Dried Blood Spot Testing for Seven Steroids Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry With Reference Interval Determination in the Korean Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. suddenbz@skku.edu
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363260
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.6.578
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Conventional screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) using immunoassays generates a large number of false-positive results. A more specific liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method has been introduced to minimize unnecessary follow-ups. However, because of limited data on its use in the Korean population, LC-MS/MS has not yet been incorporated into newborn screening programs in this region. The present study aims to develop and validate an LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of seven steroids in dried blood spots (DBS) for CAH screening, and to define age-specific reference intervals in the Korean population.
METHODS
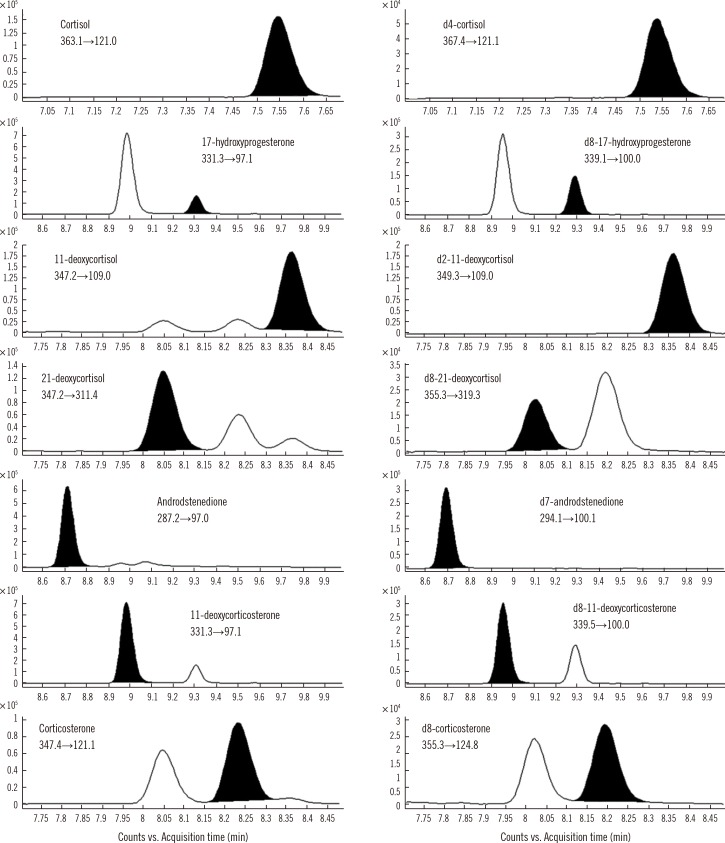
We developed and validated an LC-MS/MS method to determine the reference intervals of cortisol, 17-hydroxyprogesterone, 11-deoxycortisol, 21-deoxycortisol, androstenedione, corticosterone, and 11-deoxycorticosterone simultaneously in 453 DBS samples. The samples were from Korean subjects stratified by age group (78 full-term neonates, 76 premature neonates, 89 children, and 100 adults).
RESULTS
The accuracy, precision, matrix effects, and extraction recovery were satisfactory for all the steroids at three concentrations; values of intra- and inter-day precision coefficients of variance, bias, and recovery were 0.7-7.7%, -1.5-9.8%, and 49.3-97.5%, respectively. The linearity range was 1-100 ng/mL for cortisol and 0.5-50 ng/mL for other steroids (R2>0.99). The reference intervals were in agreement with the previous reports.
CONCLUSIONS
This LC-MS/MS method and the reference intervals validated in the Korean population can be successfully applied to analyze seven steroids in DBS for the diagnosis of CAH.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Establishment of Pediatric Reference Intervals for Routine Laboratory Tests in Korean Population: A Retrospective Multicenter Analysis
Ji Yeon Sung, Jong Do Seo, Dae-Hyun Ko, Min-Jeong Park, Sang Mee Hwang, Sohee Oh, Sail Chun, Moon-Woo Seong, Junghan Song, Sang Hoon Song, Sung Sup Park
Ann Lab Med. 2021;41(2):155-170. doi: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.2.155.Recommendations for the Use of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry in the Clinical Laboratory: Part I. Implementation and Management
Kyunghoon Lee, Soo Young Moon, Serim Kim, Hyun-Jung Choi, Sang-Guk Lee, Hyung-Doo Park, Soo-Youn Lee, Sang Hoon Song,
Lab Med Online. 2020;10(1):1-9. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2020.10.1.1.A Questionnaire Survey on General Status and Opinions about Clinical Mass Spectrometric Analysis in Korea (2018)
Sung-Eun Cho, Hyojin Chae, Hyung-Doo Park, Sail Chun, Yong-Wha Lee, Yeo-Min Yun, Sang Hoon Song, Sang-Guk Lee, Kyunghoon Lee, Junghan Song, Soo-Youn Lee
Lab Med Online. 2019;9(3):161-165. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.3.161.
Reference
-
1. Rauh M. Steroid measurement with LC-MS/MS in pediatric endocrinology. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009; 301:272–281. PMID: 19007847.
Article2. Forest MG. Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Hum Reprod Update. 2004; 10:469–485. PMID: 15514016.
Article3. Janzen N, Peter M, Sander S, Steuerwald U, Terhardt M, Holtkamp U, et al. Newborn screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia: additional steroid profile using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:2581–2589. PMID: 17456574.
Article4. Riepe FG, Sippell WG. Recent advances in diagnosis, treatment, and outcome of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2007; 8:349–363. PMID: 17885806.
Article5. Therrell BL. Newborn screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001; 30:15–30. PMID: 11344933.
Article6. Soldin SJ, Soldin OP. Steroid hormone analysis by tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2009; 55:1061–1066. PMID: 19325015.
Article7. Stanczyk FZ, Clarke NJ. Advantages and challenges of mass spectrometry assays for steroid hormones. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2010; 121:491–495. PMID: 20470886.
Article8. Hingre RV, Gross SJ, Hingre KS, Mayes DM, Richman RA. Adrenal steroidogenesis in very low birth weight preterm infants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994; 78:266–270. PMID: 8106610.
Article9. Nordenström A, Wedell A, Hagenfeldt L, Marcus C, Larsson A. Neonatal screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia: 17-hydroxyprogesterone levels and CYP21 genotypes in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2001; 108:E68. PMID: 11581476.10. Kim IS, Lee SY, Kim JW. An analysis of two-year experience in neonatal screening. Korean J Lab Med. 2004; 24:290–296.11. Seo JY, Park HD, Kim JW, Oh HJ, Yang JS, Chang YS, et al. Steroid profiling for congenital adrenal hyperplasia by tandem mass spectrometry as a second-tier test reduces follow-up burdens in a tertiary care hospital: a retrospective and prospective evaluation. J Perinat Med. 2014; 42:121–127. PMID: 23989111.
Article12. Xu RN, Fan L, Rieser MJ, El-Shourbagy TA. Recent advances in high-throughput quantitative bioanalysis by LC-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007; 44:342–355. PMID: 17360141.
Article13. Holst JP, Soldin SJ, Tractenberg RE, Guo T, Kundra P, Verbalis JG, et al. Use of steroid profiles in determining the cause of adrenal insufficiency. Steroids. 2007; 72:71–84. PMID: 17157339.
Article14. Ministry of Health and Welfare and Planned Population Federation of Korea. Analysis of blood sample records for neonatal screening test and external quality assessment for inborn errors of metabolism in Korea. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2013.15. Lee DH. Newborn screening of inherited metabolic disease in Korea. Korean J Pediatr. 2006; 49:1125–1139.
Article16. Lacey JM, Minutti CZ, Magera MJ, Tauscher AL, Casetta B, McCann M, et al. Improved specificity of newborn screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia by second-tier steroid profiling using tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2004; 50:621–625. PMID: 14656905.
Article17. Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chem. 2003; 75:3019–3030. PMID: 12964746.
Article18. Horowitz GL, editor. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Defining, establishing, and verifying reference intervals in the clinical laboratory : approved guideline. Wayne, Pa.: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2008.19. Kwon C, Farrell PM. The magnitude and challenge of false-positive newborn screening test results. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2000; 154:714–718. PMID: 10891024.
Article20. Rauh M. Steroid measurement with LC-MS/MS. Application examples in pediatrics. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2010; 121:520–527. PMID: 20036331.
Article21. Rossi C, Calton L, Hammond G, Brown HA, Wallace AM, Sacchetta P, et al. Serum steroid profiling for congenital adrenal hyperplasia using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 2010; 411:222–228. PMID: 19931522.
Article22. Mayo medical laboratories reference laboratory services for health care organizations. Accessed on Aug 2014. Available from http://www.mayomedicallaboratories.com/test-catalog/Clinical+and+Interpretive/91196.23. Janzen N, Sander S, Terhardt M, Peter M, Sander J. Fast and direct quantification of adrenal steroids by tandem mass spectrometry in serum and dried blood spots. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008; 861:117–122.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dried Blood Spot Multiplexed Steroid Profiling Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Korean Neonates
- Multiplex Assay of Second-Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs in Dried Blood Spots Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- Quantitative analysis of endogenous steroids in human urine by using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- A Simple and Rapid Method Based on Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Measurement of alpha-L-Iduronidase Activity in Dried Blood Spots: An Application to Mucopolysaccharidosis I (Hurler) Screening
- Identification of Novel Metabolic Proteins Released by Insulin Signaling of the Rat Hypothalmus Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)