J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2019 Sep;62(5):567-576. 10.3340/jkns.2018.0191.
Outcomes of Non-Operative Management for Pseudarthrosis after Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomies at Minimum 5 Years Follow-Up
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea. fissura@naver.com
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, USA.
- KMID: 2457947
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2018.0191
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
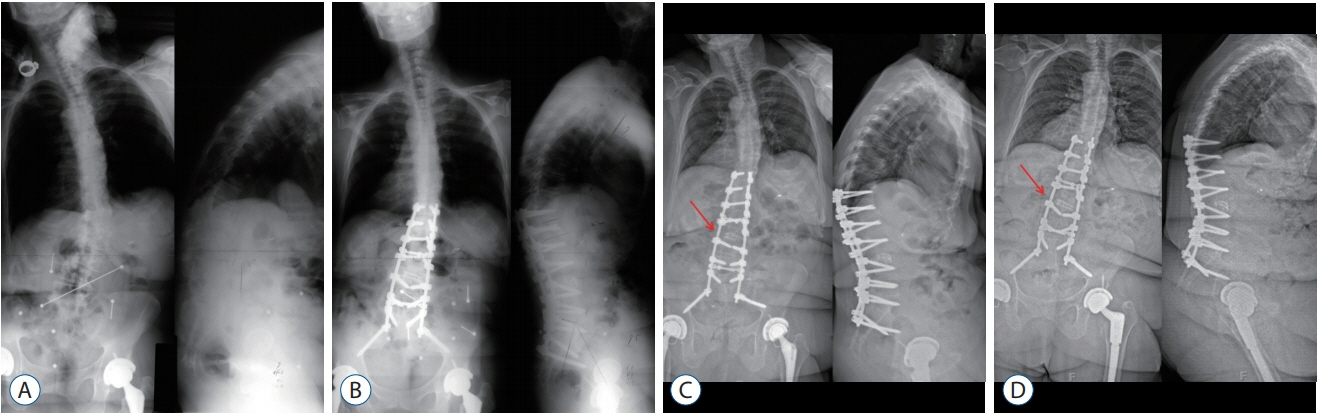
Minimal data exist regarding non-operative management of suspected pseudarthrosis after pedicle subtraction osteotomy (PSO). This study reports radiographic and clinical outcomes of non-operative management for post-PSO pseudarthrosis at a minimum 5 years post-detection.
METHODS
Nineteen consecutive patients with implant breakage indicating probable pseudarthrosis after PSO surgery (13 women/six men; mean age at surgery, 58 years) without severe pain and disability were treated with non-operative management (mean follow-up, 5.8 years; range, 5-10 years). Non-operative management included medication, intermittent brace wearing and avoidance of excessive back strain. Radiographic and clinical outcomes analysis was performed.
RESULTS
Sagittal vertical axis (SVA), proximal junctional angle, thoracic kyphosis achieved by a PSO were maintained after detection of pseudarthrosis through ultimate follow-up. Lumbar lordosis and PSO angle decreased at final follow-up. There was no significant change in Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) scores and Scoliosis Research Society (SRS) total score, or subscales of pain, self-image, function, satisfaction and mental health between detection of pseudarthrosis and ultimate follow-up. SVA greater than 11 cm showed poorer ODI and SRS total score, as well as the pain, self-image, and function subscales (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Non-operative management of implant failure of probable pseudarthrosis after PSO offers acceptable outcomes even at 5 years after detection of implant breakage, provided SVA is maintained. As SVA increased, outcome scores decreased in this patient population.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Auerbach JD, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Sehn JK, Milby AH, Bumpass D, et al. Major complications and comparison between 3-column osteotomy techniques in 105 consecutive spinal deformity procedures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 37:1198–1210. 2012.
Article2. Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Edwards C, Lenke LG, Iffrig TM, Berra A, et al. Complications and outcomes of pedicle subtraction osteotomies for fixed sagittal imbalance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 28:2093–2101. 2003.
Article3. Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Lenke LG, Baldus C, Blanke K, et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 85-A:454–463. 2003.
Article4. Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Rinella A, Lenke LG, Baldus C, Blanke K. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 86:44–50. 2004.
Article5. Cobb JR. Outline for the study of scoliosis. In: instructional course lectures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 261–275. 1948.6. Dickson DD, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Koester LA. Risk factors for and assessment of symptomatic pseudarthrosis after lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:1190–1195. 2014.
