J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2010 Jun;17(2):90-96. 10.4184/jkss.2010.17.2.90.
Pseudarthrosis at L5-S1 after Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea. srp2002@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 1459273
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2010.17.2.90
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: This is a retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
We wanted to investigate the rate of pseudarthrosis at L5-S1 after posterolateral fusion only for degenerative lumbar spinal disease, and to determine the radiological findings that help diagnose pseudarthrosis. SUMMARY OF THE LITERATURE REVIEW: The pseudarthrosis rate at L5-S1 is much higher than that at the other lumbar segments. However, there have been few studies for the rate and risk factors of pseudarthrosis at L5-S1.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
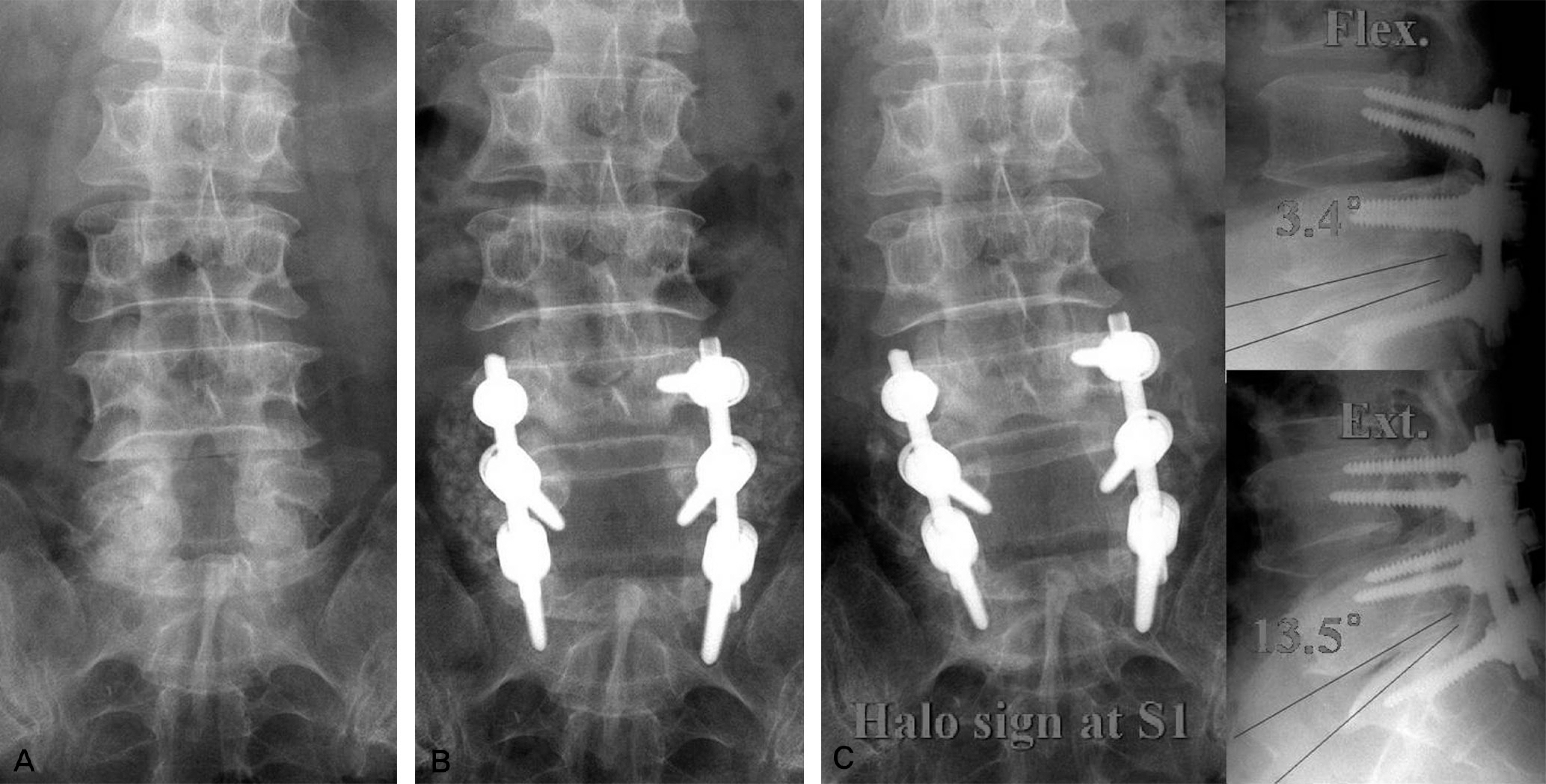
A total of 88 patients who underwent pedicle screw instrumentation and posterolateral lumbar fusion were evaluated with a minimum of 1-year follow up. Bony union was evaluated by the bony fusion mass, the angulation on the flexion-extension radiographs and the radiolucent zone around the pedicle screws. The patients' age, bony mineral density, the number of fused segments and lumbar lordosis were evaluated for their association with pseudarthrosis at L5-S1.
RESULTS
Pseudarthrosis developed in 22 patients at L5-S1 and in 8 patients at other levels. The change of angulation on the flexion-extension radiographs at the last follow-up was 5.2degrees in the pseudarthrosis group and 1.7degrees in the fusion group (P=0.3). A radiolucent zone of the sacral screws was noted in 10 patients; in 7 of the 22 patients in the pseudarthrosis group and in 3 of the 66 patients in the fusion group. The average age, the mean number of levels fused and the bone mineral density were similar in both groups. Lumbar lordosis was not associated with the development of pseudarthrosis at L5-S1.
CONCLUSION
The pseudarthrosis rate was significantly higher at L5-S1 than that at the other lumbar segments following instrumented posterolateral fusion. Pseudarthrosis was closely related to hypermobile angulation (> or =5degrees) on the flexion-extension radiographs and a radiolucent zone around the sacral screws.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Thomsen K., Christensen FB., Eiskjaer SP., Hansen ES., Fruensgaard S., Bunger CE. 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies. The effect of pedicle screw instrumentation on functional outcome and fusion rates in posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion: a prospective, randomized clinical study. Spine. 1997. 22:2813–22.2.Moller H., Hedlund R. Instrumented and noninstrumented posterolateral fusion in adult spondylolisthesis-a prospective randomized study: part 2. Spine. 2000. 25:1716–21.3.Allen BL Jr., Ferguson RL. The Galveston technique of pelvic fixation with L-rod instrumentation of the spine. Spine. 1984. 9:388–94.
Article4.Boachie-Adjei O., Dendrinos GK., Ogilvie JW., Bradford DS. Management of adult spinal deformity with combined anterior-posterior arthrodesis and Luque-Galveston instrumentation. J Spinal Disord. 1991. 4:131–41.
Article5.Camp JF., Caudle R., Ashmun RD., Roach J. Immediate complications of Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation to the sacro-pelvis. A clinical and biomechanical study. Spine. 1990. 15:932–41.
Article6.Saer EH 3rd., Winter RB., Lonstein JE. Long scoliosis fusion to the sacrum in adults with nonparalytic scoliosis. An improved method. Spine. 1990. 15:650–3.7.Kim YJ., Bridwell KH., Lenke LG., Rhim S., Cheh G. Pseudarthrosis in long adult spinal deformity instrumentation and fusion to the sacrum: prevalence and risk factor analysis of 144 cases. Spine. 2006. 31:2329–36.
Article8.Lenke LG., Bridwell KH., Bullis D., Betz RR., Baldus C., Schoenecker PL. Results of in situ fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord. 1992. 5:433–42.
Article9.Jackson RP., McManus AC. The iliac buttress. A computed tomographic study of sacral anatomy. Spine. 1993. 18:1318–28.10.Shirado O., Zdeblick TA., McAfee PC., Warden KE. Biomechanical evaluation of methods of posterior stabilization of the spine and posterior lumbar interbody arthrodesis for lumbosacral isthmic spondylolisthesis. A calf-spine model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991. 73:518–26.
Article11.Cho KJ., Suk SI., Park SR, et al. Arthrodesis to L5 versus S1 in long instrumentation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2009. 18:531–7.
Article12.Brodsky AE., Kovalsky ES., Khalil MA. Correlation of radiologic assessment of lumbar spine fusions with surgical exploration. Spine. 1991. 16:261–5.
Article13.Kim YJ., Bridwell KH., Lenke LG., Cho KJ., Edwards CC 2nd., Rinella AS. Pseudarthrosis in adult spinal deformity following multisegmental instrumentation and arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:721–8.
Article14.Wimmer C., Gluch H. Aseptic loosening after CD instrumentation in the treatment of scoliosis: a report about eight cases. J Spinal Disord. 1998. 11:440–3.15.Tokuhashi Y., Matsuzaki H., Oda H., Uei H. Clinical course and significance of the clear zone around the pedicle screws in the lumbar degenerative disease. Spine. 2008. 33:903–8.
Article16.Sanden B., Olerud C., Petren-Mallmin M., Johansson C., Larsson S. The significance of radiolucent zones surrounding pedicle screws. Definition of screw loosening in spinal instrumentation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004. 86:457–61.17.McAfee PC., Weiland DJ., Carlow JJ. Survivorship analysis of pedicle spinal instrumentation. Spine. 1991. 16:422–7.
Article18.Ohlin A., Karlsson M., Duppe H., Hasserius R., Redlund-Johnell I. Complications after transpedicular stabilization of the spine. A survivorship analysis of 163 cases. Spine. 1994. 19:2774–9.19.Roy-Camille R., Saillant G., Berteaux D., Salgado V. Osteosynthesis of thoraco-lumbar spine fractures with metal plates screwed through the vertebral pedicles. Reconstr Surg Traumatol. 1976. 15:2–16.20.Lee KY., Kim CH., Song CG. Metal failure of pedicle screw system. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2002. 9:157–63.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Change of Segmental Motion After Lumbar Posterolateral Fusion
- Incidence and Characteristics of Clinical L5–S1 Adjacent Segment Degeneration after L5 Floating Lumbar Fusion: A Multicenter Study
- Lumbopelvic Sagittal Alignment and Foraminal Height from Single Interbody Cage in L5-S1 Segment: Comparison between Anterior Cage for OLIF (Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion) and Curvilinear Cage for TLIF (Transforaminal Interbody Fusion)
- Survival Rates and Risk Factors for Cephalad and L5-S1 Adjacent Segment Degeneration after L5 Floating Lumbar Fusion : A Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up
- Failure of Long Spinal Construct and Pseudarthrosis in a Patient with Parkinson Disease for the Treatment of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Disorder: Case Report