J Adv Prosthodont.
2019 Oct;11(5):280-285. 10.4047/jap.2019.11.5.280.
Comparative clinical study of the marginal discrepancy of fixed dental prosthesis fabricated by the milling-sintering method using a presintered alloy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea. deweylee@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Periodontics and Endodontics, State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, USA.
- 3Institute for Translational Research in Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
- 4Department of Dental Biomaterials, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
- 5Department of Dental Science, Graduate School, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2462111
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2019.11.5.280
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The present study was designed to examine the clinical fit of fixed dental prosthesis fabricated by the milling-sintering method using a presintered cobalt-chromium alloy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
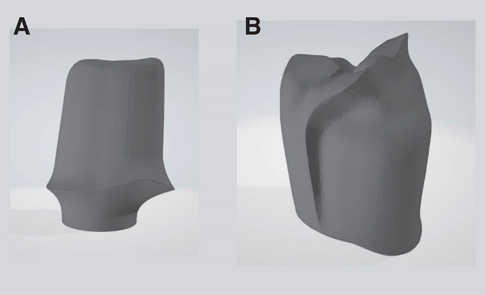
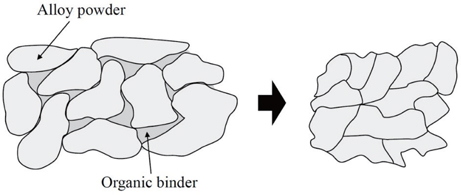
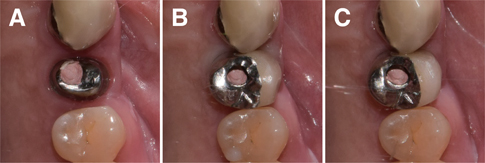
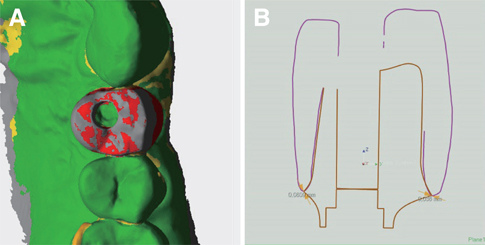
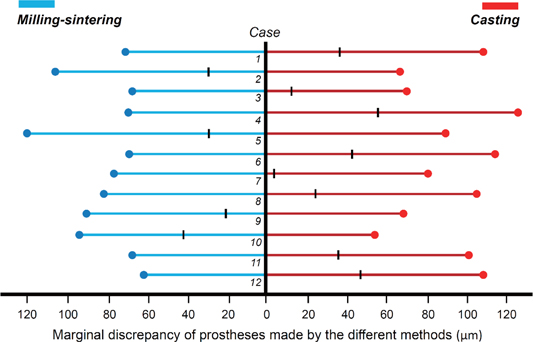
Two single metal-ceramic crowns were fabricated via milling-sintering method and casting method in each of the twelve consecutive patients who required an implant-supported fixed prosthesis. In the milling-sintering method, the prosthetic coping was designed in computer software, and the design was converted to a non-precious alloy coping using milling and post-sintering process. In the casting method, the conventional manual fabrication process was applied. The absolute marginal discrepancy of the prostheses was evaluated intraorally using the triple-scan technique. Statistical analysis was conducted using Mann-Whitney U test (α=.05).
RESULTS
Eight patients (66.7%) showed a lower marginal discrepancy of the prostheses made using the milling-sintering method than that of the prosthesis made by the casting method. Statistically, the misfit of the prosthesis fabricated using the milling-sintering method was not significantly different from that fabricated using the casting method (P=.782). There was no tendency between the amount of marginal discrepancy and the measurement point.
CONCLUSION
The overall marginal fit of prosthesis fabricated by milling-sintering using a presintered alloy was comparable to that of the prosthesis fabricated by the conventional casting method in clinical use.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wataha JC, Messer RL. Casting alloys. Dent Clin North Am. 2004; 48:vii–viii. 499–512.
Article2. Roberts HW, Berzins DW, Moore BK, Charlton DG. Metalceramic alloys in dentistry: a review. J Prosthodont. 2009; 18:188–194.
Article3. Ziebert GJ, Hurtado A, Glapa C, Schiffleger BE. Accuracy of one-piece castings, preceramic and postceramic soldering. J Prosthet Dent. 1986; 55:312–317.
Article4. Mai HN, Kwon TY, Hong MH, Lee DH. Comparative study of the fit accuracy of full-arch bar frameworks fabricated with different presintered cobalt-chromium alloys. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:1962514.
Article5. Hedberg YS, Qian B, Shen Z, Virtanen S, Wallinder IO. In vitro biocompatibility of CoCrMo dental alloys fabricated by selective laser melting. Dent Mater. 2014; 30:525–534.
Article6. Ucar Y, Brantley WA, Johnston WM, Dasgupta T. Mechanical properties, fracture surface characterization, and microstructural analysis of six noble dental casting alloys. J Prosthet Dent. 2011; 105:394–402.
Article7. Beuer F, Schweiger J, Edelhoff D. Digital dentistry: an overview of recent developments for CAD/CAM generated restorations. Br Dent J. 2008; 204:505–511.
Article8. Joda T, Brägger U. Digital vs. conventional implant prosthetic workflows: a cost/time analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015; 26:1430–1435.
Article9. Krug KP, Knauber AW, Nothdurft FP. Fracture behavior of metal-ceramic fixed dental prostheses with frameworks from cast or a newly developed sintered cobalt-chromium alloy. Clin Oral Investig. 2015; 19:401–411.
Article10. Ortorp A, Jemt T, Bäck T, Jälevik T. Comparisons of precision of fit between cast and CNC-milled titanium implant frameworks for the edentulous mandible. Int J Prosthodont. 2003; 16:194–200.11. Woo HW, Cho SA, Lee CH, Lee KB, Cho JH, Lee DH. Precision of the milled full-arch framework fabricated using pre-sintered soft alloy: A pilot study. J Adv Prosthodont. 2018; 10:128–131.
Article12. Paniz G, Stellini E, Meneghello R, Cerardi A, Gobbato EA, Bressan E. The precision of fit of cast and milled full-arch implant-supported restorations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013; 28:687–693.
Article13. Hong JT, Shin SY. A comparative study on the bond strength of porcelain to the millingable Pd-Ag alloy. J Adv Prosthodont. 2014; 6:372–378.
Article14. Stawarczyk B, Eichberger M, Hoffmann R, Noack F, Schweiger J, Edelhoff D, Beuer F. A novel CAD/CAM base metal compared to conventional CoCrMo alloys: an in-vitro study of the long-term metal-ceramic bond strength. Oral Health Dent Manag. 2014; 13:446–452.15. Park JK, Kim HY, Kim WC, Kim JH. Evaluation of the fit of metal ceramic restorations fabricated with a pre-sintered soft alloy. J Prosthet Dent. 2016; 116:909–915.
Article16. Holmes JR, Bayne SC, Holland GA, Sulik WD. Considerations in measurement of marginal fit. J Prosthet Dent. 1989; 62:405–408.
Article17. Boitelle P, Mawussi B, Tapie L, Fromentin O. A systematic review of CAD/CAM fit restoration evaluations. J Oral Rehabil. 2014; 41:853–874.
Article18. Rossetti PH, do Valle AL, de Carvalho RM, De Goes MF, Pegoraro LF. Correlation between margin fit and microleakage in complete crowns cemented with three luting agents. J Appl Oral Sci. 2008; 16:64–69.
Article19. Trajtenberg CP1, Caram SJ, Kiat-amnuay S. Microleakage of all-ceramic crowns using self-etching resin luting agents. Oper Dent. 2008; 33:392–399.
Article20. Mai HN, Lee KE, Ha JH, Lee DH. Effects of image and education on the precision of the measurement method for evaluating prosthesis misfit. J Prosthet Dent. 2018; 119:600–605.
Article21. Kocaağaoğlu H, Kılınç Hİ, Albayrak H, Kara M. In vitro evaluation of marginal, axial, and occlusal discrepancies in metal ceramic restorations produced with new technologies. J Prosthet Dent. 2016; 116:368–374.
Article22. Pasali B, Sarac D, Kaleli N, Sarac YS. Evaluation of marginal fit of single implant-supported metal-ceramic crowns prepared by using presintered metal blocks. J Prosthet Dent. 2018; 119:257–262.
Article23. Kim HR, Kim YK, Son JS, Min BK, Kim KH, Kwon TY. Comparison of in vitro biocompatibility of a Co-Cr dental alloy produced by new milling/post-sintering or traditional casting technique. Mater Lett. 2016; 178:300–303.
Article24. Kim HR, Jang SH, Kim YK, Son JS, Min BK, Kim KH, Kwon TY. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Co-Cr dental alloys fabricated by three CAD/CAM-based processing techniques. Materials (Basel). 2016; 9:E596.
Article25. Kim DY, Kim EB, Kim HY, Kim JH, Kim WC. Evaluation of marginal and internal gap of three-unit metal framework according to subtractive manufacturing and additive manufacturing of CAD/CAM systems. J Adv Prosthodont. 2017; 9:463–469.
Article26. Jang SH, Min BK, Hong MH, Kwon TY. Effect of different post-sintering temperatures on the microstructures and mechanical properties of a pre-sintered Co-Cr alloy. Metals. 2018; 8:1036–1044.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of milling and sintering process on integrity of zirconia prosthesis: a literature review
- Evaluation of marginal discrepancy in metal frameworks fabricated by sintering-based computer-aided manufacturing methods
- Comparative evaluation of marginal and internal fit of metal copings fabricated by various CAD/CAM methods
- Accuracy evaluation of metal copings fabricated by computer-aided milling and direct metal laser sintering systems
- Marginal and internal discrepancy of 3-unit fixed dental prostheses fabricated by subtractive and additive manufacturing