Lab Anim Res.
2018 Dec;34(4):264-269. 10.5625/lar.2018.34.4.264.
Generation of knockout mouse models of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors by engineered nuclease-mediated genome editing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry, College of Life Science & Biotechnology, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. hwl@yonsei.ac.kr jhlee13@gmail.com rohjaeil@gmail.com
- KMID: 2459304
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2018.34.4.264
Abstract
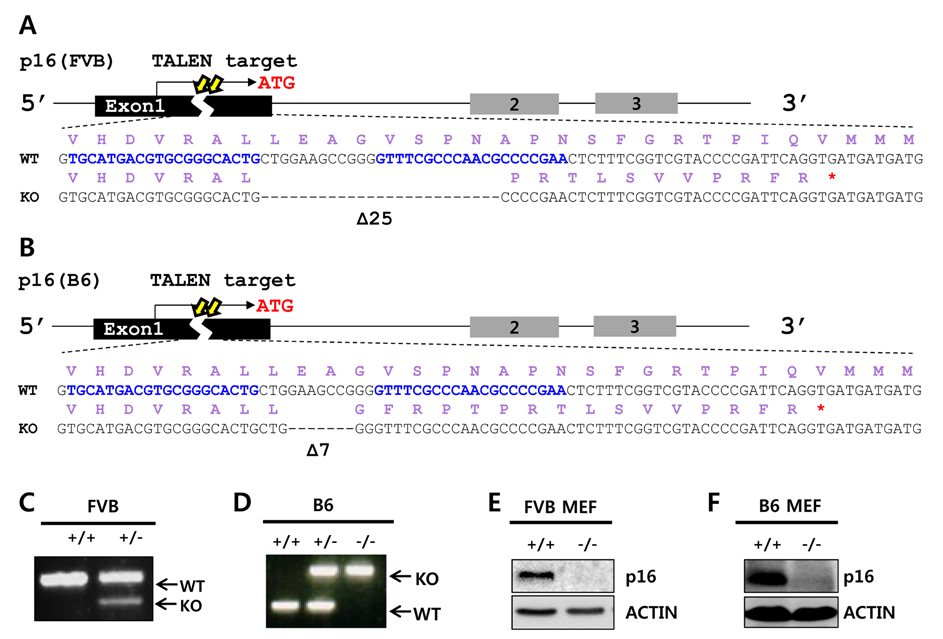
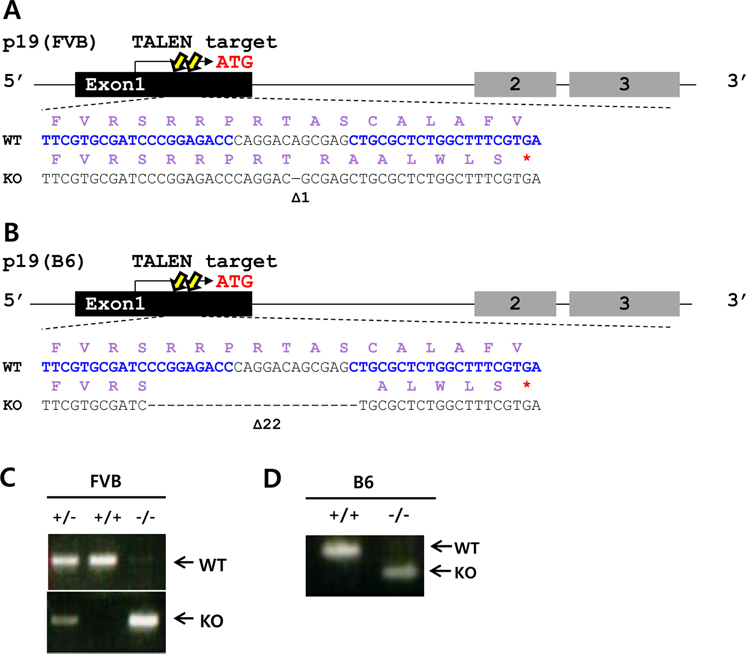
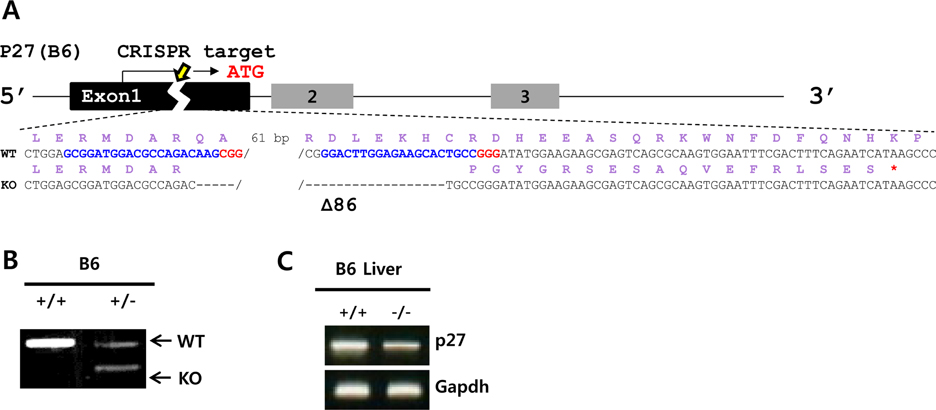
- Cell cycle dysfunction can cause severe diseases, including neurodegenerative disease and cancer. Mutations in cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors controlling the G1 phase of the cell cycle are prevalent in various cancers. Mice lacking the tumor suppressors p16(Ink4a) (Cdkn2a, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2a), p19(Arf) (an alternative reading frame product of Cdkn2a,), and p27(Kip1) (Cdkn1b, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1b) result in malignant progression of epithelial cancers, sarcomas, and melanomas, respectively. Here, we generated knockout mouse models for each of these three cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors using engineered nucleases. The p16(Ink4a) and p19(Arf) knockout mice were generated via transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs), and p27(Kip1) knockout mice via clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated nuclease 9 (CRISPR/Cas9). These gene editing technologies were targeted to the first exon of each gene, to induce frameshifts producing premature termination codons. Unlike preexisting embryonic stem cell-based knockout mice, our mouse models are free from selectable markers or other external gene insertions, permitting more precise study of cell cycle-related diseases without confounding influences of foreign DNA.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Artelt P, Grannemann R, Stocking C, Friel J, Bartsch J, Hauser H. The prokaryotic neomycin-resistance-encoding gene acts as a transcriptional silencer in eukaryotic cells. Gene. 1991; 99(2):249–254.
Article2. Baker DJ, Perez-Terzic C, Jin F, Pitel KS, Niederländer NJ, Jeganathan K, Yamada S, Reyes S, Rowe L, Hiddinga HJ, Eberhardt NL, Terzic A, van Deursen JM. Opposing roles for p16Ink4a and p19Arf in senescence and ageing caused by BubR1 insufficiency. Nat Cell Biol. 2008; 10(7):825–836.
