Dried Blood Spot Multiplexed Steroid Profiling Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Korean Neonates
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Green Cross Laboratories, Yongin, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. nayadoo@hanmail.net sy117.lee@samsung.com
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2431603
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.263
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) using immunoassays for 17α-hydroxyprogesterone generates many false-positive results. We developed and validated a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) assay for simultaneous quantification of nine steroid hormones in dried blood spot (DBS) samples, and established reference intervals for these hormones.
METHODS
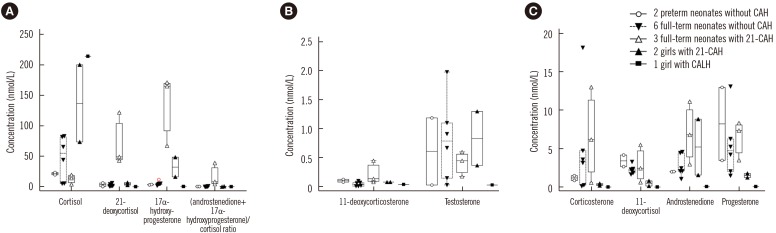
We examined our method for linearity, precision, accuracy, extraction recovery, and matrix effects and determined the reference intervals of cortisol, 17α-hydroxyproges-terone, 11-deoxycortisol, 21-deoxycortisol, androstenedione, corticosterone, 11-deoxycorticosterone, testosterone, and progesterone in 1,146 DBS samples (from 272 preterm and 874 full-term neonates). Immunoassay and LC-MS/MS methods were compared for 17α-hydroxyprogesterone. Fourteen additional samples were tested to validate the clinical applicability of the LC-MS/MS method.
RESULTS
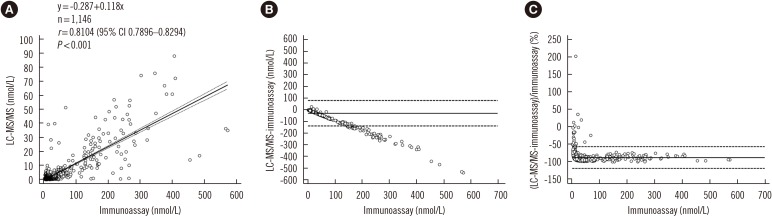
The linearity range was 2.8-828.0 nmol/L for cortisol and 0.9-40.0 nmol/L for the other steroids (R2>0.99). Intra-day and inter-day precision CVs were 2.52-12.26% and 3.53-17.12%, respectively. Accuracy was 80.81-99.94%, and extraction recovery and matrix effects were 88.0-125.4% and 61.7-74.2%, respectively. There was a negative bias, with higher values measured by immunoassay compared with LC-MS/MS (r=0.8104, P < 0.0001). The LC-MS/MS method was successfully applied to the analysis of nine steroids in DBS for screening and diagnosis of CAH using the 14 additional samples.
CONCLUSIONS
Our method enables highly sensitive and specific assessment of nine steroids from DBS and is a promising tool for clinical analysis of CAH.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adrenal Hyperplasia, Congenital
Androstenedione
Bias (Epidemiology)
Chromatography, Liquid*
Corticosterone
Cortodoxone
Diagnosis
Humans
Hydrocortisone
Immunoassay
Infant, Newborn*
Mass Screening
Mass Spectrometry
Methods
Progesterone
Steroids
Tandem Mass Spectrometry*
Testosterone
Androstenedione
Corticosterone
Cortodoxone
Hydrocortisone
Progesterone
Steroids
Testosterone
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Back to the Basics of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
Young Jin Kim, Soo-Youn Lee, Mina Hur
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(2):119-120. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.2.119.Comprehensive Evaluation of the NeoBase 2 Non-derivatized MSMS Assay and Exploration of Analytes With Significantly Different Concentrations Between Term and Preterm Neonates
Beomki Lee, Won Young Heo, Jee Ah Kim, Hyun-Seung Lee, Narae Hwang, Hyung-Doo Park, Se In Sung, Yun Sil Chang, Won Soon Park, Soo-Youn Lee
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(2):153-166. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.2.153.Clinical Usefulness of Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Low Serum Testosterone Measurement
Sung-Eun Cho, Jungsun Han, Ju-Hee Park, Euna Park, Geun Young Kim, Jun Hyung Lee, Ahram Yi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee, Yeo-Min Yun
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(1):19-28. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.19.
