Ann Clin Microbiol.
2020 Mar;23(1):45-54. 10.5145/ACM.2020.23.1.45.
Role of Efflux Pump Gene adeIJK to Multidrug Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Antimicrobial Resistance, Center for Infectious Diseases Research, Korea National Institute of Health, KCDC, Cheongju, Republic of Korea.
- 2Premedical Science, College of Medicine, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju, Republic of Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju, Republic of Korea. sjbjang@chosun.ac.kr
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju, Republic of Korea.
- 5Department of Otolaryngology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2471858
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2020.23.1.45
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The emergence of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii as a nosocomial pathogen is one of the major public health problems. The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of an efflux pump gene adeJ for the multidrug resistance of A. baumannii clinical isolates.
METHODS
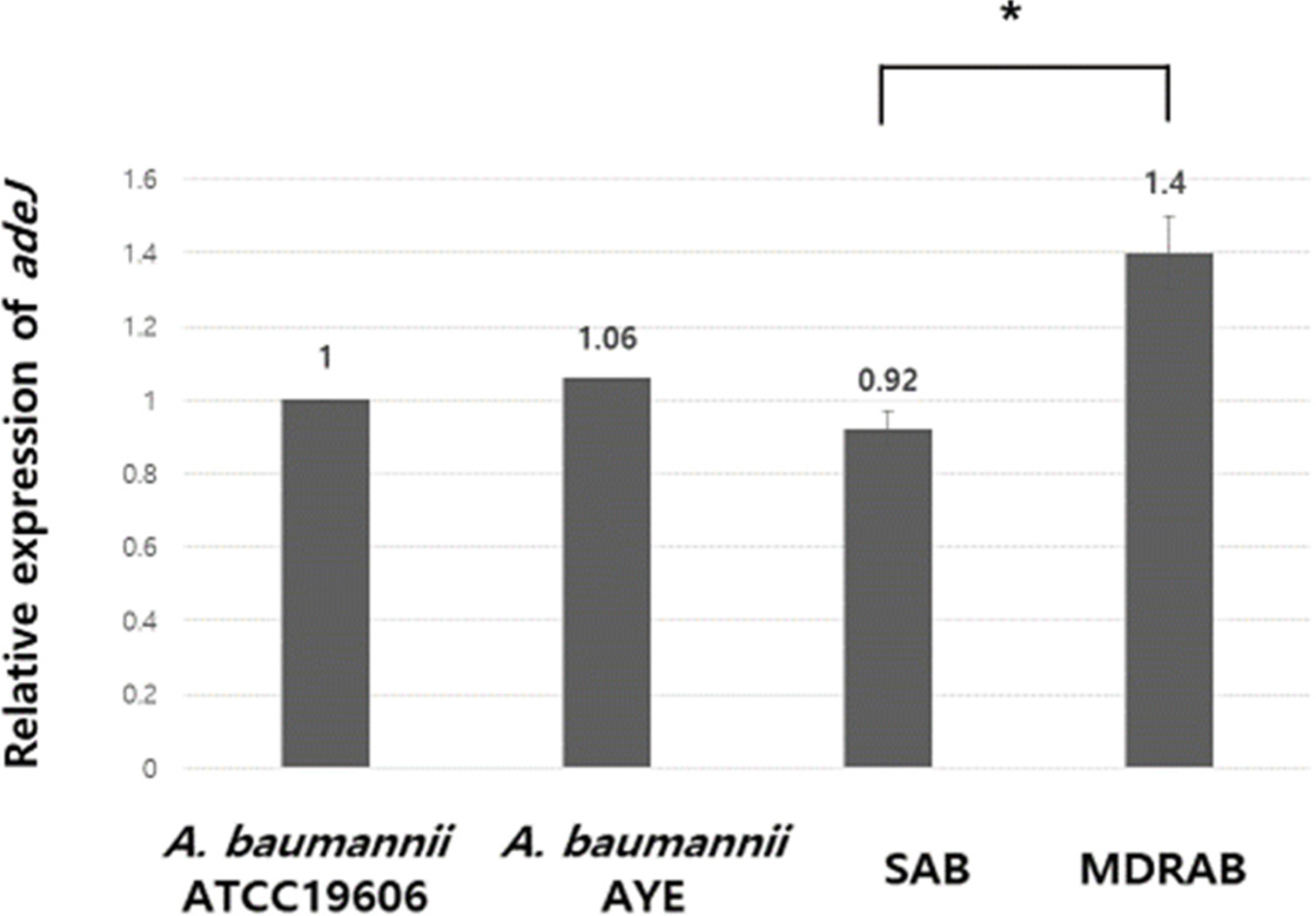
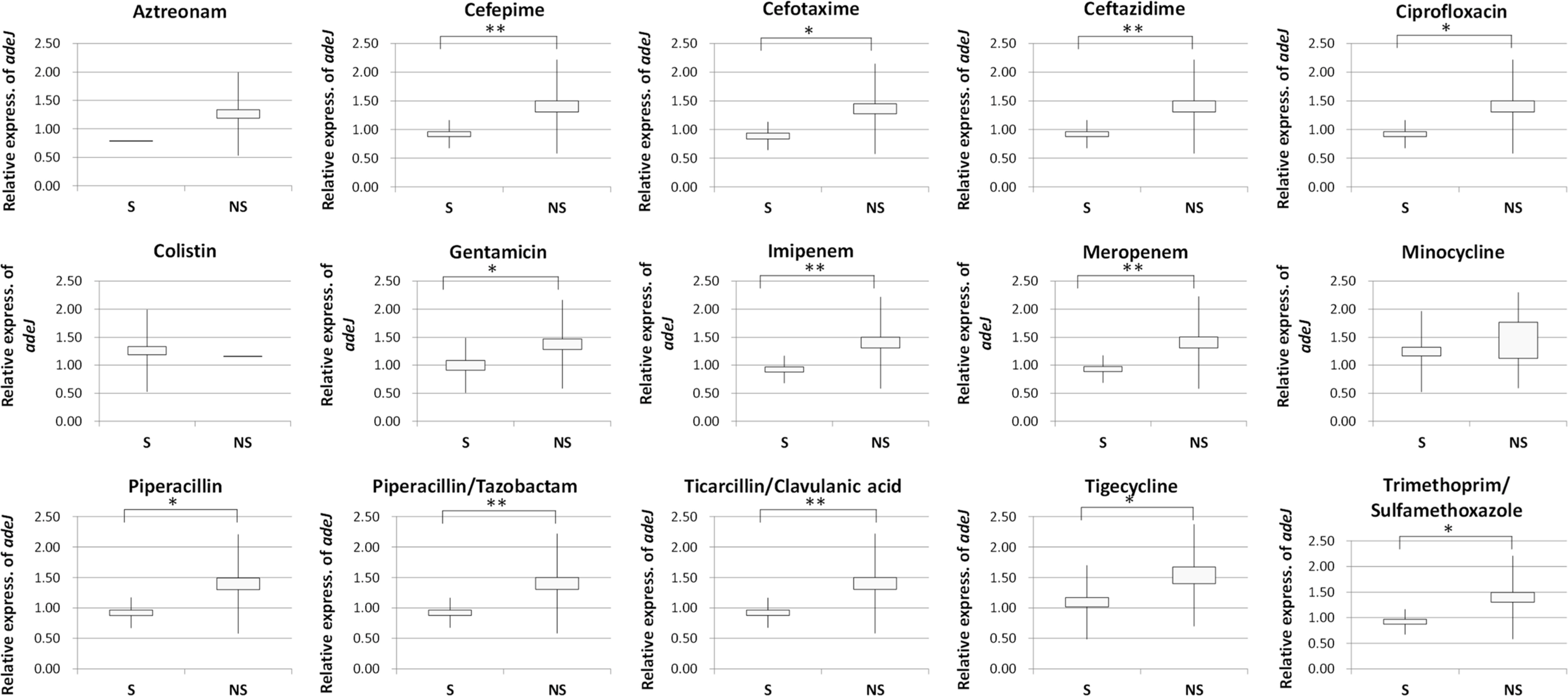
Two groups (MDRAB and SAB) of A. baumannii clinical isolates were studied. The SAB group consisted of strains that did not meet the criteria of MDRAB and were susceptible to more categories of antibiotics than MDRAB. Antimicrobial susceptibility results obtained by VITEKII system were used in data analysis and bacterial group allocation. We performed real-time reverse transcription PCR to determine relative expression of adeJ. We compared relative expression of adeJ in comparison groups by considering two viewpoints: i) MDRAB and SAB groups and ii) susceptible and non-susceptible groups for each antibiotic used in this study.
RESULTS
The mean value of relative expression of adeJ of MDRAB and SAB groups was 1.4 and 0.92, respectively, and showed significant difference (P=0.002). The mean values of relative expression of adeJ of susceptible and non-susceptible groups to the antibiotics cefepime, ceftazidime, ciprofloxacin, imipenem, meropenem, tigecycline, piperacillin/tazobactam, ticarcillin/clavulanic acid, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, piperacillin, and gentamicin showed statistically significant differences.
