Yonsei Med J.
2020 Jan;61(1):20-29. 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.1.20.
Curcumin Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Apoptosis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cell Line by Regulating MiR-21/VHL Axis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Xianning Central Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Science and Technology, Hubei, China.
- 2Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Xianning Central Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Science and Technology, Hubei, China.
- 3Cancer Center of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
- 4Administrative Department, Xianning Central Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Science and Technology, Hubei, China. hongyuzjhz@163.com
- KMID: 2466332
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2020.61.1.20
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Curcumin exerts its anti-cancer effects, partly by targeting special microRNAs, in human cancers. MiR-21 is a key oncomir in carcinogenesis of multiple human cancers. Here, we aimed to further explore the mechanistic insight into the link between curcumin and miR-21 on diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Quantitative real-time PCR assays were performed to assess the levels of miR-21 and Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) mRNA. In situ hybridization assay was used for miR-21 expression visualization in lymphoma tissues. Western blot was used for determination of VHL protein, Ki-67, caspase-3, and cleaved caspase-3 levels. Dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation assay were employed to confirm the direct target of miR-21. MTT assay, flow cytometric analysis, and transwell assay were used to evaluate cell proliferation, apoptosis, and migration and invasion capacities, respectively.
RESULTS
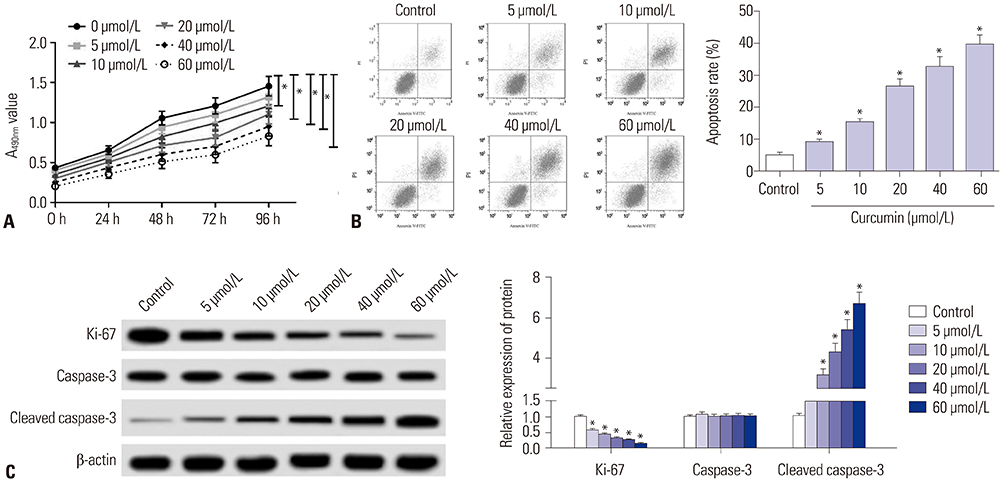
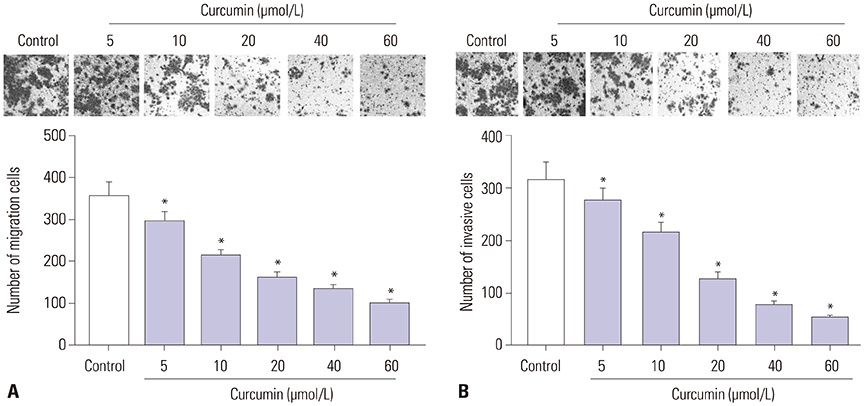
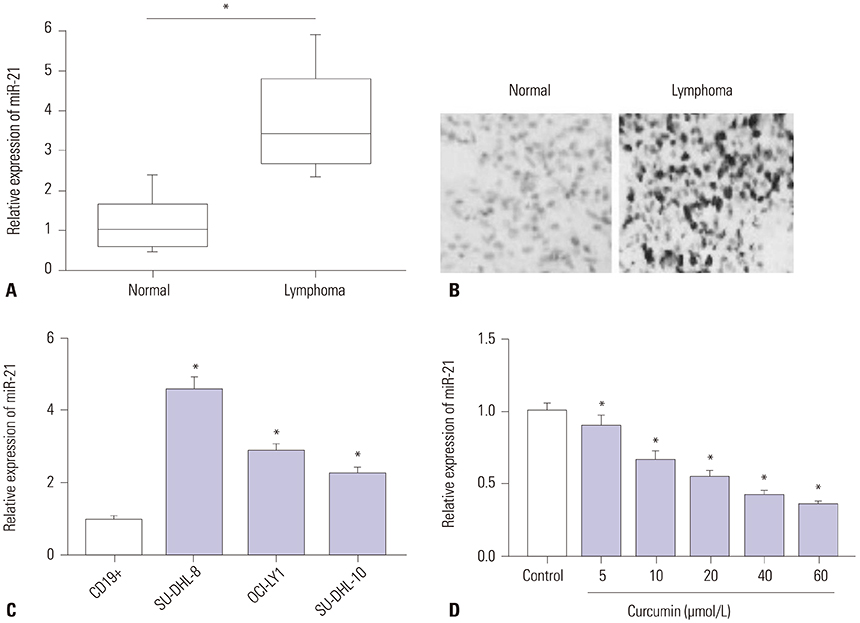
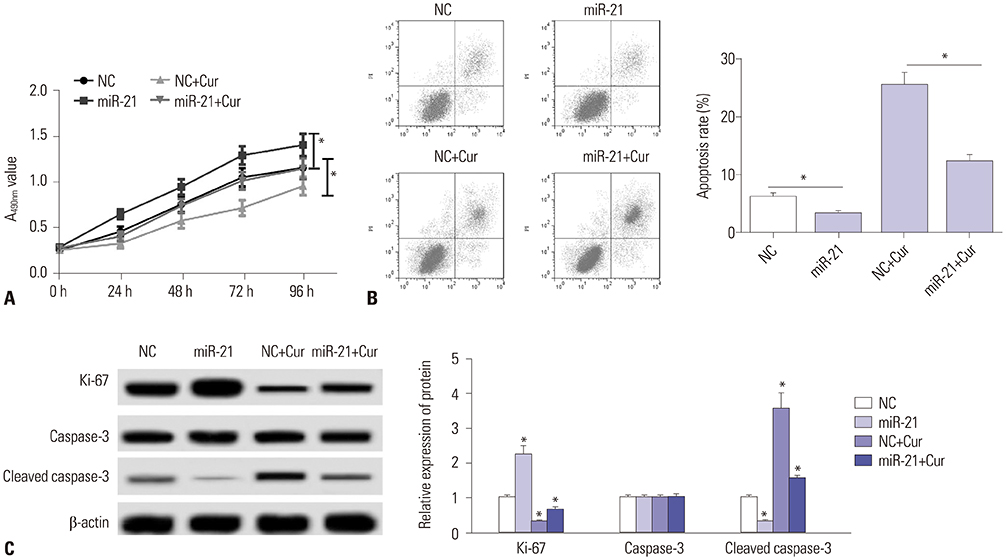
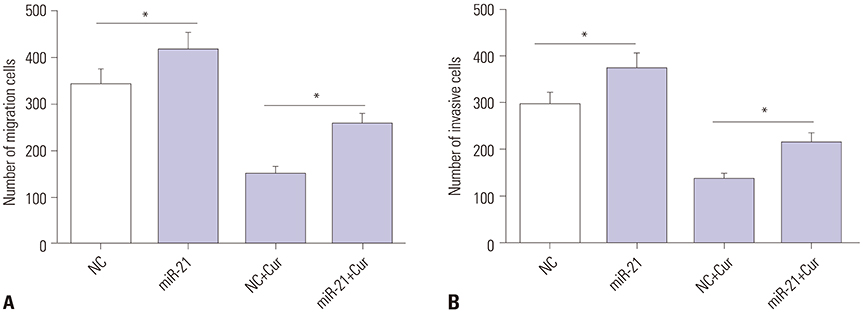
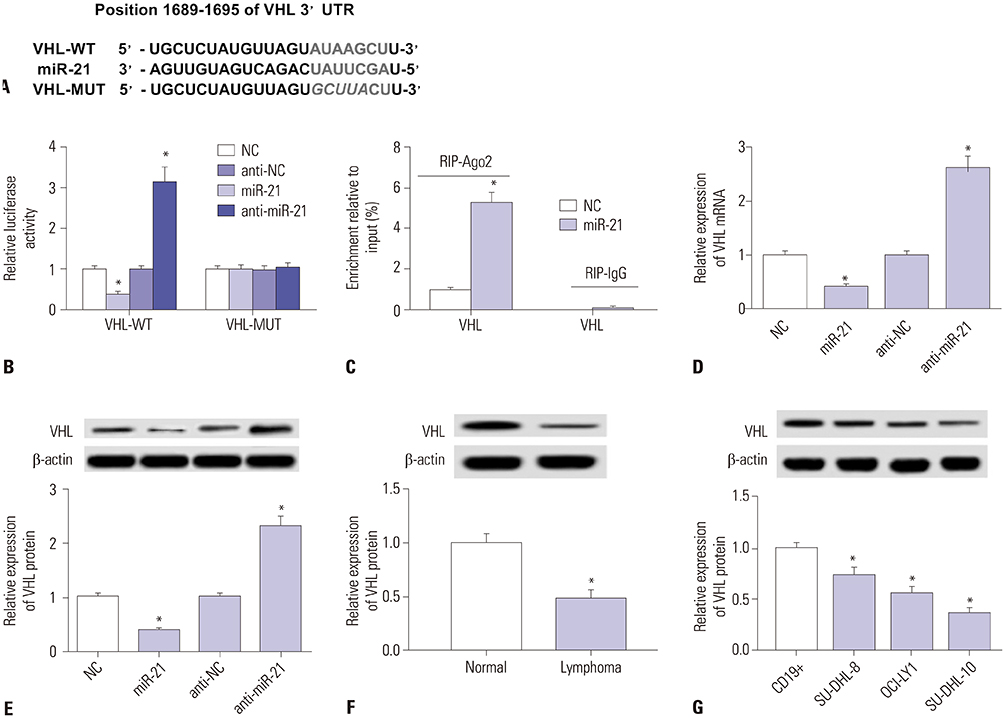
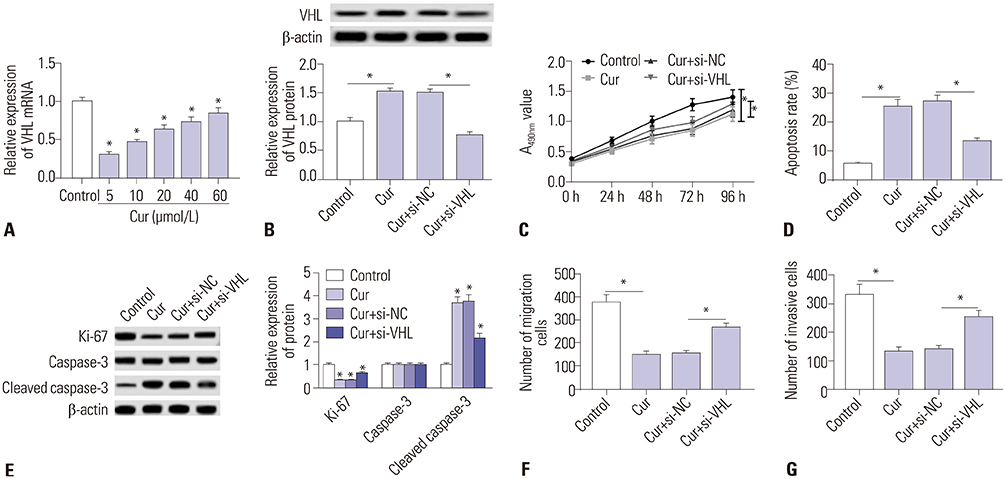
Curcumin repressed the proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities and promoted apoptosis in SU-DHL-8 cells. Curcumin inhibited miR-21 expression and curcumin exerted its anti-proliferation, anti-migration, anti-invasion, and pro-apoptosis effects by miR-21 in SU-DHL-8 cells. VHL was a direct target of miR-21. Moreover, curcumin exerted its regulatory effects on SU-DHL-8 cells by VHL.
CONCLUSION
Curcumin exerted its anti-proliferation, anti-migration, anti-invasion, and pro-apoptosis functions, at least partly, by repressing miR-21 and regulating VHL expression in DLBCL cell line. Our findings provided a possible molecular mechanism of curcumin-mediated anti-cancer effect.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Martelli M, Ferreri AJ, Agostinelli C, Di Rocco A, Pfreundschuh M, Pileri SA. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013; 87:146–171.
Article2. Shaffer AL 3rd, Young RM, Staudt LM. Pathogenesis of human B cell lymphomas. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012; 30:565–610.
Article3. Tilly H, Gomes da, Vitolo U, Jack A, Meignan M, Lopez-Guillermo A, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2015; 26 Suppl 5:v116–v125.
Article4. Nabavi SF, Thiagarajan R, Rastrelli L, Daglia M, Sobarzo-Sánchez E, Alinezhad H, et al. Curcumin: a natural product for diabetes and its complications. Curr Top Med Chem. 2015; 15:2445–2455.
Article5. Liu CH, Huang HY. Antimicrobial activity of curcumin-loaded myristic acid microemulsions against Staphylococcus epidermidis. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2012; 60:1118–1124.
Article6. Meng B, Li J, Cao H. Antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities of curcumin on diabetes mellitus and its complications. Curr Pharm Des. 2013; 19:2101–2113.
Article7. Lüer S, Troller R, Aebi C. Antibacterial and antiinflammatory kinetics of curcumin as a potential antimucositis agent in cancer patients. Nutr Cancer. 2012; 64:975–981.
Article8. Hashish EA, Elgaml SA. Hepatoprotective and nephroprotective effect of curcumin against copper toxicity in rats. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2016; 31:270–277.
Article9. Lin J, Chen A. Curcumin diminishes the impacts of hyperglycemia on the activation of hepatic stellate cells by suppressing membrane translocation and gene expression of glucose transporter-2. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011; 333:160–171.
Article10. Mudduluru G, George-William JN, Muppala S, Asangani IA, Kumarswamy R, Nelson LD, et al. Curcumin regulates miR-21 expression and inhibits invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Biosci Rep. 2011; 31:185–197.
Article11. Toden S, Okugawa Y, Jascur T, Wodarz D, Komarova NL, Buhrmann C, et al. Curcumin mediates chemosensitization to 5-fluorouracil through miRNA-induced suppression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in chemoresistant colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2015; 36:355–367.
Article12. Pandey A, Vishnoi K, Mahata S, Tripathi SC, Misra SP, Misra V, et al. Berberine and curcumin target survivin and STAT3 in gastric cancer cells and synergize actions of standard chemotherapeutic 5-fluorouracil. Nutr Cancer. 2015; 67:1293–1304.
Article13. Hammond SM. An overview of microRNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015; 87:3–14.
Article14. Reddy KB. MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2015; 15:38.
Article15. Hayes J, Peruzzi PP, Lawler S. MicroRNAs in cancer: biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol Med. 2014; 20:460–469.
Article16. Simonian M, Mosallayi M, Mirzaei H. Circulating miR-21 as novel biomarker in gastric cancer: diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018; 14:475.17. Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:1026–1033.
Article18. Chan JK, Blansit K, Kiet T, Sherman A, Wong G, Earle C, et al. The inhibition of miR-21 promotes apoptosis and chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2014; 132:739–744.
Article19. Cui Q, Vari F, Cristino AS, Salomon C, Rice GE, Sabdia MB, et al. Circulating cell-free miR-494 and miR-21 are disease response biomarkers associated with interim-positron emission tomography response in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 2018; 9:34644–34657.
Article20. Li J, Fu R, Yang L, Tu W. miR-21 expression predicts prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8:15019–15024.21. Go H, Jang JY, Kim PJ, Kim YG, Nam SJ, Paik JH, et al. MicroRNA-21 plays an oncogenic role by targeting FOXO1 and activating the PI3K/AKT pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:15035–15049.
Article22. Fu R, Li C, Shao Z. Aberrant overexpression and regulatory mechanism of mir-21 in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Am Soc Hematology. 2014; 124:5171.
Article23. Ali S, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Padhye S, Dominiak K, Schaffert JM, et al. Gemcitabine sensitivity can be induced in pancreatic cancer cells through modulation of miR-200 and miR-21 expression by curcumin or its analogue CDF. Cancer Res. 2010; 70:3606–3617.
Article24. Wilken R, Veena MS, Wang MB, Srivatsan ES. Curcumin: a review of anti-cancer properties and therapeutic activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2011; 10:12.
Article25. Ye M, Zhang J, Zhang J, Miao Q, Yao L, Zhang J. Curcumin promotes apoptosis by activating the p53-miR-192-5p/215-XIAP pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015; 357:196–205.
Article26. Epelbaum R, Schaffer M, Vizel B, Badmaev V, Bar-Sela G. Curcumin and gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Nutr Cancer. 2010; 62:1137–1141.
Article27. Bansal SS, Goel M, Aqil F, Vadhanam MV, Gupta RC. Advanced drug delivery systems of curcumin for cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2011; 4:1158–1171.
Article28. Li Y, Zhang T. Targeting cancer stem cells by curcumin and clinical applications. Cancer Lett. 2014; 346:197–205.
Article29. Bassiouny AR, Atteya MA, El-Rashidy FAH, Neenaa HM. Curcumin and EGCG suppress apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 and induce complete remission in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients. Funct Foods Health Dis. 2011; 1:525–544.
Article30. Pancione M, Giordano G, Remo A, Febbraro A, Sabatino L, Manfrin E, et al. Immune escape mechanisms in colorectal cancer pathogenesis and liver metastasis. J Immunol Res. 2014; 2014:686879.
Article31. Saini S, Arora S, Majid S, Shahryari V, Chen Y, Deng G, et al. Curcumin modulates microRNA-203-mediated regulation of the Src-Akt axis in bladder cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2011; 4:1698–1709.
Article32. Taverna S, Giallombardo M, Pucci M, Flugy A, Manno M, Raccosta S, et al. Curcumin inhibits in vitro and in vivo chronic myelogenous leukemia cells growth: a possible role for exosomal disposal of miR-21. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:21918–21933.
Article33. Chen W, Wang H, Chen H, Liu S, Lu H, Kong D, et al. Clinical significance and detection of microRNA-21 in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Chinese population. Eur J Haematol. 2014; 92:407–412.
Article34. Liu K, Du J, Ruan L. MicroRNA-21 regulates the viability and apoptosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by upregulating B cell lymphoma-2. Exp Ther Med. 2017; 14:4489–4496.
Article35. Moore LE, Nickerson ML, Brennan P, Toro JR, Jaeger E, Rinsky J, et al. Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) inactivation in sporadic clear cell renal cancer: associations with germline VHL polymorphisms and etiologic risk factors. PLoS Genet. 2011; 7:e1002312.
Article36. Kong W, He L, Richards EJ, Challa S, Xu CX, Permuth-Wey J, et al. Upregulation of miRNA-155 promotes tumour angiogenesis by targeting VHL and is associated with poor prognosis and triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene. 2014; 33:679–689.
Article37. Amara K, Trimeche M, Ziadi S, Laatiri A, Hachana M, Korbi S. Prognostic significance of aberrant promoter hypermethylation of CpG islands in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Ann Oncol. 2008; 19:1774–1786.
Article38. Zhang KL, Han L, Chen LY, Shi ZD, Yang M, Ren Y, et al. Blockage of a miR-21/EGFR regulatory feedback loop augments anti-EGFR therapy in glioblastomas. Cancer Lett. 2014; 342:139–149.
Article39. Wang Y, Wang S, Wu Y, Ren Y, Li Z, Yao X, et al. Suppression of the growth and invasion of human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas via regulating STAT3 signaling and the miR-21/β-catenin axis with HJC0152. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017; 16:578–590.
Article40. Sikora E, Bielak-Zmijewska A, Piwocka K, Skierski J, Radziszewska E. Inhibition of proliferation and apoptosis of human and rat T lymphocytes by curcumin, a curry pigment. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997; 54:899–907.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- miR-379 Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells by Targeting Insulin-Like Factor-1
- Up-Regulation of MiR-1915 Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Cancer Cells via Targeting RAGE
- circ_SPEF2 Regulates the Balance of Treg Cells by Regulating miR-16-5p/BACH2 in Lymphoma and Participates in the Immune Response
- The Circular RNA Circ_0043947 Promoted Gastric Cancer Progression by Sponging miR-384 to Regulate CREB1 Expression
- AC092127.1-miR-451a-AE binding protein 2 Signaling Facilitates Malignant Properties of Breast Cancer