Article3. Besson A, Dowdy SF, Roberts JM. CDK inhibitors: cell cycle regulators and beyond. Dev Cell. 2008; 14(2):159–169.
Article4. Capparelli C, Chiavarina B, Whitaker-Menezes D, Pestell TG, Pestell RG, Hulit J, Andò S, Howell A, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Sotgia F, Lisanti MP. CDK inhibitors (p16/p19/p21) induce senescence and autophagy in cancer-associated fibroblasts, “fueling” tumor growth via paracrine interactions, without an increase in neo-angiogenesis. Cell Cycle. 2012; 11(19):3599–3610.
Article5. Choi JY, Yun WB, Kim JE, Lee MR, Park JJ, Song BR, Kim HR, Park JW, Kang MJ, Kang BC, Lee HW, Hwang DY. Successful development of squamous cell carcinoma and hyperplasia in RGEN-mediated p27 KO mice after the treatment of DMBA and TPA. Lab Anim Res. 2018; 34(3):118–125.
Article6. Deng D, Yan C, Pan X, Mahfouz M, Wang J, Zhu JK, Shi Y, Yan N. Structural basis for sequence-specific recognition of DNA by TAL effectors. Science. 2012; 335(6069):720–723.
Article7. Doench JG, Fusi N, Sullender M, Hegde M, Vaimberg EW, Donovan KF, Smith I, Tothova Z, Wilen C, Orchard R, Virgin HW, Listgarten J, Root DE. Optimized sgRNA design to maximize activity and minimize off-target effects of CRISPR-Cas9. Nat Biotechnol. 2016; 34(2):184–191.
Article8. Hsu PD, Scott DA, Weinstein JA, Ran FA, Konermann S, Agarwala V, Li Y, Fine EJ, Wu X, Shalem O, Cradick TJ, Marraffini LA, Bao G, Zhang F. DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nat Biotechnol. 2013; 31(9):827–832.
Article9. Joung JK, Sander JD. TALENs: a widely applicable technology for targeted genome editing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013; 14(1):49–55.
Article10. Kurokawa K, Tanaka T, Kato J. p19ARF prevents G1 cyclin-dependent kinase activation by interacting with MDM2 and activating p53 in mouse fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1999; 18(17):2718–2727.
Article11. Lee JH, Rho JI, Devkota S, Sung HY, Lee HW. Developing genetically engineered mouse models using engineered nucleases: Current status, challenges, and the way forward. Drug Discov Today. 2016; 20:13–20.
Article12. Li J, Poi MJ, Tsai MD. Regulatory mechanisms of tumor suppressor P16(INK4A) and their relevance to cancer. Biochemistry. 2011; 50(25):5566–5582.13. Liggett WH Jr, Sidransky D. Role of the p16 tumor suppressor gene in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1998; 16(3):1197–1206.
