J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Jul;35(26):e206. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e206.
Long-term Renal Outcome of Biopsy-proven Acute Tubular Necrosis and Acute Interstitial Nephritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Kandong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2503680
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e206
Abstract
- Background
Although emerging evidence suggest acute kidney injury (AKI) progress to chronic kidney disease (CKD), long-term renal outcome of AKI still remains unclear. Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is the most common cause of AKI due to ischemia, toxin or sepsis. Acute interstitial nephritis (AIN), caused by drugs or autoimmune diseases is also increasingly recognized as an important cause of AKI. Unlike glomerular diseases, AKI is usually diagnosed in the clinical context without kidney biopsies, and lack of histology might contribute to this uncertainty.
Methods
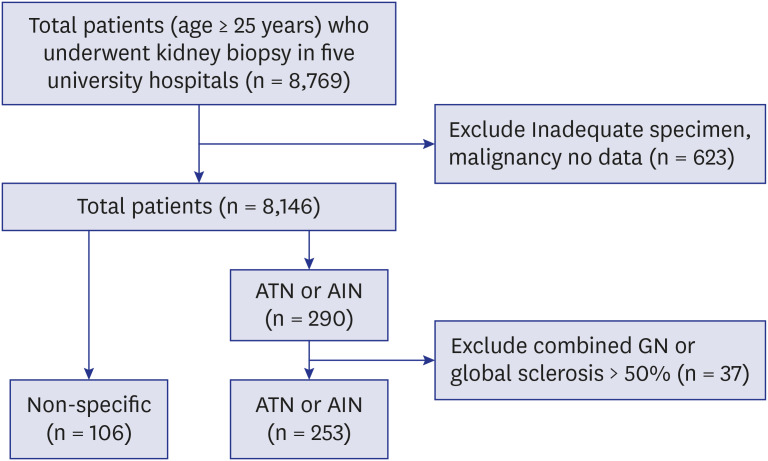
Among 8,769 biopsy series, 253 adults who were histologically diagnosed with ATN and AIN from 1982 to 2018 at five university hospitals were included. Demographic and pathological features that are associated with the development of end stage renal disease (ESRD) were also examined.
Results
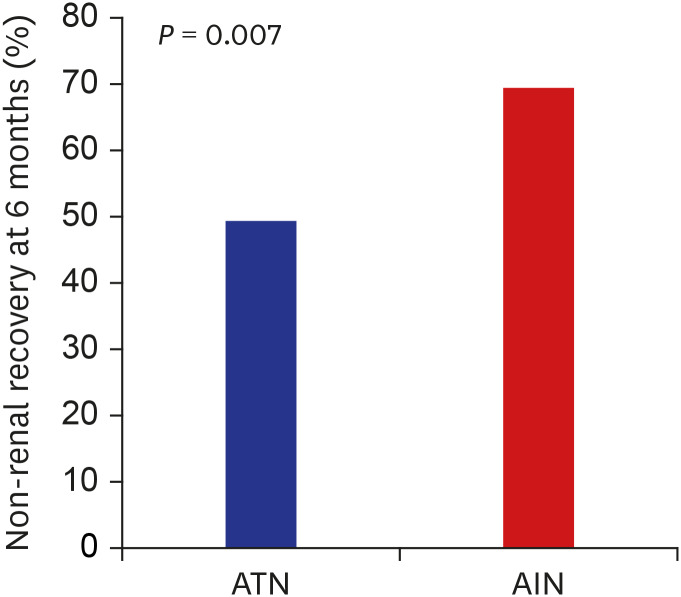
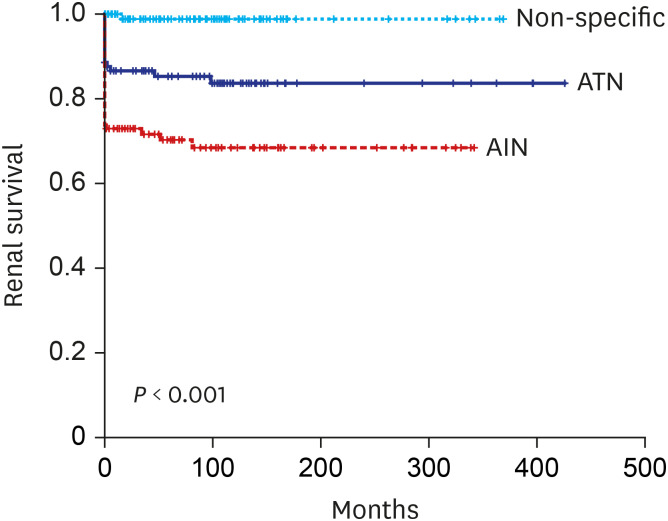
Rate of non-recovery of renal function at 6 month was significantly higher in the AIN (ATN vs AIN 49.3 vs 69.4%, P = 0.007) with a 2.71-fold higher risk of non- recovery compared to ATN (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.20–6.47). During the mean follow up of 76.5 ± 91.9 months, ESRD developed in 39.4% of patients with AIN, and 21.5% patients of ATN. The risk of ESRD was significantly higher in AIN (23.05; 95% CI, 2.42–219.53) and also in ATN (12.14; 95% CI, 1.19–24.24) compared to control with non-specific pathology. Older age, female gender, renal function at the time of biopsy and at 6 months, proteinuria and pathological features including interstitial inflammation and fibrosis, tubulitis, vascular lesion were significantly associated with progression to ESRD.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrated that patients with biopsy proven ATN and AIN are at high risk of developing ESRD. AIN showed higher rate of non-renal recovery at 6 month than ATN.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Coca SG, Singanamala S, Parikh CR. Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2012; 81(5):442–448. PMID: 22113526.
Article2. Heung M, Steffick DE, Zivin K, Gillespie BW, Banerjee T, Hsu CY, et al. Acute kidney injury recovery pattern and subsequent risk of CKD: an analysis of veterans health administration data. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016; 67(5):742–752. PMID: 26690912.3. Foley RN, Sexton DJ, Reule S, Solid C, Chen SC, Collins AJ. End-stage renal disease attributed to acute tubular necrosis in the United States, 2001–2010. Am J Nephrol. 2015; 41(1):1–6. PMID: 25613997.
Article4. Rosen S, Stillman IE. Acute tubular necrosis is a syndrome of physiologic and pathologic dissociation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008; 19(5):871–875. PMID: 18235086.
Article5. Praga M, González E. Acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010; 77(11):956–961. PMID: 20336051.
Article6. Raghavan R, Eknoyan G. Acute interstitial nephritis - a reappraisal and update. Clin Nephrol. 2014; 82(3):149–162. PMID: 25079860.
Article7. Su T, Gu Y, Sun P, Tang J, Wang S, Liu G, et al. Etiology and renal outcomes of acute tubulointerstitial nephritis: a single-center prospective cohort study in China. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018; 33(7):1180–1188. PMID: 28992223.
Article8. Levey AS, Coresh J, Greene T, Stevens LA, Zhang YL, Hendriksen S, et al. Using standardized serum creatinine values in the modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2006; 145(4):247–254. PMID: 16908915.
Article9. Kim SY, Jin DC, Bang BK. Current status of dialytic therapy in Korea. Nephrology (Carlton). 2003; 8(Suppl):S2–S9. PMID: 15012684.
Article10. Oh SW, Kim S, Na KY, Chae DW, Kim S, Jin DC, et al. Clinical implications of pathologic diagnosis and classification for diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012; 97(3):418–424. PMID: 22521535.
Article11. Goicoechea M, Rivera F, López-Gómez JM. Spanish Registry of Glomerulonephritis. Increased prevalence of acute tubulointerstitial nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013; 28(1):112–115. PMID: 22759386.
Article12. Muriithi AK, Leung N, Valeri AM, Cornell LD, Sethi S, Fidler ME, et al. Biopsy-proven acute interstitial nephritis, 1993–2011: a case series. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014; 64(4):558–566. PMID: 24927897.13. Su T, Gu Y, Sun P, Tang J, Wang S, Liu G, et al. Etiology and renal outcomes of acute tubulointerstitial nephritis: a single-center prospective cohort study in China. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018; 33(7):1180–1188. PMID: 28992223.
Article14. Prendecki M, Tanna A, Salama AD, Tam FW, Cairns T, Taube D, et al. Long-term outcome in biopsy-proven acute interstitial nephritis treated with steroids. Clin Kidney J. 2017; 10(2):233–239. PMID: 28396740.
Article15. López-Gómez JM, Rivera F. Spanish Registry of Glomerulonephritis. Renal biopsy findings in acute renal failure in the cohort of patients in the Spanish Registry of Glomerulonephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008; 3(3):674–681. PMID: 18354075.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Acute Interstitial Nephritis Associated with Acute Hepatitis A
- A Case of Biopsy-Proven Acute Tubular Necrosis Associated with Vancomycin Overdose
- A Case of Carbamazepine-Induced Acute Interstitial Nephritis
- A Case of Acetaminophen-induced Acute Interstitial Nephritis Presenting with Acute Renal Failure
- A case of sarcoidosis associated with acute tubular necrosis and pulmonary hemorrhage