Ann Dermatol.
2019 Dec;31(6):601-610. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.6.601.
The Effects of Systemic Psoriasis Therapies on the C-Reactive Protein and the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Bahçeşehir University, Faculty of Medicine, Istanbul, Turkey. ezgiaktasmd@gmail.com
- 2Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Health Sciences University, Sisli Hamidiye Etfal Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey.
- KMID: 2461982
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.6.601
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Currently, no generally accepted laboratory marker for monitorizing the disease activity and therapy response of psoriasis is known.
OBJECTIVE
The aim of the study is to evaluate the effects of systemic therapies on C-reactive protein (CRP) and the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in psoriasis.
METHODS
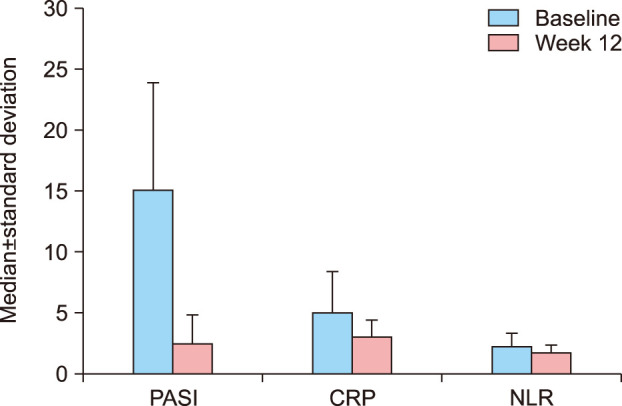
One hundred patients with psoriasis treated with narrow band ultraviolet B, acitretin, cyclosporine, methotrexate, adalimumab, etanercept, and ustekinumab were prospectively evaluated. At baseline and at week 12, CRP, NLR, and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) were evaluated.
RESULTS
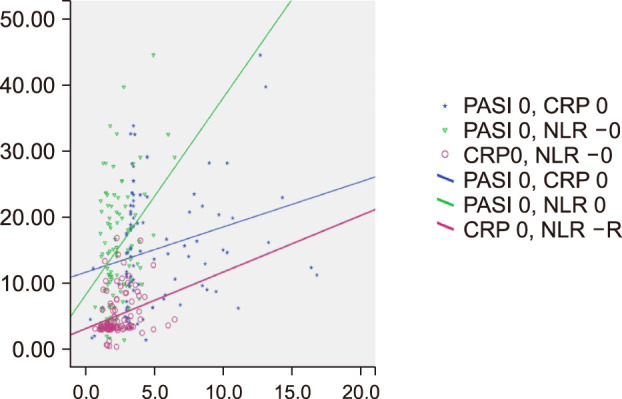
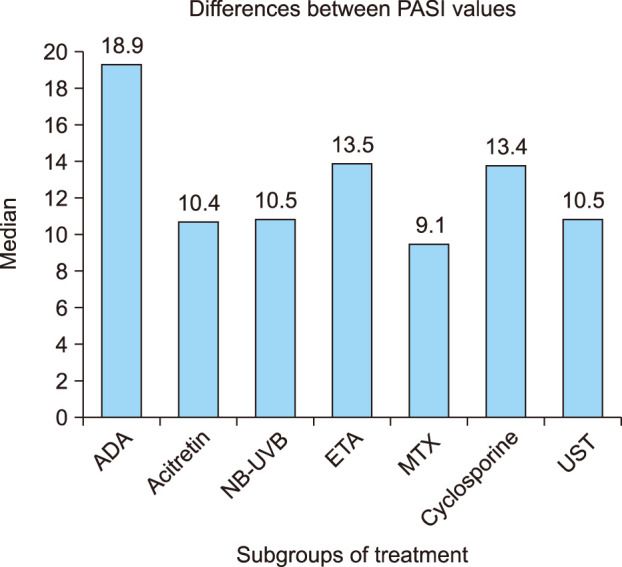
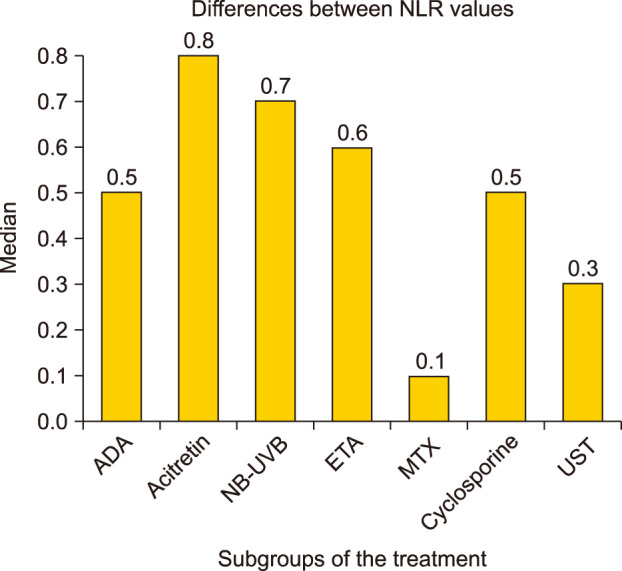
A statistically significant decrease was observed in PASI scores, CRP, and NLR values from the baseline to the 12-week visit (p=0.001, p=0.001, p=0.001, respectively). The reduction in PASI scores and NLR values was positively correlated (r=0.460, p=0.001). The comparisons between treatment groups revealed that the median decrease in NLR values was statistically higher in the adalimumab group than in the methotrexate group (p=0.007). And the median decrease in PASI scores was significantly higher in the adalimumab group compared with the methotrexate and acitretin therapy group (p=0.007, p=0.042, respectively).
CONCLUSION
In the present study, systemic therapy of psoriasis was demonstrated to decrease the levels of CRP and NLR, which are known to be indicators of systemic inflammation and cardiovascular comorbidities.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Biljan D, Situm M, Kostović K, Batinac T, Matisić D. Acute phase proteins in psoriasis. Coll Antropol. 2009; 33:83–86. PMID: 19408608.2. Langley RG, Ellis CN. Evaluating psoriasis with Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, Psoriasis Global Assessment, and Lattice System Physician's Global Assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004; 51:563–569. PMID: 15389191.
Article3. Coimbra S, Oliveira H, Reis F, Belo L, Rocha S, Quintanilha A, et al. C-reactive protein and leucocyte activation in psoriasis vulgaris according to severity and therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010; 24:789–796. PMID: 20002653.
Article4. Coimbra S, Oliveira H, Reis F, Belo L, Rocha S, Quintanilha A, et al. Circulating adipokine levels in Portuguese patients with psoriasis vulgaris according to body mass index, severity and therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010; 24:1386–1394. PMID: 20337818.
Article5. Ctirad A, Lenka B, David P, Zdenek F, Kveta H, Karel E, et al. Goeckerman's therapy for psoriasis with special reference to serum pentraxin 3 level. Int J Dermatol. 2008; 47:1011–1014. PMID: 18986345.
Article6. Chodorowska G, Wojnowska D, Juszkiewicz-Borowiec M. C-reactive protein and alpha2-macroglobulin plasma activity in medium-severe and severe psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004; 18:180–183. PMID: 15009298.
Article7. Coimbra S, Oliveira H, Reis F, Belo L, Rocha S, Quintanilha A, et al. Interleukin (IL)-22, IL-17, IL-23, IL-8, vascular endothelial growth factor and tumour necrosis factor-α levels in patients with psoriasis before, during and after psoralenultraviolet A and narrowband ultraviolet B therapy. Br J Dermatol. 2010; 163:1282–1290. PMID: 20716219.
Article8. Sen BB, Rifaioglu EN, Ekiz O, Inan MU, Sen T, Sen N. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a measure of systemic inflammation in psoriasis. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2014; 33:223–227. PMID: 24147939.
Article9. Yurtdaş M, Yaylali YT, Kaya Y, Ozdemir M, Ozkan I, Aladağ N. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio may predict subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with psoriasis. Echocardiography. 2014; 31:1095–1104. PMID: 24447343.
Article10. Ataseven A, Bilgin AU, Kurtipek GS. The importance of neutrophil lymphocyte ratio in patients with psoriasis. Mater Sociomed. 2014; 26:231–233. PMID: 25395882.
Article11. Kim DS, Shin D, Lee MS, Kim HJ, Kim DY, Kim SM, et al. Assessments of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in Korean patients with psoriasis vulgaris and psoriatic arthritis. J Dermatol. 2016; 43:305–310. PMID: 26381893.
Article12. Polat M, Bugdayci G, Kaya H, Oğuzman H. Evaluation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in Turkish patients with chronic plaque psoriasis. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2017; 26:97–100. PMID: 29264899.
Article13. Gerkowicz A, Pietrzak A, Szepietowski JC, Radej S, Chodorowska G. Biochemical markers of psoriasis as a metabolic disease. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2012; 50:155–170. PMID: 22763973.
Article14. Strober BE, Poulin Y, Teller C, Wang Y, Williams DA, Goldblum OM. Changes in C-reactive protein in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis switched to adalimumab therapy after suboptimal response to etanercept, methotrexate or phototherapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014; 28:1701–1706. PMID: 24422992.
Article15. Strober B, Teller C, Yamauchi P, Miller JL, Hooper M, Yang YC, et al. Effects of etanercept on C-reactive protein levels in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Br J Dermatol. 2008; 159:322–330. PMID: 18503600.
Article16. Zhang L, Wiles C, Martinez LR, Han G. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio decreases after treatment of psoriasis with therapeutic antibodies. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017; 31:e491–e492. PMID: 28502119.
Article17. Asahina A, Kubo N, Umezawa Y, Honda H, Yanaba K, Nakagawa H. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio and mean platelet volume in Japanese patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: response to therapy with biologics. J Dermatol. 2017; 44:1112–1121. PMID: 28493493.
Article18. Nast A, Gisondi P, Ormerod AD, Saiag P, Smith C, Spuls PI, et al. European S3-Guidelines on the systemic treatment of psoriasis vulgaris--update 2015--short version--EDF in cooperation with EADV and IPC. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015; 29:2277–2294. PMID: 26481193.19. Alexandroff AB, Pauriah M, Camp RD, Lang CC, Struthers AD, Armstrong DJ. More than skin deep: atherosclerosis as a systemic manifestation of psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2009; 161:1–7.
Article20. Ahlehoff O, Skov L, Gislason G, Lindhardsen J, Kristensen SL, Iversen L, et al. Cardiovascular disease event rates in patients with severe psoriasis treated with systemic antiinflammatory drugs: a Danish real-world cohort study. J Intern Med. 2013; 273:197–204. PMID: 22963528.
Article21. Adışen E, Uzun S, Erduran F, Gürer MA. Prevalence of smoking, alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriasis. An Bras Dermatol. 2018; 93:205–211.
Article22. Fortes C, Mastroeni S, Leffondré K, Sampogna F, Melchi F, Mazzotti E, et al. Relationship between smoking and the clinical severity of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 2005; 141:1580–1584. PMID: 16365261.
Article23. Kinahan CE, Mazloom S, Fernandez AP. Impact of smoking on response to systemic treatment in patients with psoriasis: a retrospective case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 2015; 172:428–436. PMID: 25142556.
Article24. Daulatabad D, Grover C, Kashyap B, Dhawan AK, Singal A, Kaur IR. Clinical and serological characteristics of nail psoriasis in Indian patients: a cross-sectional study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2017; 83:650–655. PMID: 28656915.
Article25. Abuabara K, Lee H, Kimball AB. The effect of systemic psoriasis therapies on the incidence of myocardial infarction: a cohort study. Br J Dermatol. 2011; 165:1066–1073. PMID: 21777216.
Article26. Boehncke S, Salgo R, Garbaraviciene J, Beschmann H, Hardt K, Diehl S, et al. Effective continuous systemic therapy of severe plaque-type psoriasis is accompanied by amelioration of biomarkers of cardiovascular risk: results of a prospective longitudinal observational study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011; 25:1187–1193. PMID: 21241371.
Article27. Coimbra S, Oliveira H, Reis F, Belo L, Rocha S, Quintanilha A, et al. Psoriasis therapy and cardiovascular risk factors: a 12-week follow-up study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010; 11:423–432. PMID: 20429617.28. Montaudié H, Albert-Sabonnadière C, Acquacalda E, Fontas E, Danré A, Roux C, et al. Impact of systemic treatment of psoriasis on inflammatory parameters and markers of comorbidities and cardiovascular risk: results of a prospective longitudinal observational study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014; 28:1186–1191. PMID: 23981008.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio as Inflammatory Marker for Delirium: An Exploratory Study
- The Relationship between Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio and Age-related Macular Degeneration
- Correlation between the size of the ureter stone and the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet lymphocyte ratio, and C-reactive protein in patients with ureter stone visiting the emergency department
- Hematologic parameters to predict negative cerebrospinal fluid examination results among neurologically intact patients who underwent lumbar puncture on suspicion of central nervous system infection
- Clinical Significance of Preoperative Inflammatory Parameters in Gastric Cancer Patients