Ann Lab Med.
2012 Sep;32(5):319-323. 10.3343/alm.2012.32.5.319.
Analysis of Acid Sphingomyelinase Activity in Dried Blood Spots Using Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Women's and Children's Health Department, University of Padua, Italy.
- 2New York State Department of Health, Wadsworth Center, Albany, New York, USA.
- 3Centogene GmbH, Rostock, Germany.
- 4Dr. John T. Macdonald Foundation Department of Human Genetics, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, USA. obodamer@med.miami.edu
- KMID: 1387345
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2012.32.5.319
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Niemann Pick disease (NP) is a rare, lysosomal storage disorder due to deficiency of the intra-lysosomal enzyme acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) resulting in intracellular accumulation of sphingomyelin. We evaluated a tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) method to analyze ASM activity in dried blood spots (DBS) that may be suitable for laboratory diagnosis of NP including high throughput screening of at-risk populations and potentially for newborn screening.
METHODS
ASM activity was measured in 3.2 mm punches from DBS. The eluate was incubated with the ASM substrate (N-Hexanoyl-D-erythro-sphingosylphosphorylcholine [C6-sphingomyelin (C29H59N2O6P)]) and an internal standard (N-butyroyl-D-erythro-sphingosine [C4-ceramide (C22H43NO3)]). ASM product and IS were analyzed using MS/MS in multiple reaction monitoring mode for transitions m/z 370.6>264.3 (ASM internal standard) and m/z 398.6>264.3 (ASM product).
RESULTS
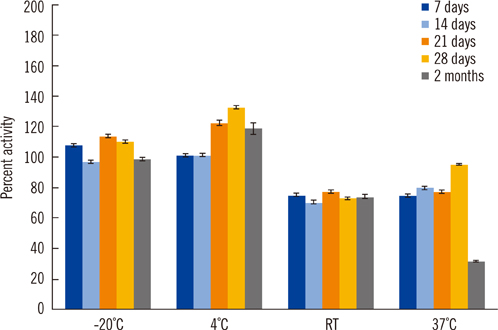
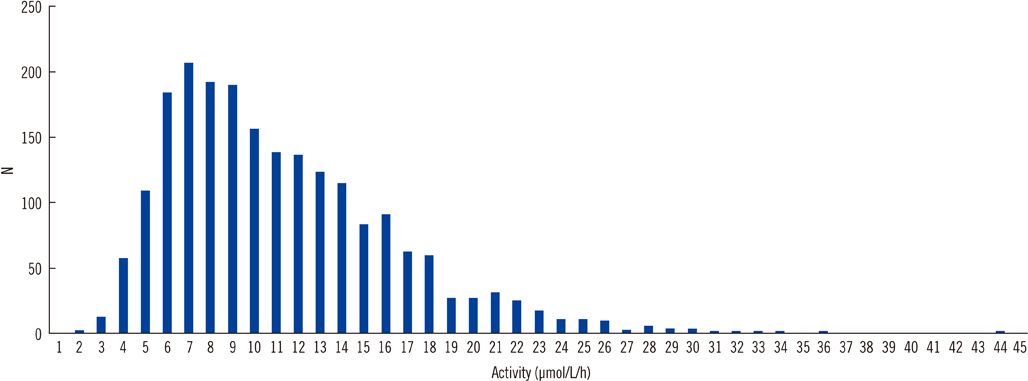
ASM activities were stable for up to 2 months at or below 4degrees C. Position of the punch in the DBS and/or hematocrit of the DBS had a limited effect on ASM activities. Both intra- and inter-assay variability were below 10%. There was no carry-over. The median ASM activity in 2,085 newborn infants was 9.5 micromol/h/L (mean 10.6) with a SD of 5.06 micromol/h/L. Six of 2,085 (0.3%) infants were found to have ASM activities below the cut-off of 2.5 micromol/h/L. ASM activities were below the cut-off level in all 10 previously diagnosed cases with NP (range: 0.16 to 2.08 micromol/h/L).
CONCLUSIONS
This MS/MS method for the measurement of ASM activity in DBS is robust and suitable for laboratory diagnosis of NP.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schuchman EH, Desnick RJ. Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, Childs B, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, editors. Niemann-Pick Disease Types A and B: acid sphingomyelinase deficiencies. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. 2001. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;3589–3610.2. Simonaro CM, Desnick RJ, McGovern MM, Wasserstein MP, Schuchman EH. The demographics and distribution of type B Niemann-Pick disease: novel mutations lead to new genotype/phenotype correlations. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. 71:1413–1419.
Article3. Vanier MT. Niemann-Pick disease type C. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010. 5:16.
Article4. Schuchman EH. The pathogenesis and treatment of acid sphingomyelinase-deficient Niemann-Pick disease. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009. 47:Suppl 1. S48–S57.
Article5. He X, Chen F, Dagan A, Gatt S, Schuchman EH. A fluorescence-based, high-performance liquid chromatographic assay to determine acid sphingomyelinase activity and diagnose types A and B Niemann-Pick disease. Anal Biochem. 2003. 314:116–120.
Article6. Gelb MH, Turecek F, Scott CR, Chamoles NA. Direct multiplex assay of enzymes in dried blood spots by tandem mass spectrometry for the newborn screening of lysosomal storage disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2006. 29:397–404.
Article7. Mechtler TP, Stary S, Metz TF, DeJesús VR, Greber-Platzer S, Pollak A, et al. Neonatal screening for lysosomal storage disorders: feasibility and incidence from a nationwide study in Austria. Lancet. 2012. 379:335–341.
Article8. Wittmann J, Karg E, Turi S, Legnini E, Wittmann G, Giese AK, et al. Newborn screening for lysosomal storage disorders in Hungary. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2012. (in press).
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Simple and Rapid Method Based on Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Measurement of alpha-L-Iduronidase Activity in Dried Blood Spots: An Application to Mucopolysaccharidosis I (Hurler) Screening
- Report on the External Quality Assessment Scheme for Metabolite Testing in Korea (2016–2017)
- Multiplex Assay of Second-Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs in Dried Blood Spots Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- A Case of Maple Syrup Urine Disease detected by Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Newborn Screening Test
- Annual Report on External Quality Assessment of Biochemical Genetics in Korea (2013)