Ann Lab Med.
2015 Jan;35(1):41-49. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.41.
A Simple and Rapid Method Based on Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Measurement of alpha-L-Iduronidase Activity in Dried Blood Spots: An Application to Mucopolysaccharidosis I (Hurler) Screening
- Affiliations
-
- 1Clinical Trial Center, Clinical Research Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. nayadoo@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2363146
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.41
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
We developed an analytical method to measure alpha-L-iduronidase (IDUA) activity in dried blood spots. This was achieved by using liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) with electrospray ionization in the positive ion mode.
METHODS
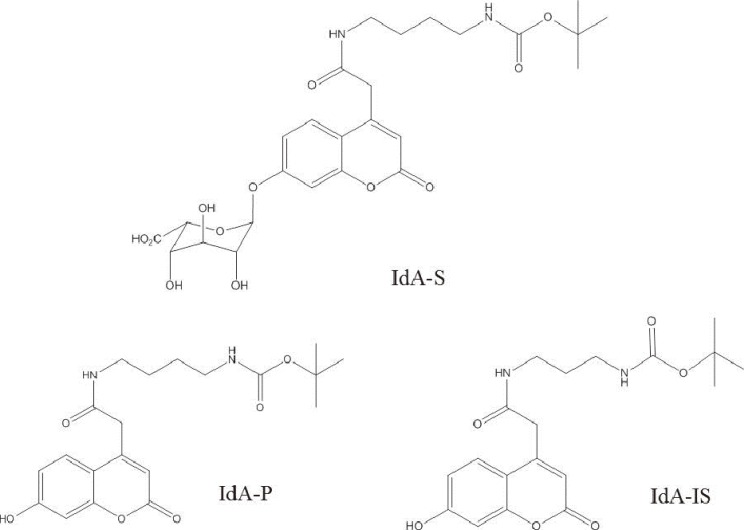
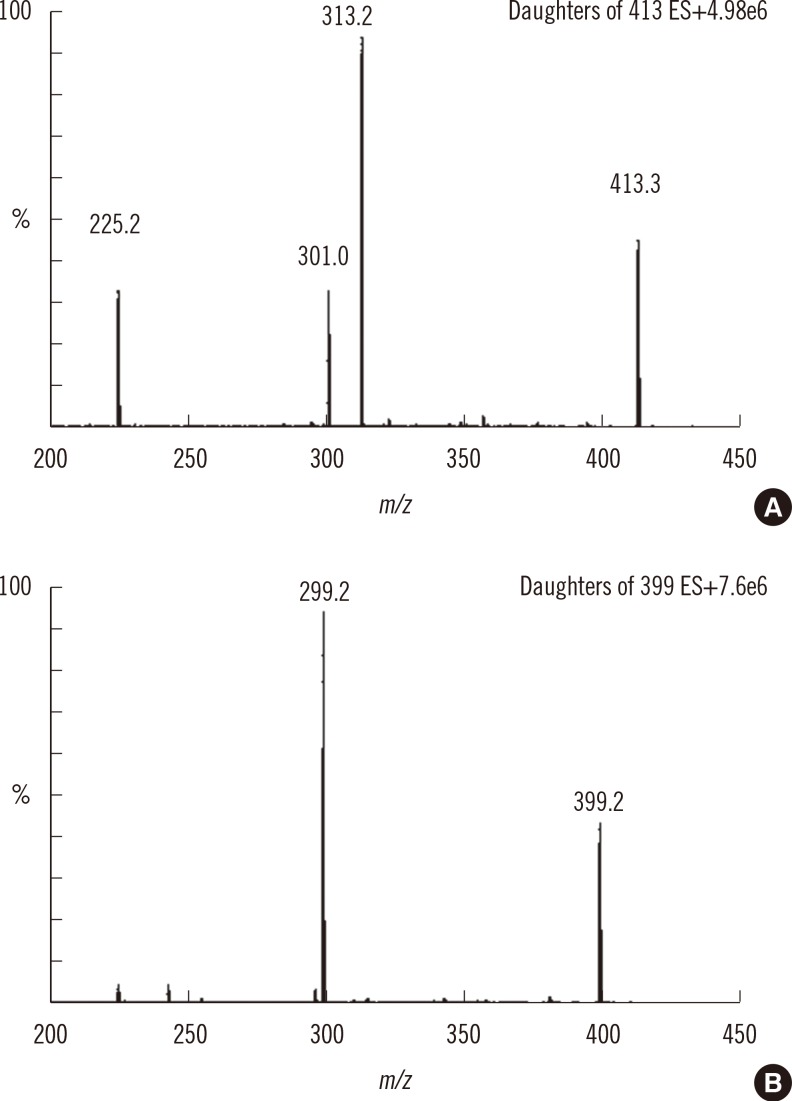
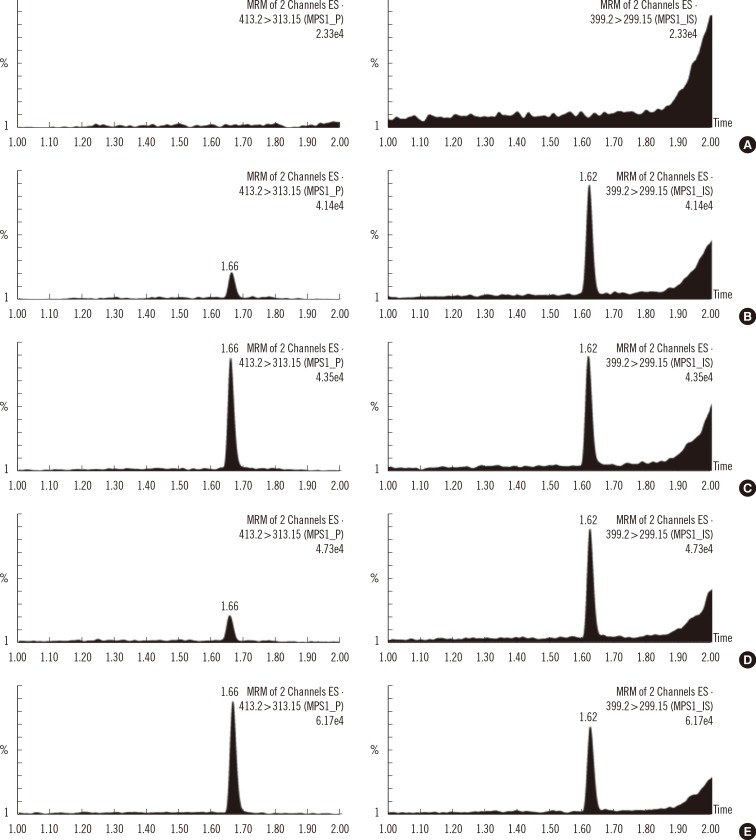
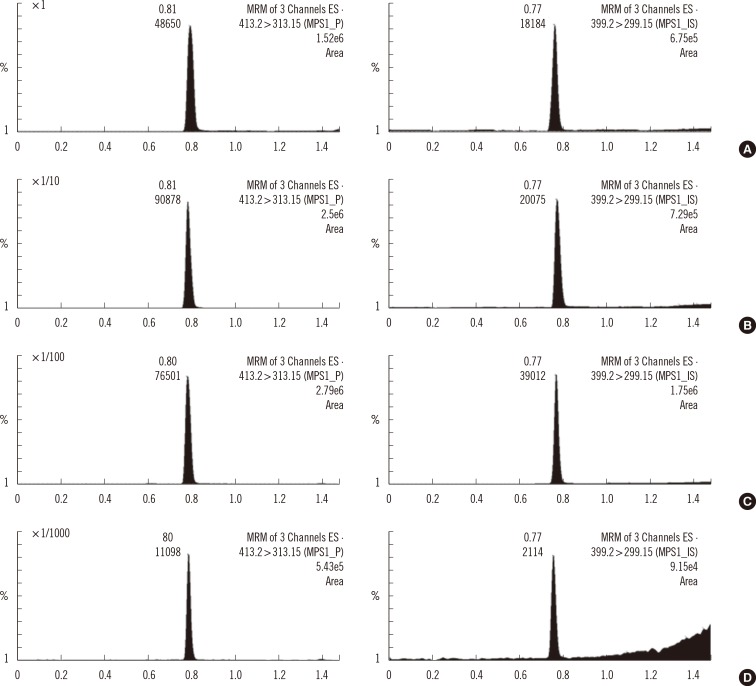
Chromatographic separation was completed using mobile phase involving water-formic acid and acetonitrile-formic acid over 2.8 min of run time on a column with a Kinetex XB-C18 (Phenomenex, USA). The detection of column effluent was performed using a Xevo TQ-S triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Waters, USA) in the multiple-reaction monitoring mode. This method was verified with blank and control samples at four activity levels: base, low, medium, and high. Control materials were provided from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
RESULTS
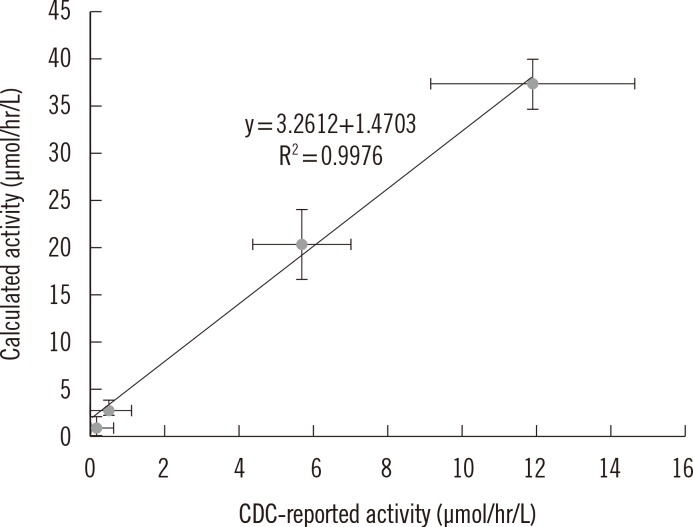
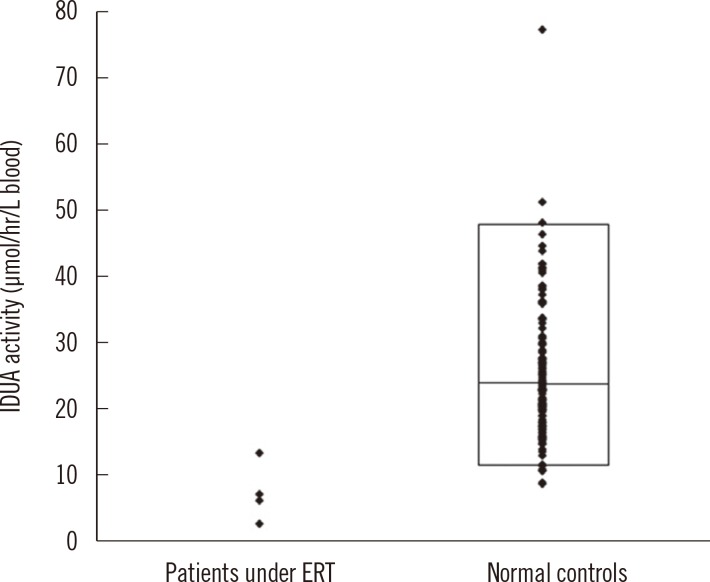