Article14. Lim S, Kaldis P. Cdks, cyclins and CKIs: roles beyond cell cycle regulation. Development. 2013; 140(15):3079–3093.
Article15. McKeller RN, Fowler JL, Cunningham JJ, Warner N, Smeyne RJ, Zindy F, Skapek SX. The Arf tumor suppressor gene promotes hyaloid vascular regression during mouse eye development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002; 99(6):3848–3853.16. Nagy Z. The dysregulation of the cell cycle and the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007; 1772(4):402–408.
Article17. Nakayama K, Ishida N, Shirane M, Inomata A, Inoue T, Shishido N, Horii I, Loh DY, Nakayama K. Mice lacking p27(Kip1) display increased body size, multiple organ hyperplasia, retinal dysplasia, and pituitary tumors. Cell. 1996; 85(5):707–720.
Article18. Popp MW, Maquat LE. Leveraging Rules of Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay for Genome Engineering and Personalized Medicine. Cell. 2016; 165(6):1319–1322.
Article19. Roh JI, Cheong C, Sung YH, Lee J, Oh J, Lee BS, Lee JE, Gho YS, Kim DK, Park CB, Lee JH, Lee JW, Kang SM, Lee HW. Perturbation of NCOA6 leads to dilated cardiomyopathy. Cell Rep. 2014; 8(4):991–998.
Article20. Roh JI, Kim Y, Oh J, Kim Y, Lee J, Lee J, Chun KH, Lee HW. Hexokinase 2 is a molecular bridge linking telomerase and autophagy. PLoS One. 2018; 13(2):e0193182.
Article21. Roh JI, Lee J, Park SU, Kang YS, Lee J, Oh AR, Choi DJ, Cha JY, Lee HW. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated generation of obese and diabetic mouse models. Exp Anim. 2018; 67(2):229–237.
Article22. Romagosa C, Simonetti S, López-Vicente L, Mazo A, Lleonart ME, Castellvi J, Ramon y. p16(Ink4a) overexpression in cancer: a tumor suppressor gene associated with senescence and high-grade tumors. Oncogene. 2011; 30(18):2087–2097.
Article23. Sa G, Guo Y, Stacey DW. The regulation of S phase initiation by p27Kip1 in NIH3T3 cells. Cell Cycle. 2005; 4(4):618–627.
Article24. Sander JD, Joung JK. CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nat Biotechnol. 2014; 32(4):347–355.
Article25. Shankland SJ. Cell-cycle control and renal disease. Kidney Int. 1997; 52(2):294–308.
Article26. Sharpless NE, Ramsey MR, Balasubramanian P, Castrillon DH, DePinho RA. The differential impact of p16(INK4a) or p19(ARF) deficiency on cell growth and tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2004; 23(2):379–385.
Article27. Sung YH, Baek IJ, Kim DH, Jeon J, Lee J, Lee K, Jeong D, Kim JS, Lee HW. Knockout mice created by TALEN-mediated gene targeting. Nat Biotechnol. 2013; 31(1):23–24.
Article28. Sung YH, Jin Y, Kim S, Lee HW. Generation of knockout mice using engineered nucleases. Methods. 2014; 69(1):85–93.
Article29. Sung YH, Kim JM, Kim HT, Lee J, Jeon J, Jin Y, Choi JH, Ban YH, Ha SJ, Kim CH, Lee HW, Kim JS. Highly efficient gene knockout in mice and zebrafish with RNA-guided endonucleases. Genome Res. 2014; 24(1):125–131.
Article30. Ulanet DB, Hanahan D. Loss of p19(Arf) facilitates the angiogenic switch and tumor initiation in a multi-stage cancer model via p53-dependent and independent mechanisms. PLoS One. 2010; 5(8):e12454.
Article31. Valera A, Perales JC, Hatzoglou M, Bosch F. Expression of the neomycin-resistance (neo) gene induces alterations in gene expression and metabolism. Hum Gene Ther. 1994; 5(4):449–456.
Article32. Weber JD, Jeffers JR, Rehg JE, Randle DH, Lozano G, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ, Zambetti GP. p53-independent functions of the p19(ARF) tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 2000; 14(18):2358–2365.
Article33. Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S. Cell cycle and cell death in disease: past, present and future. J Intern Med. 2010; 268(5):395–409.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Genome Editing Using Engineered Nucleases
- Production of α1,3-galactosyltransferase targeted pigs using transcription activator-like effector nuclease-mediated genome editing technology
- Extracting Extra-Telomeric Phenotypes from Telomerase Mouse Models
- Genetically Engineered Mouse Models for Drug Development and Preclinical Trials
- Electroporation of AsCpf1/RNP at the Zygote Stage is an Efficient Genome Editing Method to Generate Knock-Out Mice Deficient in Leukemia Inhibitory Factor