Ann Lab Med.
2021 Jan;41(1):108-113. 10.3343/alm.2021.41.1.108.
A Sensitive and Specific Liquid ChromatographyTandem Mass Spectrometry Assay for Simultaneous Quantification of Salivary Melatonin and Cortisol: Development and Comparison With Immunoassays
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Neurology, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- 3Department of Neurology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2512740
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2021.41.1.108
Abstract
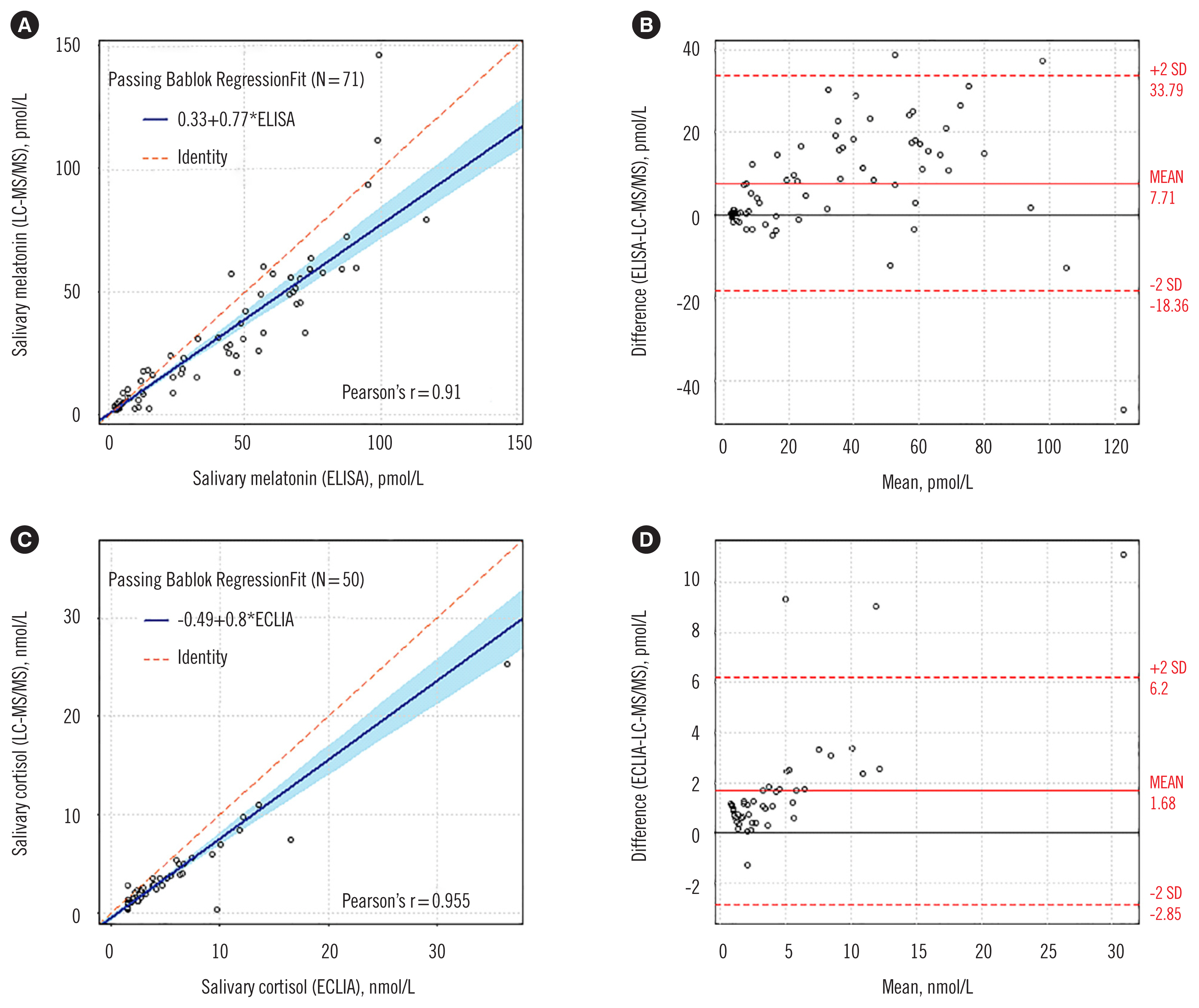
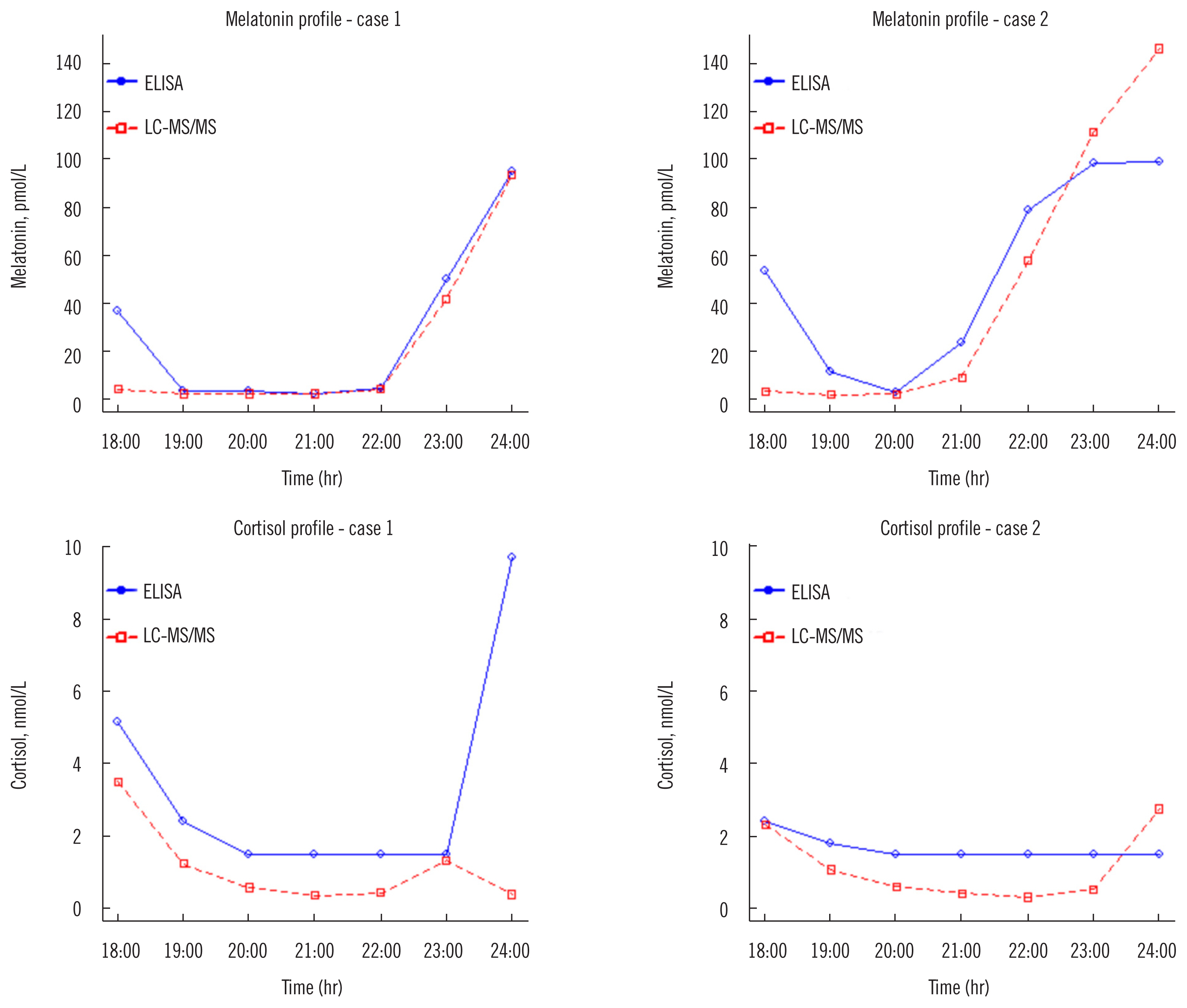
- Melatonin and cortisol are clinically important for diagnosing sleep and mood disorders. We developed and validated a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/ MS) assay for simultaneous measurement of salivary melatonin and cortisol concentrations according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute guidelines. Additionally, we compared the LC-MS/MS assay with immunoassays, ELISA (Direct Salivary Melatonin Elisa EK-DSM, Bühlmann Laboratories AG, Schönenbuch, Switzerland) and electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (Cortisol II, Roche, Mannheim, Germany), using 121 saliva samples. The LC-MS/MS assay exhibited good performance in terms of linearity, precision, accuracy, limit of detection, lower limit of quantification, extraction recovery, carry-over, and matrix effect. The LC-MS/MS assay and immunoassays showed strong correlation (Pearson’s r = 0.910 for melatonin, r = 0.955 for cortisol), but demonstrated a significant mean bias of 23.2% (range 54.0–143.7%) for melatonin and 48.9% (range 59.7–184.7%) for cortisol. Our LC-MS/MS assay provided more sensitive and reliable salivary melatonin and cortisol quantification results compared with immunoassays.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Back to the Basics of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
Young Jin Kim, Soo-Youn Lee, Mina Hur
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(2):119-120. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.2.119.