Intra- and inter-day precisions were between 2.6% and 16.5% and between 7.9% and 17.0%, respectively. A correlative regression study on the IDUA activity in CDC-control samples performed to assess the validity of the developed method showed a highly significant linear association (r2=0.9976) between the calculated and CDC-reported values and an obvious difference in activity among the four levels. This reliable analytical method was applied to mucopolysaccharidosis I (Hurler) screening of patients under treatment (n=4) and in normal controls (n=129). IDUA activity ranged from 8.98 to 77.12 micromol/hr/L) in normal controls, and patients undergoing medical treatment showed low IDUA activity.
CONCLUSIONS
This method had advantages of simplicity, rapid sample preparation, and liquid chromatographic separation, which efficiently inhibited ionization suppression induced by matrix effects in mass spectrometric detection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Giugliani R, Federhen A, Rojas MV, Vieira T, Artigalás O, Pinto LL, et al. Mucopolysaccharidosis I, II, and VI: Brief review and guidelines for treatment. Genet Mol Biol. 2010; 33:589–604. PMID: 21637564.
Article2. Tylki-Szymanska A, Marucha J, Jurecka A, Syczewska M, Czartoryska B. Efficacy of recombinant human alpha-L-iduronidase (laronidase) on restricted range of motion of upper extremities in mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2010; 33:151–157. PMID: 20217237.3. Martins AM, Dualibi AP, Norato D, Takata ET, Santos ES, Valadares ER, et al. Guidelines for the management of mucopolysaccharidosis type I. J Pediatr. 2009; 155(4S):S32–S46. PMID: 19765409.
Article4. Blanchard S, Sadilek M, Scott CR, Turecek F, Gelb MH. Tandem mass spectrometry for the direct assay of lysosomal enzymes in dried blood spots: application to screening newborns for mucopolysaccharidosis I. Clin Chem. 2008; 54:2067–2070. PMID: 19042989.