Reference
-
1. Rauh M. Steroid measurement with LC-MS/MS in pediatric endocrinology. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009; 301:272–281. PMID: 19007847.2. Rossi C, Calton L, Hammond G, Brown HA, Wallace AM, Sacchetta P, et al. Serum steroid profiling for congenital adrenal hyperplasia using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 2010; 411:222–228. PMID: 19931522.3. Janzen N, Sander S, Terhardt M, Steuerwald U, Peter M, Das AM, et al. Rapid steroid hormone quantification for congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) in dried blood spots using UPLC liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Steroids. 2011; 76:1437–1442. PMID: 21839763.4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. NSQAP: Newborn Screening Quality Assurance Program. Laboratory Quality Assurance and Standardization Programs. Updated on Sep 2018. https://www.cdc.gov/labstandards/nsqap.html.5. Travers S, Martinerie L, Bouvattier C, Boileau P, Lombès M, Pussard E. Multiplexed steroid profiling of gluco- and mineralocorticoids pathways using a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017; 165:202–211. PMID: 27339652.6. Kim B, Lee MN, Park HD, Kim JW, Chang YS, Park WS, et al. Dried blood spot testing for seven steroids using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with reference interval determination in the Korean population. Ann Lab Med. 2015; 35:578–585. PMID: 26354345.7. Seo JY, Park HD, Kim JW, Oh HJ, Yang JS, Chang YS, et al. Steroid profiling for congenital adrenal hyperplasia by tandem mass spectrometry as a second-tier test reduces follow-up burdens in a tertiary care hospital: a retrospective and prospective evaluation. J Perinat Med. 2014; 42:121–127. PMID: 23989111.8. Magnisali P, Chalioti MB, Livadara T, Mataragas M, Paliatsiou S, Malamitsi-Puchner A, et al. Simultaneous quantification of 17α-OH progesterone, 11-deoxycortisol, Δ4-androstenedione, cortisol and cortisone in newborn blood spots using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2011; 879:1565–1572.9. Horowitz GL, Altaie S, Boyd JC. Defining, establishing, and verifying reference intervals in the clinical laboratory, approved guideline. EP28-A3. 3rd ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2010.10. International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH). ICH topic Q2 (R1) Validation of analytical procedures: text and methodology. Int Conf Harmon. 2005; 1994:17.11. Lacey JM, Minutti CZ, Magera MJ, Tauscher AL, Casetta B, McCann M, et al. Improved specificity of newborn screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia by second-tier steroid profiling using tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2004; 50:621–625. PMID: 14656905.12. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Bioanalytical method validation guidance for industry 2018. Updated on Sep 2018. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidances/ucm070107.pdf.13. European Medicines Agency Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP). Guideline on bioanalytical method validation. 2011. Updated on Sep 2018. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2011/08/WC500109686.pdf.14. CLSI. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: A statistical approach; approved guideline. CLSI document EP06A. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2003.15. CLSI. Spectrometry for androgen and estrogen measurements in serum. CLSI guideline C57. 1st ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2015.16. CLSI. Screening by tandem mass spectrometry. CLSI guideline NBS04. 2nd ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2017.17. CLSI. Measurement procedure comparison and bias estimation using patient samples. CLSI guideline EP09c. 3rd ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2018.18. Dietzen DJ, Bennett MJ, Lo SF, Grey VL, Jones PM. Dried blood spot reference intervals for steroids and amino acids in a neonatal cohort of the National Children's Study. Clin Chem. 2016; 62:1658–1667. PMID: 27784706.19. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Republic of Korea. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation 2013;12. Updated on Sep 2018. http://www.nifds.go.kr/brd/m_15/view.do?seq=7018.20. Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chem. 2003; 75:3019–3030. PMID: 12964746.21. Hicks RA, Yee JK, Mao CS, Graham S, Kharrazi M, Lorey F, et al. Precursor-to-product ratios reflect biochemical phenotype in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Metabolomics. 2014; 10:123–131. PMID: 24489528.22. IUPAC. IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (The “Gold Book”). version 2.3.3. 2014. Updated on Nov 2018. http://goldbook.iupac.org/.23. Janzen N, Sander S, Terhardt M, Peter M, Sander J. Fast and direct quantification of adrenal steroids by tandem mass spectrometry in serum and dried blood spots. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008; 861:117–122.24. Janzen N, Peter M, Sander S, Steuerwald U, Terhardt M, Holtkamp U, et al. Newborn screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia: additional steroid profile using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:2581–2589. PMID: 17456574.25. Boelen A, Ruiter AF, Claahsen-van der Grinten HL, Endert E, Ackermans MT. Determination of a steroid profile in heel prick blood using LC-MS/MS. Bioanalysis. 2016; 8:375–384. PMID: 26891684.26. Fiet J, Le Bouc Y, Guéchot J, Hélin N, Maubert MA, Farabos D, et al. A liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectometry profile of 16 serum steroids, including 21-deoxycortisol and 21-deoxycorticosterone, for management of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Endocr Soc. 2017; 1:186–201. PMID: 29264476.27. Monostori P, Szabó P, Marginean O, Bereczki C, Karg E. Concurrent confirmation and differential diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia from dried blood spots: application of a second-tier LC-MS/MS assay in a cross-border cooperation for newborn screening. Horm Res Paediatr. 2015; 84:311–318. PMID: 26397944.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dried Blood Spot Testing for Seven Steroids Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry With Reference Interval Determination in the Korean Population
- Multiplex Assay of Second-Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs in Dried Blood Spots Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- Sporozoite proteome analysis of Cryptosporidium parvum by one-dimensional SDS-PAGE and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
- Identification of Novel Metabolic Proteins Released by Insulin Signaling of the Rat Hypothalmus Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
- A Simple and Rapid Method Based on Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Measurement of alpha-L-Iduronidase Activity in Dried Blood Spots: An Application to Mucopolysaccharidosis I (Hurler) Screening