Article7. Dvorak MF, Kwon BK, Fisher CG, Eiserloh HL 3rd, Boyd M, Wing PC. Effectiveness of titanium mesh cylindrical cages in anterior column reconstruction after thoracic and lumbar vertebral body resection. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 28:902–908. 2003.
Article8. Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB. The oswestry disability index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:2940–2952. discussion 2952. 2000.
Article9. Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30:2024–2029. 2005.
Article10. Gupta MC, Kebaish K, Blondel B, Klineberg E. Spinal osteotomies for rigid deformities. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 24:203–211. 2013.
Article11. Haher TR, Gorup JM, Shin TM, Homel P, Merola AA, Grogan DP, et al. Results of the scoliosis research society instrument for evaluation of surgical outcome in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. A multicenter study of 244 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 24:1435–1440. 1999.
Article12. Hassanzadeh H, Jain A, El Dafrawy MH, Ain MC, Mesfin A, Skolasky RL, et al. Three-column osteotomies in the treatment of spinal deformity in adult patients 60 years old and older: outcome and complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:726–731. 2013.
Article13. Helenius I, Serlo J, Pajulo O. The incidence and outcomes of vertebral column resection in paediatric patients: a population-based, multicentre, follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 94:950–955. 2012.14. Kim YC, Lenke LG, Hyun SJ, Lee JH, Koester LA, Blanke KM. Results of revision surgery after pedicle subtraction osteotomy for fixed sagittal imbalance with pseudarthrosis at the prior osteotomy site or elsewhere: minimum 5 years post-revision. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:1817–1828. 2014.
Article15. Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Cheh G, Baldus C. Results of lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomies for fixed sagittal imbalance: a minimum 5-year follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 32:2189–2197. 2007.
Article16. Le Huec JC, Cogniet A, Demezon H, Rigal J, Saddiki R, Aunoble S. Insufficient restoration of lumbar lordosis and FBI index following pedicle subtraction osteotomy is an indicator of likely mechanical complication. Eur Spine J 24 Suppl. 1:S112–S120. 2015.
Article17. Lenke LG, Sides BA, Koester LA, Hensley M, Blanke KM. Vertebral column resection for the treatment of severe spinal deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 468:687–699. 2010.
Article18. O’Shaughnessy BA, Kuklo TR, Hsieh PC, Yang BP, Koski TR, Ondra SL. Thoracic pedicle subtraction osteotomy for fixed sagittal spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 34:2893–2899. 2009.
Article19. Rose PS, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Cronen GA, Mulconrey DS, Buchowski JM, et al. Role of pelvic incidence, thoracic kyphosis, and patient factors on sagittal plane correction following pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Spine (Phila pa 1976). 34:785–791. 2009.
Article20. Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, Farcy JP, Lafage V. Adult spinal deformitypostoperative standing imbalance: how much can you tolerate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 35:2224–2231. 2010.21. Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Ames CP, Demakakos J, Fu KM, Keshavarzi S, et al. Assessment of symptomatic rod fracture after posterior instrumented fusion for adult spinal deformity. Neurosurgery. 71:862–867. 2012.
Article22. Smith JS, Shaffrey E, Klineberg E, Shaffrey CI, Lafage V, Schwab FJ, et al. Prospective multicenter assessment of risk factors for rod fracture following surgery for adult spinal deformity. J Neurosurg Spine. 21:994–1003. 2014.
Article23. Sponseller PD, Jain A, Lenke LG, Shah SA, Sucato DJ, Emans JB, et al. Vertebral column resection in children with neuromuscular spine deformity. Spine (Phila PA 1976). 37:E655–E661. 2012.
Article24. Suk SI, Chung ER, Kim JH, Kim SS, Lee JS, Choi WK. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe rigid scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30:1682–1687. 2005.
Article25. Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim WJ, Lee SM, Chung ER, Nah KH. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe spinal deformities. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 27:2374–2382. 2002.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Smith-Petersen Osteotomy versus Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy for the Correction of Fixed Sagittal Imbalance
- Multiple-Rod Constructs Do Not Reduce Pseudarthrosis and Rod Fracture After Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy for Adult Spinal Deformity Correction but Improve Quality of Life
- Pseudarthrosis at L5-S1 after Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion
- The Treatment of Spinal Pseudarthrosis in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Three-Column Osteotomy for the Treatment of Rigid Cervical Deformity