poland
- KMID: 2553388
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.0250
Abstract
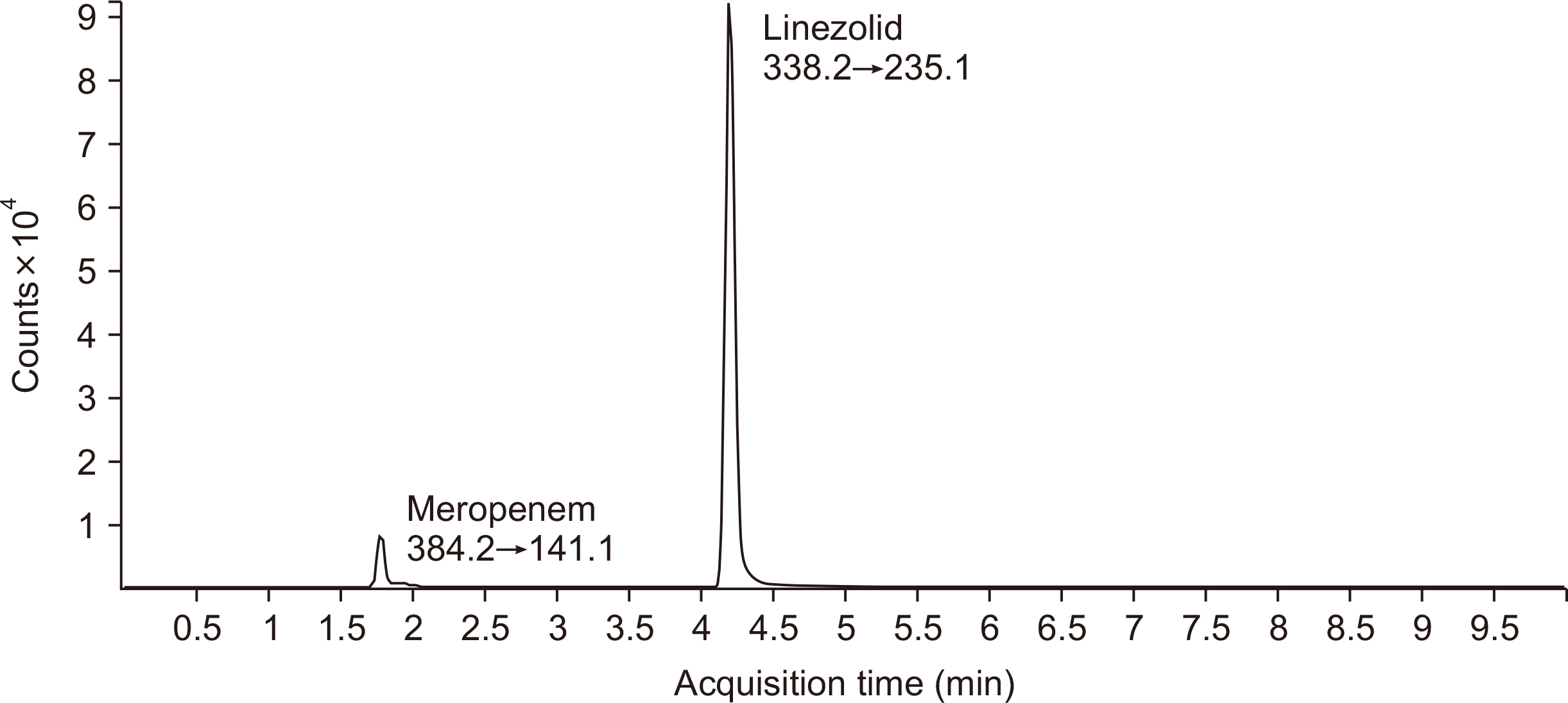
- Antibiotic therapy requires appropriate dosage of drugs for effective treatment. Too low antibiotic concentrations may lead to treatment failure and the development of resistant pathogens, whereas overdosing may cause neurological side effects or hemolytic diseases. Meropenem and linezolid are used only in the treatment of serious infections or when other antibiotics are no longer effective as well as for treating central nervous system infections. It is difficult or sometimes even impossible to predict the relation between dosing of antibiotics and its cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentration; thus, a method of determining antibiotics not only in the blood but also in the CSF is needed. Analytical method validation is an integral part of good laboratory practice and ensures high accuracy of the results. We performed complete validation process according to the Food and Drug Administration and European Medicine Agency, covering the aspects precision, specificity, accuracy, recovery, limit of detection, limit of quantification, stability, carry-over, and matrix effects. Our liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous measurement of meropenem and linezolid in different matrix meets all the acceptance criteria. The method was successfully applied to determine meropenem and linezolid concentrations in serum and CSF samples obtained from children treated with these antibiotics
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mian P, Flint RB, Tibboel D, van den Anker JN, Allegaert K, Koch BCP. 2017; Therapeutic drug monitoring in neonates: what makes them unique? Curr Pharm Des. 23:5790–800. DOI: 10.2174/1381612823666170926143820. PMID: 28950825.
Article2. Wicha SG, Kees MG, Kuss J, Kloft C. 2015; Pharmacodynamic and response surface analysis of linezolid or vancomycin combined with meropenem against Staphylococcus aureus. Pharm Res. 32:2410–8. DOI: 10.1007/s11095-015-1632-3. PMID: 25630818.
Article3. Tan YC, Gill AK, Kim KS. 2015; Treatment strategies for central nervous system infections: an update. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 16:187–203. DOI: 10.1517/14656566.2015.973851. PMID: 25328149.
Article4. Schneider F, Gessner A, El-Najjar N. 2022; Efficacy of vancomycin and meropenem in central nervous system infections in children and adults: current update. Antibiotics (Basel). 11:173. DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11020173. PMID: 35203776. PMCID: PMC8868565.
Article5. U.S Food and Drug Administration, Bioanalytical method validation guidance for industry. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/bioanalytical-method-validation-guidance-industry. Updated on May 2018.6. European Medicines Agency. Guideline on bioanalytical method validation. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-bioanalytical-method-validation_en.pdf. Updated on July 2011.7. Nau R, Sörgel F, Eiffert H. 2010; Penetration of drugs through the blood-cerebrospinal fluid/blood-brain barrier for treatment of central nervous system infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 23:858–83. DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00007-10. PMID: 20930076. PMCID: PMC2952976.
Article8. Tsona A, Metallidis S, Foroglou N, Selviaridis P, Chrysanthidis T, Lazaraki G, et al. 2010; Linezolid penetration into cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue. J Chemother. 22:17–9. DOI: 10.1179/joc.2010.22.1.17. PMID: 20227987.
Article9. Germovsek E, Lutsar I, Kipper K, Karlsson MO, Planche T, Chazallon C, et al. 2018; Plasma and CSF pharmacokinetics of meropenem in neonates and young infants: results from the NeoMero studies. J Antimicrob Chemother. 73:1908–16. DOI: 10.1093/jac/dky128. PMID: 29684147. PMCID: PMC6005047.
Article10. Cojutti P, Maximova N, Crichiutti G, Isola M, Pea F. 2015; Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic evaluation of linezolid in hospitalized paediatric patients: a step toward dose optimization by means of therapeutic drug monitoring and Monte Carlo simulation. J Antimicrob Chemother. 70:198–206. DOI: 10.1093/jac/dku337. PMID: 25182066.
Article11. Roth T, Fiedler S, Mihai S, Parsch H. 2017; Determination of meropenem levels in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. Biomed Chromatogr. 31:e3880. DOI: 10.1002/bmc.3880. PMID: 27797104.
Article12. Milla P, Ferrari F, Muntoni E, Sartori M, Ronco C, Arpicco S. 2020; Validation of a simple and economic HPLC-UV method for the simultaneous determination of vancomycin, meropenem, piperacillin and tazobactam in plasma samples. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1148:122151. DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122151. PMID: 32417718.
Article13. Decosterd LA, Mercier T, Ternon B, Cruchon S, Guignard N, Lahrichi S, et al. 2020; Validation and clinical application of a multiplex high performance liquid chromatography - tandem mass spectrometry assay for the monitoring of plasma concentrations of 12 antibiotics in patients with severe bacterial infections. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1157:122160. DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122160. PMID: 32891946.
Article14. Phillips OA, Abdel-Hamid ME, Al-Hassawi NA. 2001; Determination of linezolid in human plasma by LC-MS-MS. Analyst. 126:609–14. DOI: 10.1039/b100076o. PMID: 11394301.
Article15. Rehm S, Rentsch KM. 2020; HILIC LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of cefepime, imipenem and meropenem. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 186:113289. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113289. PMID: 32428767.
Article16. Zander J, Maier B, Suhr A, Zoller M, Frey L, Teupser D, et al. 2015; Quantification of piperacillin, tazobactam, cefepime, meropenem, ciprofloxacin and linezolid in serum using an isotope dilution UHPLC-MS/MS method with semi-automated sample preparation. Clin Chem Lab Med. 53:781–91. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2014-0746. PMID: 25301676.
Article17. Paal M, Zoller M, Schuster C, Vogeser M, Schütze G. 2018; Simultaneous quantification of cefepime, meropenem, ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin, linezolid and piperacillin in human serum using an isotope-dilution HPLC-MS/MS method. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 152:102–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.01.031. PMID: 29414000.
Article18. Ferrari D, Ripa M, Premaschi S, Banfi G, Castagna A, Locatelli M. 2019; LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of linezolid, meropenem, piperacillin and teicoplanin in human plasma samples. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 169:11–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.02.037. PMID: 30826487.
Article19. Barco S, Bandettini R, Maffia A, Tripodi G, Castagnola E, Cangemi G. 2015; Quantification of piperacillin, tazobactam, meropenem, ceftazidime, and linezolid in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J Chemother. 27:343–7. DOI: 10.1179/1973947814Y.0000000209. PMID: 25178412.
Article20. Sun H, Xing H, Tian X, Zhang X, Yang J, Wang P. 2022; UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of 14 antimicrobials in human plasma and cerebrospinal fluid: application to therapeutic drug monitoring. J Anal Methods Chem. 2022:7048605. DOI: 10.1155/2022/7048605. PMID: 35036023. PMCID: PMC8754666.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Identification of Novel Metabolic Proteins Released by Insulin Signaling of the Rat Hypothalmus Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
- Sporozoite proteome analysis of Cryptosporidium parvum by one-dimensional SDS-PAGE and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
- Development and validation of analytical method for the determination of radotinib in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- A Novel Simultaneous Determination of Sarpogrelate and its Active Metabolite (M-1) in Human Plasma, Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Clinical Application
- Multiplex Assay of Second-Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs in Dried Blood Spots Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry