Korean J Radiol.
2019 Jul;20(7):1138-1145. 10.3348/kjr.2018.0899.
Analysis of Apparent Diffusion Coefficients of the Brain in Healthy Controls: A Comparison Study between Single-Shot Echo-Planar Imaging and Read-out-Segmented Echo-Planar Imaging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. hyunchoi@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Research Institute of Radiological Science, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2467024
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.0899
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) of brain segments by using two diffusion-weighted imaging acquisition modes, single-shot echo-planar imaging (ss-EPI) and read-out-segmented echo-planar imaging (rs-EPI), and to assess their correlation and agreement in healthy controls.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
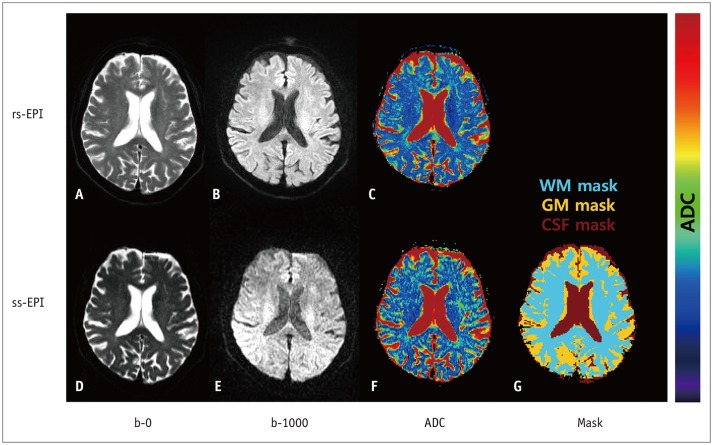
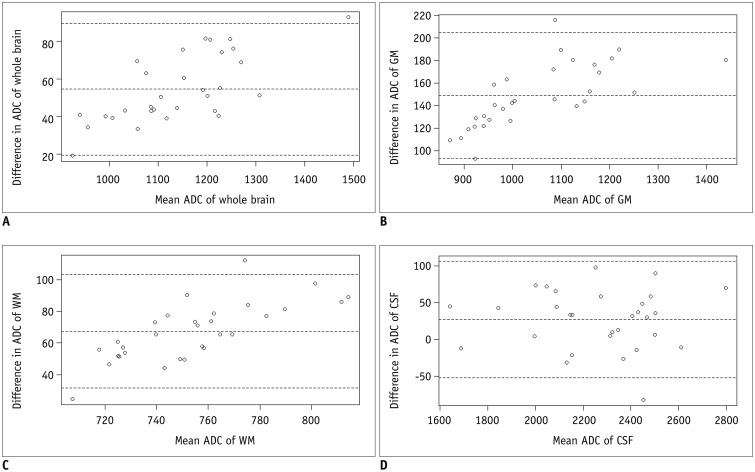
T2-weighted (T2W) images, rs-EPI, and ss-EPI of 30 healthy subjects were acquired using a 3T magnetic resonance scanner. The T2W images were co-registered to the rs-EPI and ss-EPI, which were then segmented into the gray matter (GM), white matter (WM), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to generate masking templates. ADC maps of rs-EPI and ss-EPI were also segmented into the GM, WM, and CSF by using the generated templates. ADCs of rs-EPI and ss-EPI were compared using Student's t tests and correlated using Pearson's correlation coefficients. Bland-Altman plots were used to assess the agreement between acquisitions.
RESULTS
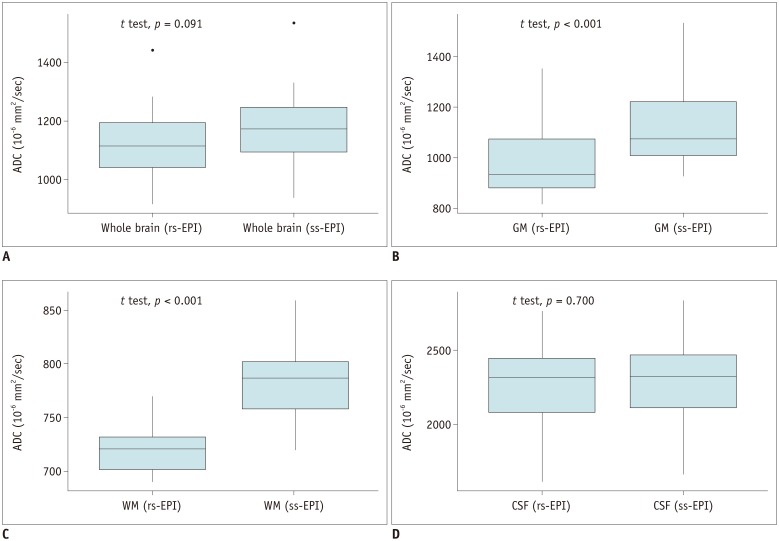
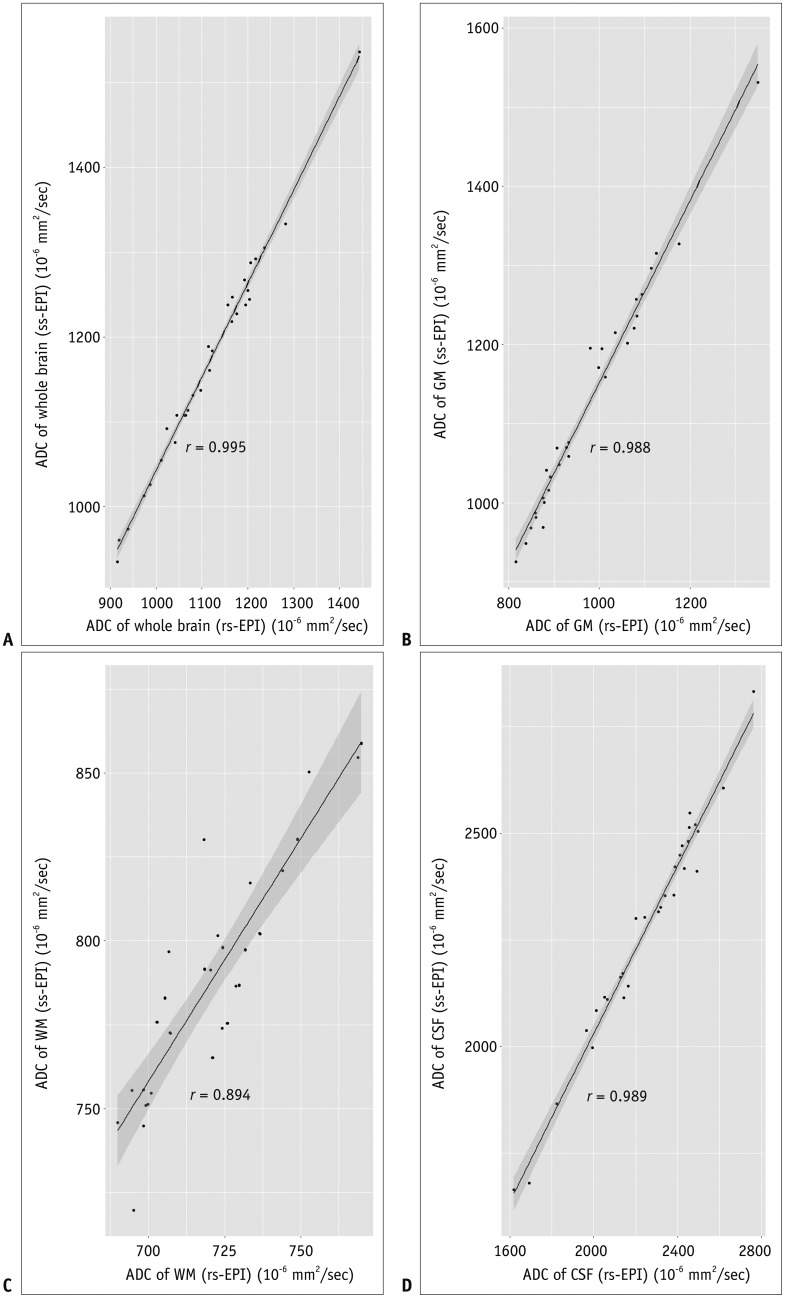
ADCs of rs-EPI and ss-EPI were significantly different in the GM (p < 0.001) and WM (p < 0.001). ADCs showed high agreement and correlation in the whole brain and CSF (r > 0.988; p < 0.001). ADC of the WM showed the least correlation (r = 0.894; p < 0.001), and ADCs of the WM and GM showed poor agreement. Pearson's correlation equations for each brain segment were y = 1.1x - 59.4 (GM), y = 1.45x - 255 (WM), and y = 0.98x - 63.5 (CSF), where x and y indicated ADCs of rs-EPI and ss-EPI, respectively.
CONCLUSION
While ADCs of rs-EPI and ss-EPI showed high correlation and agreement in the whole brain and CSF, ADCs of the WM and GM showed significant differences and large variability, reflecting brain parenchymal inhomogeneity due to different regional microenvironments. ADCs of different acquisition methods should be interpreted carefully, especially in intra-individual comparisons.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Purushotham A, Campbell BC, Straka M, Mlynash M, Olivot JM, Bammer R, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient threshold for delineation of ischemic core. Int J Stroke. 2015; 10:348–353. PMID: 23802548.
Article2. Bonati LH, Lyrer PA, Wetzel SG, Steck AJ, Engelter ST. Diffusion weighted imaging, apparent diffusion coefficient maps and stroke etiology. J Neurol. 2005; 252:1387–1393. PMID: 15942704.
Article3. Kidwell CS, Jahan R, Gornbein J, Alger JR, Nenov V, Ajani Z, et al. ; MR RESCUE Investigators. A trial of imaging selection and endovascular treatment for ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:914–923. PMID: 23394476.4. Brandão LA, Shiroishi MS, Law M. Brain tumors: a multimodality approach with diffusion-weighted imaging, diffusion tensor imaging, magnetic resonance spectroscopy, dynamic susceptibility contrast and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2013; 21:199–239. PMID: 23642551.5. Hamstra DA, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging: a biomarker for treatment response in oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:4104–4109. PMID: 17827460.
Article6. Moffat BA, Chenevert TL, Lawrence TS, Meyer CR, Johnson TD, Dong Q, et al. Functional diffusion map: a noninvasive MRI biomarker for early stratification of clinical brain tumor response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:5524–5529. PMID: 15805192.
Article7. Hayashida Y, Yakushiji T, Awai K, Katahira K, Nakayama Y, Shimomura O, et al. Monitoring therapeutic responses of primary bone tumors by diffusion-weighted image: initial results. Eur Radiol. 2006; 16:2637–2643. PMID: 16909220.
Article8. Atay M, Aralasmak A, Sharifov R, Kilicarslan R, Asil T, Alkan A. Transient cytotoxic edema caused by hypoglycemia: follow-up diffusion-weighted imaging features. Emerg Radiol. 2012; 19:473–475. PMID: 22527358.
Article9. Kishimoto K, Tajima S, Maeda I, Takagi M, Ueno T, Suzuki N, et al. Endometrial cancer: correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) with tumor cellularity and tumor grade. Acta Radiol. 2016; 57:1021–1028. PMID: 26486600.
Article10. Abdel Razek A, Mazroa J, Baz H. Assessment of white matter integrity of autistic preschool children with diffusion weighted MR imaging. Brain Dev. 2014; 36:28–34. PMID: 23398955.
Article11. Porter DA, Heidemann RM. High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magn Reson Med. 2009; 62:468–475. PMID: 19449372.
Article12. Holdsworth SJ, Skare S, Newbould RD, Guzmann R, Blevins NH, Bammer R. Readout-segmented EPI for rapid high resolution diffusion imaging at 3 T. Eur J Radiol. 2008; 65:36–46. PMID: 17980534.13. Tokoro H, Fujinaga Y, Ohya A, Ueda K, Shiobara A, Kitou Y, et al. Usefulness of free-breathing readout-segmented echo-planar imaging (RESOLVE) for detection of malignant liver tumors: comparison with single-shot echo-planar imaging (SS-EPI). Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:1728–1733. PMID: 25043495.
Article14. Zhao M, Liu Z, Sha Y, Wang S, Ye X, Pan Y, et al. Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging in the evaluation of sinonasal lesions: a comprehensive comparison of image quality in single-shot echo-planar imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2016; 34:166–172. PMID: 26541548.
Article15. Bogner W, Pinker-Domenig K, Bickel H, Chmelik M, Weber M, Helbich TH, et al. Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging improves the diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted MR breast examinations at 3.0 T. Radiology. 2012; 263:64–67. PMID: 22438442.
Article16. Li L, Wang L, Deng M, Liu H, Cai J, Sah VK, et al. Feasibility study of 3-T DWI of the prostate: readout-segmented versus single-shot echo-planar imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015; 205:70–76. PMID: 26102382.
Article17. Holdsworth SJ, Yeom K, Skare S, Gentles AJ, Barnes PD, Bammer R. Clinical application of readout-segmented- echo-planar imaging for diffusion-weighted imaging in pediatric brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:1274–1279. PMID: 21596809.
Article18. Iima M, Yamamoto A, Brion V, Okada T, Kanagaki M, Togashi K, et al. Reduced-distortion diffusion MRI of the craniovertebral junction. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012; 33:1321–1325. PMID: 22383239.
Article19. Friedli I, Crowe LA, Viallon M, Porter DA, Martin PY, de Seigneux S, et al. Improvement of renal diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with readout-segmented echo-planar imaging at 3T. Magn Reson Imaging. 2015; 33:701–708. PMID: 25732925.
Article20. Le Bihan D, Johansen-Berg H. Diffusion MRI at 25: exploring brain tissue structure and function. Neuroimage. 2012; 61:324–341. PMID: 22120012.
Article21. Kunz N, Zhang H, Vasung L, O'Brien KR, Assaf Y, Lazeyras F, et al. Assessing white matter microstructure of the newborn with multi-shell diffusion MRI and biophysical compartment models. Neuroimage. 2014; 96:288–299. PMID: 24680870.
Article22. Assaf Y, Freidlin RZ, Rohde GK, Basser PJ. New modeling and experimental framework to characterize hindered and restricted water diffusion in brain white matter. Magn Reson Med. 2004; 52:965–978. PMID: 15508168.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multi-slice Multi-echo Pulsed-gradient Spin-echo (MePGSE) Sequence for Diffusion Tensor Imaging MRI: A Preliminary Result
- Ultrafast Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Echo Planar Imaging and Spiral Scan Imaging
- Review of Recent Advancement of Ultra High Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging: from Anatomy to Tractography
- Readout-Segmented Echo-Planar Imaging in Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Breast Cancer: Comparison with Single-Shot Echo-Planar Imaging in Image Quality
- Comparison of Fast FLAIR and Echo-Planar FLAIR Imaging in Cere b ral Lesions