Reference
-
1. Claustrat B, Leston J. Melatonin: physiological effects in humans. Neurochirurgie. 2015; 61:77–84.
Article2. Debono M, Ghobadi C, Rostami-Hodjegan A, Huatan H, Campbell MJ, Newell-Price J, et al. Modified-release hydrocortisone to provide circadian cortisol profiles. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94:1548–54.
Article3. Blair J, Adaway J, Keevil B, Ross R. Salivary cortisol and cortisone in the clinical setting. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2017; 24:161–8.
Article4. Voultsios A, Kennaway DJ, Dawson D. Salivary melatonin as a circadian phase marker: validation and comparison to plasma melatonin. J Biol Rhythms. 1997; 12:457–66.
Article5. Jung C, Greco S, Nguyen HH, Ho JT, Lewis JG, Torpy DJ, et al. Plasma, salivary and urinary cortisol levels following physiological and stress doses of hydrocortisone in normal volunteers. BMC Endocr Disord. 2014; 14:91.
Article6. Taylor AE, Keevil B, Huhtaniemi IT. Mass spectrometry and immunoassay: how to measure steroid hormones today and tomorrow. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015; 173:D1–12.
Article7. Kennaway DJ. A critical review of melatonin assays: past and present. J Pineal Res. 2019; 67:e12572.
Article8. Doi M, Sekizawa N, Tani Y, Tsuchiya K, Kouyama R, Tateno T, et al. Late-night salivary cortisol as a screening test for the diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome in Japan. Endocr J. 2008; 55:121–6.
Article9. Turpeinen U, Hämäläinen E. Determination of cortisol in serum, saliva and urine. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 27:795–801.
Article10. van Faassen M, Bischoff R, Kema IP. Relationship between plasma and salivary melatonin and cortisol investigated by LC-MS/MS. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017; 55:1340–8.
Article11. Fustinoni S, Polledri E, Mercadante R. High-throughput determination of cortisol, cortisone, and melatonin in oral fluid by on-line turbulent flow liquid chromatography interfaced with liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2013; 27:1450–60.
Article12. Jensen MA, Hansen AM, Abrahamsson P, N⊘rgaard AW. Development and evaluation of a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous determination of salivary melatonin, cortisol and testosterone. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2011; 879:2527–32.
Article13. Jensen MA, Mortier L, Koh E, Keevil B, Hyttinen S, Hansen ÅM. An interlaboratory comparison between similar methods for determination of melatonin, cortisol and testosterone in saliva. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2014; 74:454–61.
Article14. CLSI. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry methods. 1st ed. CLSI C62-A. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2014.15. Vogeser M, Kratzsch J, Ju Bae Y, Bruegel M, Ceglarek U, Fiers T, et al. Multicenter performance evaluation of a second generation cortisol assay. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017; 55:826–35.
Article16. Shirtcliff EA, Granger DA, Schwartz E, Curran MJ. Use of salivary biomarkers in biobehavioral research: cotton-based sample collection methods can interfere with salivary immunoassay results. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2001; 26:165–73.
Article17. Nölte I, Lütkhoff AT, Stuck BA, Lemmer B, Schredl M, Findeisen P, et al. Pineal volume and circadian melatonin profile in healthy volunteers: an interdisciplinary approach. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009; 30:499–505.
Article18. Riemann D, Klein T, Rodenbeck A, Feige B, Horny A, Hummel R, et al. Nocturnal cortisol and melatonin secretion in primary insomnia. Psychiatry Res. 2002; 113:17–27.
Article19. Corbalán-Tutau D, Madrid JA, Nicolás F, Garaulet M. Daily profile in two circadian markers “melatonin and cortisol” and associations with metabolic syndrome components. Physiol Behav. 2014; 123:231–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cortisol Measurements in Cushing's Syndrome: Immunoassay or Mass Spectrometry?
- Comparison of Direct and Extraction Immunoassay Methods With Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Measurement of Urinary Free Cortisol for the Diagnosis of Cushing’s Syndrome
- Clinical and Technical Aspects in Free Cortisol Measurement
- Dried Blood Spot Multiplexed Steroid Profiling Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Korean Neonates
- Recommendations for the Use of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry in the Clinical Laboratory: Part I. Implementation and Management