Korean J Gastroenterol.
2020 Jan;75(1):11-16. 10.4166/kjg.2020.75.1.11.
Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Changwon, Korea. imdrkim@naver.com
- KMID: 2471134
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2020.75.1.11
Abstract
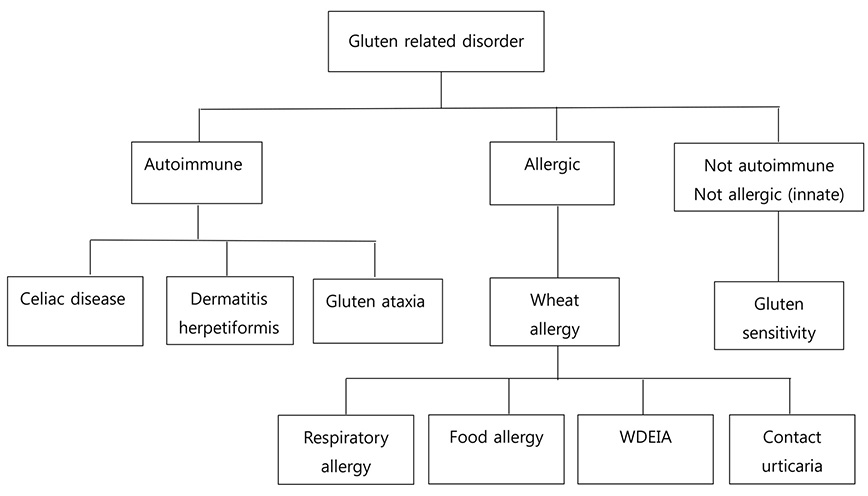
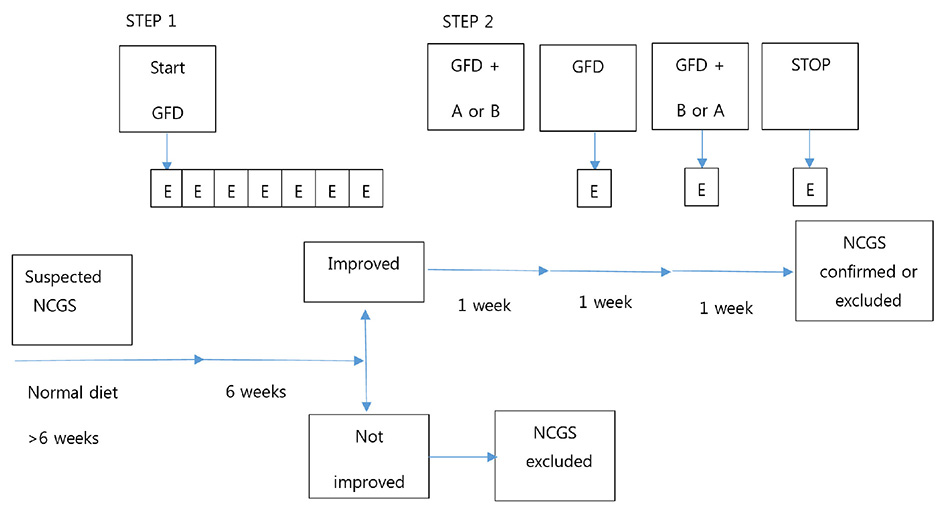
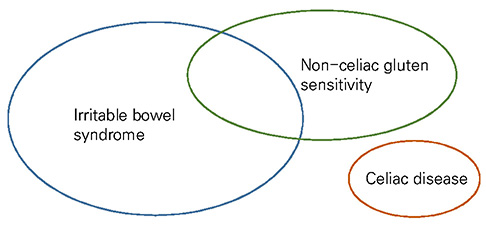
- Non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) is a term that is used to describe individuals who are not affected by celiac disease or wheat allergy, yet they have intestinal and/or extra-intestinal symptoms related to gluten ingestion with improvement of their symptoms upon withdrawing gluten from their diet. Gluten-related disorder groups are manifested by symptoms of gastrointestinal tract disorders, as well as hematological dermatological endocrinological, gynecological, rheumatological and nervous system symptoms. It is believed that NCGS represents heterogeneous groups with different subgroups characterized by different etiologies, clinical histories and clinical courses. There also appears to be an overlap between NCGS and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). There is a need for establishing strict criteria for diagnosing NCGS. The absence of validated biomarkers remains a significant limitation for research studies on NCGS. New evidence shows that a gluten-free diet may be beneficial for some patients with gastrointestinal symptoms, such as those symptoms commonly found in patients with IBS. Further studies about NCGS are needed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wieser H. Chemistry of gluten proteins. Food Microbiol. 2007; 24:115–119.
Article2. Fasano A, Sapone A, Zevallos V, Schuppan D. Nonceliac gluten sensitivity. Gastroenterology. 2015; 148:1195–1204.
Article3. Di Sabatino A, Corazza GR. Coeliac disease. Lancet. 2009; 373:1480–1493.
Article4. Lebwohl B, Sanders DS, Green PHR. Coeliac disease. Lancet. 2018; 391:70–81.
Article5. Gweon TG, Lim CH, Byeon SW, et al. A case of celiac disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2013; 61:338–342.
Article6. Molina-Infante J, Santolaria S, Sanders DS, Fernández-Bañares F. Systematic review: noncoeliac gluten sensitivity. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 41:807–820.
Article7. Catassi C, Elli L, Bonaz B, et al. Diagnosis of non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS): the Salerno experts' criteria. Nutrients. 2015; 7:4966–4977.
Article8. Ellis A, Linaker BD. Non-coeliac gluten sensitivity? Lancet. 1978; 1:1358–1359.9. Jonas A. Wheat-sensitive--but not coeliac. Lancet. 1978; 2:1047.10. Sapone A, Lammers KM, Mazzarella G, et al. Differential mucosal IL-17 expression in two gliadin-induced disorders: gluten sensitivity and the autoimmune enteropathy celiac disease. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010; 152:75–80.
Article11. DiGiacomo DV, Tennyson CA, Green PH, Demmer RT. Prevalence of gluten-free diet adherence among individuals without celiac disease in the USA: results from the Continuous National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009-2010. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2013; 48:921–925.
Article12. Lee HJ, Kim HJ, Kang EH, et al. Self-reported food intolerance in Korean patients with irritable bowel syndrome. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019; 25:222–232.
Article13. Sapone A, Lammers KM, Casolaro V, et al. Divergence of gut permeability and mucosal immune gene expression in two gluten-associated conditions: celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. BMC Med. 2011; 9:23.
Article14. Volta U, Tovoli F, Cicola R, et al. Serological tests in gluten sensitivity (nonceliac gluten intolerance). J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012; 46:680–685.
Article15. Caio G, Volta U, Tovoli F, D Giorgioe R. Effect of gluten free diet on immune response to gliadin in patients with non-celiac gluten sensitivity. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014; 14:26.
Article16. Carroccio A, Giambalvo O, Blasca F, Iacobucci R, D'Alcamo A, Mansueto P. Self-reported non-celiac wheat sensitivity in high school students: demographic and clinical characteristics. Nutrients. 2017; 9:E771.
Article17. Czaja-Bulsa G. Non coeliac gluten sensitivity - a new disease with gluten intolerance. Clin Nutr. 2015; 34:189–194.
Article18. Aziz I, Hadjivassiliou M, Sanders DS. The spectrum of noncoeliac gluten sensitivity. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 12:516–526.
Article19. Catassi C, Bai JC, Bonaz B, et al. Non-celiac gluten sensitivity: the new frontier of gluten related disorders. Nutrients. 2013; 5:3839–3853.
Article20. Catassi C, Alaedini A, Bojarski C, et al. The overlapping area of non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) and wheat-sensitive irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): an update. Nutrients. 2017; 9:E1268.
Article21. Vazquez-Roque MI, Camilleri M, Smyrk T, et al. A controlled trial of gluten-free diet in patients with irritable bowel syndrome-diarrhea: effects on bowel frequency and intestinal function. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144:903–911.e3.
Article22. Vazquez-Roque MI, Camilleri M, Carlson P, et al. HLA-DQ genotype is associated with accelerated small bowel transit in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 23:481–487.
Article23. Staudacher HM, Lomer MC, Anderson JL, et al. Fermentable carbohydrate restriction reduces luminal bifidobacteria and gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. J Nutr. 2012; 142:1510–1518.
Article24. Volta U, Pinto-Sanchez MI, Boschetti E, Caio G, De Giorgio R, Verdu EF. Dietary triggers in irritable bowel syndrome: is there a role for gluten? J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016; 22:547–557.
Article25. Diez-Sampedro A, Olenick M, Maltseva T, Flowers M. A gluten-free diet, not an appropriate choice without a medical diagnosis. J Nutr Metab. 2019; 2019:2438934.
Article26. Niland B, Cash BD. Health benefits and adverse effects of a gluten-free diet in non-celiac disease patients. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2018; 14:82–91.27. Stevens L, Rashid M. Gluten-free and regular foods: a cost comparison. Can J Diet Pract Res. 2008; 69:147–150.
Article28. Zarkadas M, Cranney A, Case S, et al. The impact of a gluten-free diet on adults with coeliac disease: results of a national survey. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2006; 19:41–49.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Emergence of Celiac Disease and Gluten-related Disorders in Asia
- Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity or Celiac Disease, This Is Still the Question
- Symptomatic improvement with gluten restriction in irritable bowel syndrome: a prospective, randomized, double blinded placebo controlled trial
- Self-reported Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity in the Korean Population: Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
- Self-reported Wheat Sensitivity in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Healthy Subjects: Prevalence of Celiac Markers and Response to Wheat-free Diet