Yonsei Med J.
2020 Feb;61(2):186-191. 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.2.186.
NOTCH1 Pathway is Involved in Polyhexamethylene Guanidine-Induced Humidifier Disinfectant Lung Injuries
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Asan Medical Center, Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Environmental Health Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Medicine, University of Ulsan Collage of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Childhood Asthma Atopy Center, Environmental Health Center, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sjhong@amc.seoul.kr
- 5Department of Pediatrics, International St. Mary's hospital, Catholic Kwandong University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 6Department of Pediatrics, Mediplex Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 7Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 8Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2468494
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2020.61.2.186
Abstract
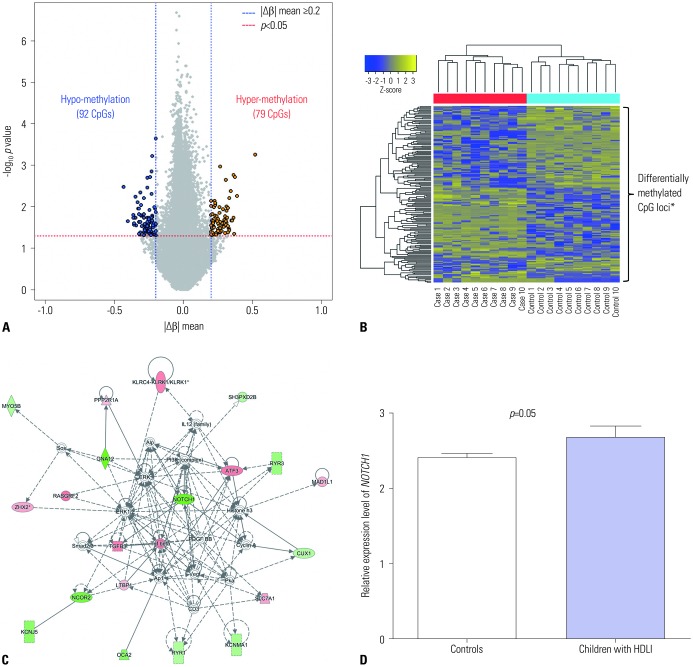
- An outbreak of fatal humidifier disinfectant lung injuries (HDLI) occurred in Korea. Human studies on mechanisms underlying HDLI have yet to be conducted. This study aimed to investigate methylation changes and their potential role in HDLI after exposure to HDs containing polyhexamethylene guanidine-phosphate. DNA methylation analysis was performed in blood samples from 10 children with HDLI and 10 healthy children using Infinium Human MethylationEPIC BeadChip. Transcriptome analysis was performed using lung tissues from 5 children with HDLI and 5 controls. Compared to healthy controls, 92 hypo-methylated and 79 hyper-methylated CpG sites were identified in children with HDLI at the statistical significance level of |Δβ|>0.2 and p<0.05. NOTCH1 was identified as a candidate network hub gene in cases. NOTCH1 transcripts significantly increased in lung tissues from HDLI cases compared to unexposed controls (p=0.05). NOTCH1 may play an important role in pulmonary fibrosis of HDLI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim KW, Ahn K, Yang HJ, Lee S, Park JD, Kim WK, et al. Humidifier disinfectant-associated children's interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014; 189:48–56. PMID: 24199596.2. Hong SB, Kim HJ, Huh JW, Do KH, Jang SJ, Song JS, et al. A cluster of lung injury associated with home humidifier use: clinical, radiological and pathological description of a new syndrome. Thorax. 2014; 69:694–702. PMID: 24473332.
Article3. Ryu SH, Park DU, Lee E, Park S, Lee SY, Jung S, et al. Humidifier disinfectant and use characteristics associated with lung injury in Korea. Indoor Air. 2019; 29:735–747. PMID: 31278778.
Article4. Park DU, Ryu SH, Lim HK, Kim SK, Choi YY, Ahn JJ, et al. Types of household humidifier disinfectant and associated risk of lung injury (HDLI) in South Korea. Sci Total Environ. 2017; 596-597:53–60. PMID: 28415004.
Article5. Yoon J, Cho HJ, Lee E, Choi YJ, Kim YH, Lee JL, et al. Rate of humidifier and humidifier disinfectant usage in Korean children: a nationwide epidemiologic study. Environ Res. 2017; 155:60–63. PMID: 28189074.
Article6. Yang IV, Pedersen BS, Rabinovich E, Hennessy CE, Davidson EJ, Murphy E, et al. Relationship of DNA methylation and gene expression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014; 190:1263–1272. PMID: 25333685.
Article7. Sanders YY, Ambalavanan N, Halloran B, Zhang X, Liu H, Crossman DK, et al. Altered DNA methylation profile in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012; 186:525–535. PMID: 22700861.
Article8. Zong D, Ouyang R, Li J, Chen Y, Chen P. Notch signaling in lung diseases: focus on Notch1 and Notch3. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2016; 10:468–484. PMID: 27378579.
Article9. Jiang J, Xiao K, Chen P. NOTCH signaling in lung diseases. Exp Lung Res. 2017; 43:217–228. PMID: 28636457.
Article10. Kage H, Borok Z. EMT and interstitial lung disease: a mysterious relationship. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2012; 18:517–523. PMID: 22854509.11. Yin Q, Wang W, Cui G, Yan L, Zhang S. Potential role of the Jagged1/Notch1 signaling pathway in the endothelial-myofibroblast transition during BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Physiol. 2018; 233:2451–2463. PMID: 28776666.
Article12. Li T, Yang X, Xin S, Cao Y, Wang N. Paraquat poisoning induced pulmonary epithelial mesenchymal transition through Notch1 pathway. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:924. PMID: 28424456.
Article13. Liu T, Hu B, Choi YY, Chung M, Ullenbruch M, Yu H, et al. Notch1 signaling in FIZZ1 induction of myofibroblast differentiation. Am J Pathol. 2009; 174:1745–1755. PMID: 19349363.
Article14. Shin DY, Jeong MH, Bang IJ, Kim HR, Chung KH. MicroRNA regulatory networks reflective of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate-induced fibrosis in A549 human alveolar adenocarcinoma cells. Toxicol Lett. 2018; 287:49–58. PMID: 29337256.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Major concerns regarding lung injury and related health conditions caused by the use of humidifier disinfectant
- An analysis of a humidifier disinfectant case from a toxicological perspective
- Toxic hepatitis after exposure to humidifier disinfectant: A case series report
- Mitochondria disease due to humidifier disinfectants: diagnostic criteria and its evidences
- Problems with diagnostic criteria for humidifier disinfectant lung injury (HDLI): two cases of radiologically improved HDLI