Article5. Duffey TA, Bellamy G, Elliott S, Fox AC, Glass M, Turecek F, et al. A tandem mass spectrometry triplex assay for the detection of Fabry, Pompe, and mucopolysaccharidosis-I (Hurler). Clin Chem. 2010; 56:1854–1861. PMID: 20940330.
Article6. Spáčil Z, Elliott S, Reeber SL, Gelb MH, Scott CR, Tureček F. Comparative triplex tandem mass spectrometry assays of lysosomal enzyme activities in dried blood spots using fast liquid chromatography: application to newborn screening of Pompe, Fabry, and Hurler diseases. Anal Chem. 2011; 83:4822–4828. PMID: 21548611.
Article7. Spáčil Z, Tatipaka H, Barcenas M, Scott CR, Turecek F, Gelb MH. High-throughput assay of 9 lysosomal enzymes for newborn screening. Clin Chem. 2013; 59:502–511. PMID: 23315484.8. Mechtler TP, Metz TF, Müller HG, Ostermann K, Ratschmann R, De Jesus VR, et al. Short-incubation mass spectrometry assay for lysosomal storage disorders in newborn and high-risk population screening. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2012; 908:9–17.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiplex Assay of Second-Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs in Dried Blood Spots Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- Simultaneous Screening of 177 Drugs of Abuse in Urine Using Ultra-performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Drug-intoxicated Patients
- Dried Blood Spot Testing for Seven Steroids Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry With Reference Interval Determination in the Korean Population
- Analysis of Acid Sphingomyelinase Activity in Dried Blood Spots Using Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- A Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Simultaneously Determining Meropenem and Linezolid in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid