J Pathol Transl Med.
2019 Nov;53(6):354-360. 10.4132/jptm.2019.10.01.
MicroRNA-374a Expression as a Prognostic Biomarker in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. medartisan@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2465434
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.10.01
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer-related death, and adenocarcinoma is the most common histologic subtype. MicroRNA is a small non-coding RNA that inhibits multiple target gene expression at the post-transcriptional level and is commonly dysregulated in malignant tumors. The purpose of this study was to analyze the expression of microRNA-374a (miR-374a) in lung adenocarcinoma and correlate its expression with various clinicopathological characteristics.
METHODS
The expression level of miR-374a was measured in 111 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded lung adenocarcinoma tissues using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction assays. The correlation between miR-374a expression and clinicopathological parameters, including clinical outcome, was further analyzed.
RESULTS
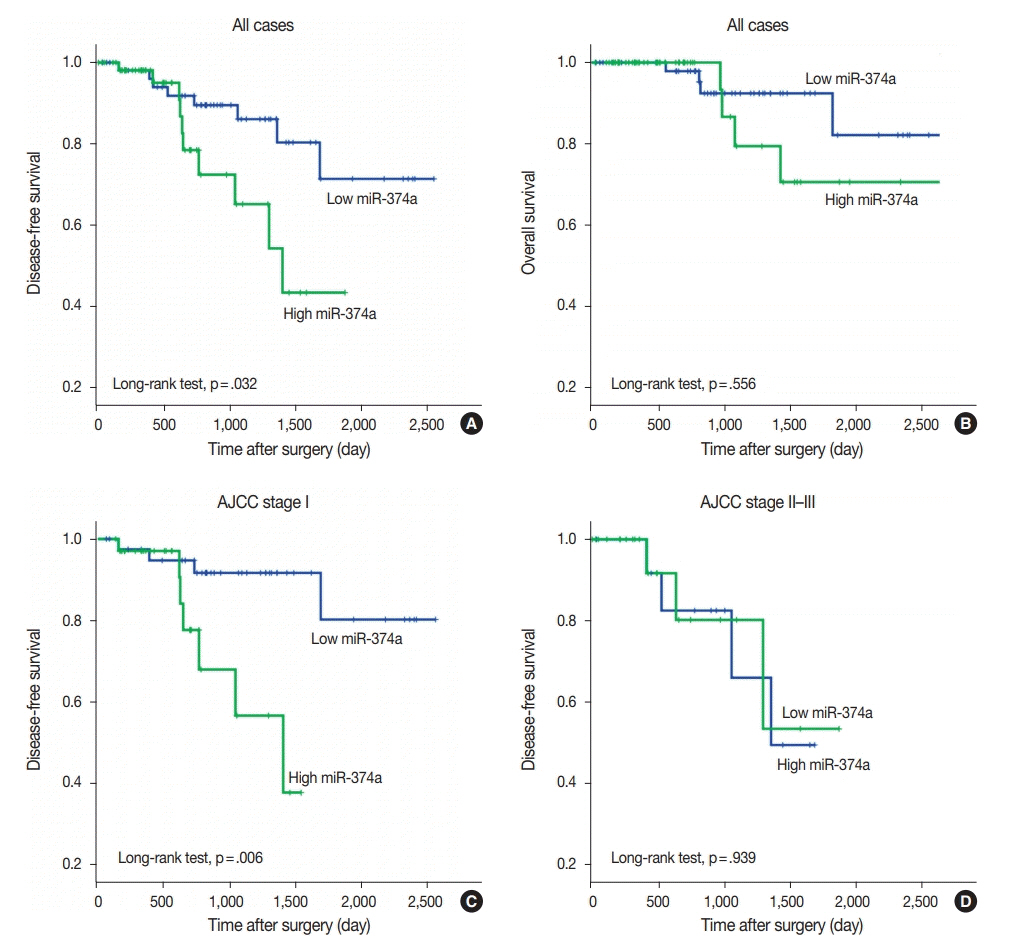
High miR-374 expression was correlated with advanced pT category (chi-square test, p=.004) and pleural invasion (chi-square test, p=.034). Survival analysis revealed that patients with high miR-374a expression had significantly shorter disease-free survival relative to those with low miR-374a expression (log-rank test, p=.032).
CONCLUSIONS
miR-374a expression may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker for predicting recurrence in early stage lung adenocarcinoma after curative surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cronin KA, Lake AJ, Scott S, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, part I: national cancer statistics. Cancer. 2018; 124:2785–800.
Article2. Kim HC, Jung CY, Cho DG, et al. Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of lung cancer in Korea: a pilot study of data from the Korean Nationwide Lung Cancer Registry. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2019; 82:118–25.
Article3. Chen K, Rajewsky N. The evolution of gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2007; 8:93–103.
Article4. Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004; 116:281–97.5. Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006; 6:857–66.
Article6. Trang P, Weidhaas JB, Slack FJ. MicroRNAs as potential cancer therapeutics. Oncogene. 2008; 27 Suppl 2:S52–7.
Article7. Lu T, Zhang C, Chai MX, An YB, Jia JL. MiR-374a promotes the proliferation of osteosarcoma cell proliferation by targeting Axin2. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8:10776–83.8. Wang Y, Xin H, Han Z, Sun H, Gao N, Yu H. MicroRNA-374a promotes esophageal cancer cell proliferation via Axin2 suppression. Oncol Rep. 2015; 34:1988–94.
Article9. Cai J, Guan H, Fang L, et al. MicroRNA-374a activates Wnt/ β-catenin signaling to promote breast cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2013; 123:566–79.10. Li H, Chen H, Wang H, et al. MicroRNA-374a promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting mitogen-inducible gene 6 (MIG-6). Oncol Res. 2018; 26:557–63.
Article11. Zhang J, He Y, Yu Y, et al. Upregulation of miR-374a promotes tumor metastasis and progression by downregulating LACTB and predicts unfavorable prognosis in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2018; May. 23. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1576.
Article12. Ma L, Shao Z, Zhao Y. MicroRNA-374a promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting SRCIN1. Pathol Res Pract. 2019; 215:152382.
Article13. Son D, Kim Y, Lim S, et al. MiR-374a-5p promotes tumor progression by targeting ARRB1 in triple negative breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019; 454:224–33.
Article14. Chen Y, Jiang J, Zhao M, et al. MicroRNA-374a suppresses colon cancer progression by directly reducing CCND1 to inactivate the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:41306–19.
Article15. Qian D, Chen K, Deng H, et al. MicroRNA-374b suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma by repressing AKT1 and Wnt-16. Clin Cancer Res. 2015; 21:4881–91.
Article16. Zhao M, Xu P, Liu Z, et al. Dual roles of miR-374a by modulated cJun respectively targets CCND1-inducing PI3K/AKT signal and PTEN-suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018; 9:78.
Article17. Hall JS, Taylor J, Valentine HR, et al. Enhanced stability of microRNA expression facilitates classification of FFPE tumour samples exhibiting near total mRNA degradation. Br J Cancer. 2012; 107:684–94.
Article18. Zhang X, Chen J, Radcliffe T, Lebrun DP, Tron VA, Feilotter H. An array-based analysis of microRNA expression comparing matched frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human tissue samples. J Mol Diagn. 2008; 10:513–9.
Article19. Weng L, Wu X, Gao H, et al. MicroRNA profiling of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by whole-genome small RNA deep sequencing of paired frozen and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue specimens. J Pathol. 2010; 222:41–51.
Article20. Glud M, Klausen M, Gniadecki R, et al. MicroRNA expression in melanocytic nevi: the usefulness of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded material for miRNA microarray profiling. J Invest Dermatol. 2009; 129:1219–24.
Article21. Hui AB, Shi W, Boutros PC, et al. Robust global micro-RNA profiling with formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded breast cancer tissues. Lab Invest. 2009; 89:597–606.
Article22. Zheng J, Xu T, Chen F, Zhang Y. MiRNA-195-5p functions as a tumor suppressor and a predictive of poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer by directly targeting CIAPIN1. Pathol Oncol Res. 2019; 25:1181–90.
Article23. Chen Y, Min L, Ren C, et al. MiRNA-148a serves as a prognostic factor and suppresses migration and invasion through Wnt1 in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0171751.
Article24. Zheng W, Zhao J, Tao Y, et al. MicroRNA-21: a promising biomarker for the prognosis and diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 2018; 16:2777–82.25. Wang XC, Wang W, Zhang ZB, Zhao J, Tan XG, Luo JC. Overexpression of miRNA-21 promotes radiation-resistance of non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol. 2013; 8:146.
Article26. Gao W, Lu X, Liu L, Xu J, Feng D, Shu Y. MiRNA-21: a biomarker predictive for platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012; 13:330–40.27. He W, Feng L, Xia D, Han N. MiR-374a promotes the proliferation of human osteosarcoma by downregulating FOXO1 expression. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8:3482–9.28. Zhen Y, Fang W, Zhao M, et al. MiR-374a-CCND1-pPI3K/AKT-c-JUN feedback loop modulated by PDCD4 suppresses cell growth, metastasis, and sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma to cisplatin. Oncogene. 2017; 36:275–85.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- ZNF821 as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker and its Correlation with Infiltrating Immune Cells in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
- Prognostic Implications of MicroRNA-21 Overexpression in Invasive Ductal Carcinomas of the Breast
- Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I and Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Coexpression Is an Independent Poor Prognostic Factor in Adenocarcinoma of the Lung
- Serum miR-3620-3p as a Novel Biomarker for Ankylosing Spondylitis
- The Correlation between Radiologic Findings and Clinicopathological Prognostic Factors in Small Peripheral Adenocarcinoma of Lung