CONCLUSION
The overexpression of adeIJK might contribute to the multi-drug resistance in A. baumannii clinical isolates. Further, the overexpression of adeIJK might be one of the factors contributing to the resistance to numerous antibiotics.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Yoon EJ, Balloy V, Fiette L, Chignard M, Courvalin P, Grillot-Courvalin C. Contribution of the ade resistance-nodulation-cell division-type efflux pumps to fitness and pathogenesis of Acinetobacter baumannii. MBio. 2016; 7:e00697–16.
Article2. Mera RM, Miller LA, Amrine-Madsen H, Sahm DF. Acinetobacter baumannii 2002–2008: increase of carbapenem-associated multiclass resistance in the United States. Microb Drug Resist. 2010; 16:209–15.
Article3. Hong SK, Seong MW, Lee DH, Kim EC. Correlation between carbapenem prescription trends and imipenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii at an intensive care unit between 2006 and 2010. Lab Med Online. 2012; 2:232–4.4. Wong D, Nielsen TB, Bonomo RA, Pantapalangkoor P, Luna B, Spellberg B. Clinical and pathophysiological overview of Acinetobacter infections: a century of challenges. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2017; 30:409–47.
Article5. Coyne S, Courvalin P, Perichon B. Efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in Acinetobacter spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011; 55:947–53.6. Nikaido H and Takatsuka Y. Mechanisms of RND multidrug efflux pumps. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009; 1794:769–81.7. Lin MF, Lin YY, Tu CC, Lan CY. Distribution of different efflux pump genes in clinical isolates of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and their correlation with antimicrobial resistance. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017; 50:224–31.
Article8. Choi IS, Choi JA, Jang SJ, Park G, Jeong SH, Kim CM, et al. Distribution of adeG, adeB, adeE, adeY, abeM, and adeJ efflux pump genes in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter species from Korea. Lab Med Online. 2019; 9:201–9.
Article9. Yoon EJ, Chabane YN, Goussard S, Snesrud E, Courvalin P, De E, et al. Contribution of resistance-nodulation-cell division efflux systems to antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation in Acinetobacter baumannii. MBio. 2015; 6:e00309–15.
Article10. Fournier PE, Vallenet D, Barbe V, Audic S, Ogata H, Poirel L, et al. Comparative genomics of multidrug resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS Genet. 2006; 2:e7.
Article11. Higgins PG, Wisplinghoff H, Krut O, Seifert H. A PCR-based method to differentiate between Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter genomic species 13TU. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007; 13:1199–201.
Article12. Woodford N, Ellington MJ, Coelho JM, Turton JF, Ward ME, Brown S, et al. Multiplex PCR for genes encoding prevalent OXA carbapenemases in Acinetobacter spp. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006; 27:351–3.
Article13. Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012; 18:268–81.
Article14. Fernando D and Kumar A. Growth phase-dependent expression of RND efflux pump- and outer membrane porin-encoding genes in Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012; 67:569–72.15. Rosenfeld N, Bouchier C, Courvalin P, Perichon B. Expression of the resistance-nodulation-cell division pump AdeIJK in Acinetobacter baumannii is regulated by AdeN, a TetR-type regulator. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012; 56:2504–10.
Article16. Fernando DM, Xu W, Loewen PC, Zhanel GG, Kumar A. Triclosan can select for an AdeIJK-overexpressing mutant of Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978 that displays reduced susceptibility to multiple antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014; 58:6424–31.
Article17. Rumbo C, Gato E, Lopez M, Ruiz de Alegria C, Fernandez-Cuenca F, Martinez-Martinez L, et al. Contribution of efflux pumps, porins, and beta-lactamases to multidrug resistance in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013; 57:5247–57.18. Amin IM, Richmond GE, Sen P, Koh TH, Piddock LJ, Chua KL. A method for generating marker-less gene deletions in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. BMC Microbiol. 2013; 13:158.
Article19. Jeong SH. Mechanisms of acquiring carbapenem-resistance in Acinetobacter species. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 12:1–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Distribution of adeG, adeB, adeE, adeY, abeM, and adeJ Efflux Pump Genes in Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter Species from Korea
- ISAba15 Inserted into Outer Membrane Protein Gene carO in Acinetobacter baumannii
- RND efflux pump systems in Acinetobacter, with special emphasis on their role in quorum sensing
- Correlation of Ciprofloxacin Resistance with the AdeABC Efflux System in Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates
- Assessment of Efflux Activity Using H33342 Accumulation in Tigecycline-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates